
Hello,
Dr. Batman
Hello Doctor, Welcome!
Profile

Name: Batman
Email: batman@gotham.com
CARDIOLOGY REVIEW
(Total Questions - 225)Q.1. An old patient presented with abdominal pain, back pain and pulsatile abdomen, what is the next step to confirm diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
This is a case of aortic aneurysm, initial investigation US, confirmed by CT.
Incorrect options-
- Abdominal ultrasound- This is a good initial step to look, but is not detailed enough to see aorta clearly.
- Abdominal MRI- More expensive and takes longer than CT.
- Abdominal X-ray- Doesn't give clear enough view of the aorta.
Q.2. How to diagnose DVT?
Correct Answer : B
A duplex ultrasound is the preferred method for diagnosing DVT because it's non-invasive, readily available, and provides accurate images of veins and blood flow.
Q.3. Which of the following drug will delay need of surgery in AR?
Correct Answer : C
Nifedipine is the best evidence-based treatment in AR. It is a calcium channel blocker and works by relaxing blood vessels which decreases the BP. This improves the blood flow to heart and reduces worklod.
Incorrect options-
- Digoxin- Used to treat heart faliure and atrial fibrillation.
- Verapamil- It's a calcium channel blocker but not as potent as nifedipine in relaxing blood vessels.
- Enalapril- It is an ACE inhibitor benificial in managing heart conditions but is not used as a first-line treatment for delaying AR surgery.
Q.4. Anticoagulants are prescribed for how long?
Correct Answer : B
The likely answer is B, but we should pay attention to the patient's hemodynamic status and specifically the bleeding potential.
Q.5. A patient with left bundle branch block needs to go for dental procedure, what's the recommendation regarding endocarditis prophylaxis?
Correct Answer : A
Left bundle branch block is a condition in which the electrical signals that control the heartbeat are disrupted causing a delay in the contraction of the left ventricle,it is not responsible for increaing the risk of infective endocarditis.
Prophylaxis is not needed as long as there is no a structural abnormality, prosthetic valves, or previous history of endocarditis.
- [Prophylaxis: Adults- Amoxicillin 2 Grams orally, 1hour before procedure].
Q.6. Which the following is the commonest complication of patients with chronic atrial fibrillation?
Correct Answer : B
Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disorder where the upper chambers of heart [atria] beat irregularyly and rapidly. This irregular beating leads to the accumulation of blood in the atria increasing the risk of clot formation. These clots can travel to the brain and cause a stroke.
- Incorrect options- Sudden death, heart attack, MI can occur in patients with atrial fibrillation but it does not directly cause them.
Complications of stroke-
- Thromboembolic events- stroke, systemic embolism
- Heart faliure
- Cognitive decline and dementia
- Cardiovascular events- MI, sudden cardiac death
- Bleeding complications due to anticoagulant therapy
- Quality of life impairment
Q.7. A 59-year-old patient presented with new onset supraventricular tachycardia with palpitation, no history of SOB or chest pain, chest examination normal ,oxygen saturation in room air = 98%, no peripheral edema, others normal, what's the best initial investigation?
Correct Answer : D
SVT is a rapid heart rate rhythm originating above the ventricles. TSH is the correct choice because if the patient has hyperthyroidism it can cause an increase in heart rate and can trigger SVT. Checking TSH will rule out hyperthyroidism as a potential cause of SVT.
- Incorrect options-- ECG stress test ,CT scan are not the preferred initial treatment, and ECG is likely already been performed.
Q.8. In patients with hypertension and diabetes, which antihypertensive agent you want to add first?
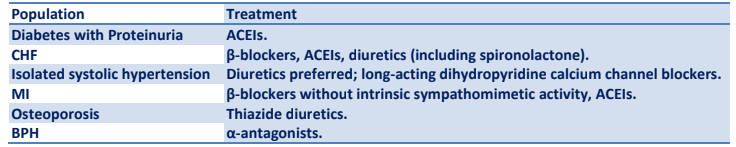
Correct Answer : B
DM + HTN = ACE inhibitors.
Incorrect options-
Diuretics (inexpensive and particularly effective in African-Americans) and beta-blockers (beneficial for patients with CAD) have been shown to reduce mortality in ''uncomplicated hypertension''. They are first-line agents unless a co-morbid condition requires another medication. (see table)
Q.9. ECG finding of acute pericarditis?
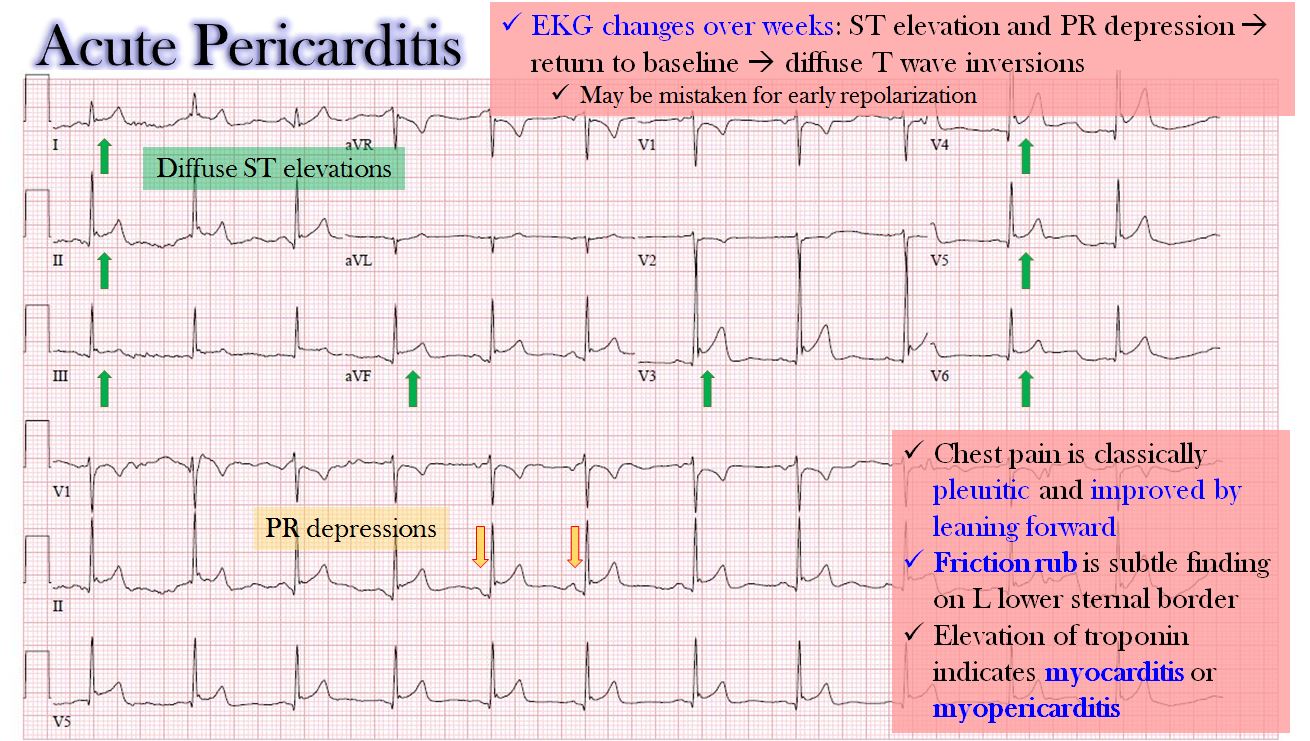
Correct Answer : B
Pericarditis is the inflammation of the pericardim, the sac-like membrane surrounding the heart.
ECG findings-
- Low voltage- The electrical signals from heart have to pass through inflamed pericardium, which acts as an insulator. This reduces the amplitude of the electrical signals.
- Diffuse change- Look for wide ST elevation [not limited to specific reigons like MI]
- PR depression- A hallmark of pericarditis.
- T wave changes- May become inverted in later stage.
Q.10. A known case of chronic atrial fibrillation on warfarin 5 mg, came for follow up, you find INR 7 but no signs of bleeding, what is your advice?
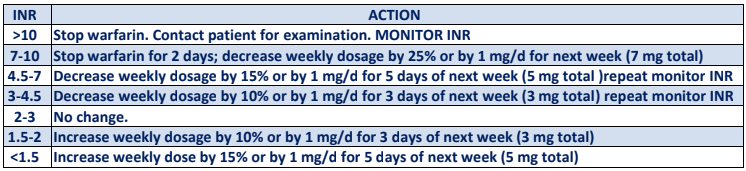
Correct Answer : B
INR is a test used to measure time taken by blood to clot. A normal INR ranges between 0.8-1.2. Warfarin is a blood thinner medication used to prevent stroke in people with atrial fibrillation. An INR of 7 is very high compared to the normal range, so we will stop warfarin dose immediately and repeat the INR test next day.
Q.11. A patient is a known case of CAD, the best exercise is?
Correct Answer : C
Anaerobic exercise (endurance): It is the best option for patients with CAD. This type of exercise involves short bursts of intense activity typically lasting for less than 2 minutes.
- Isotonic exercises, like running or swimming can improve cardiovascular health, but might not be suitble for patients with severe symptoms.
- Weight-bearing exercise (isometric) may build muscle strength, and bone density they can cause spike rise in BP and is bad for CAD patients.
- Yoga may not be enough to prevent cramps, stiffness, and back pain but is not enogh to improve cardivascular health.
Q.12. Which of the following is a complication of sleep apnea?
Correct Answer : A
Sleep apnea→ Hypoxemia and hypercapnia→ sympathetic activity increased→ increased afterload on heart →worsened CHF →pulmonary congestion→ narrowed upper airway→ increased apnea events →worsened sleep apnea.
Incorrect options-
- MI- it is not a direct complication of sleep apnea.
- Pericarditis- it usually does not occur due to sleep apnea.
- Endocarditis- not a direct complication of sleep apnea.
Q.13. Which of the following medication if taken without indication, will need to take the patient immediately to the hospital?
Correct Answer : D
Quinidine /quinine is an antiarrhythmic medication. However thay can have certain serious side effects like dangerously abnormal heart rhythm, tinnitus, and hearing loss.
Incorrect options-
- Penicillin can cause allergic reaction which do not require hospitalization.
- Diphenhydramine is an antihistamine with no seious complications.
- OCP's have no life threatening side effects.
Q.14. What is true about alpha blocker?
Correct Answer : C
Alpha-blocker can cause tachycardia and orthostatic hypotension.
Q.15. Which of the following drugs increases the survival in patients with heart failure?
Correct Answer : B
ACE inhibitors Increase survival and decreases mortality. ACE inhibitors inhibit aldosterone which if present in high concentrations causes modification of the cardiac myocytes in the long term.
Q.16. Which of the following is the recommended diet to prevent IHD?
Correct Answer : C
Fruits and vegetables contain nutrients.and are stongly recommended to prevent IHD. They contain vitamins, minerals, antioxidants and fiber which help lower the blood cholestrol levels, that improves the overall health.
Q.17. An elderly patient presented with SOB, rales in auscultation, high JVP, +2 lower limb oedema, what is the main pathophysiology?
Correct Answer : A
[Tricky question] Here we have symptoms of both left ventricular failure (SOB, Rales) & right ventricular failure (High JVP & LL edema). So, more commonly left ventricular failure leads to right ventricular failure due to overload and not vice versa. So the most correct option is left ventricular dilatation.
Q.18. An IV drug abuser presented with fever, arthralgia and conjunctival hemorrhage, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
The combination of symptoms in the given scenario strongly indicate towards bacterial endocarditis.
Q.19. What is arterial injury characterized by?
Correct Answer : D
Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart. Oxygen content gives the arterial blood bright red color. The high pressure in arteries causes the blood to spurt out in a pulsatile manner with each heartbeat.
Q.20. A patient had fatigue while walking last night. He is on atorvastatin for 8 months, ciprofloxacin, diltiazem and alphaco, what's the cause of his fatigue?
Correct Answer : B
Statins cause myopathy which leads to muscle weakness. Atorvastatin is a statin medication, used to lower cholesterol. A side effect of which can be muscle weakness and fatigue.
Q.21. All of the following are risk factors for heart disease, except?
Correct Answer : A
HDL is also called ''good cholesterol''. HDL cholesterol plays a crucial role in removing excess cholesterol from the bloodstream and transporting it to the liver for processing and removal from the body.
Q.22. What's true about systolic hypertension?
Correct Answer : C
Systolic hypertension is defined as an elevated systolic BP while the diastolic pressure remains within a normal range.
Q.23. A patient presents with continuous murmur, what's the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
A continous murmur is defined as a murmur that is audible throughout the cardiac cycle, it is a typical feature of Patent Ductus Arteriosus.
Q.24. A patient has high blood pressure on multiple visits, he was diagnosed with hypertension, what is the pathophysiology?
Correct Answer : A
The main pathophysiology behind most cases of HTN is an increase in peripheral resistance.
Peripheral resistance is defined as resistance that blood encounters when it flows through the small blood vessels. When the blood vessels constrict, the resistance to blood flow increases, this increased resistance leads to an elevation in BP.
Q.25. What's the drug of choice for supraventricular tachycardia?
Correct Answer : A
Adenosine is the drug of choice in supraventricular tachycardia. Its acts by blocking the electrical signals in the heart which allows the SA node to regain control of heart rhythm.
Q.26. Which of the following pulse character goes with the disease?
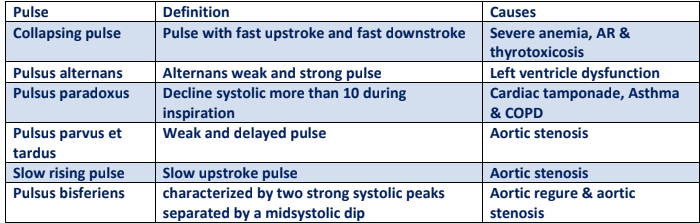
Correct Answer : A
In severe anaemia the blood volume is significantly reduced leading to decreased BP. Therefore the pulse feels weak and collapses easily when palpated.
Q.27. An old patient presents with history of dizziness & falling down 1 day ago accompanied by history of epigastric discomfort. He has very high tachycardia “around 130-140 bpm” and BP 100/60. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Symptoms and vitals go in favour of leaking aortic aneurysm. Aortic aneurysm is a bulge in the wall of aorta, when the wall weakens it can tear or rupture, causing blood to leak into chest cavity. This immense bleeding puts immense preassure on heart, leading to the symptoms being experienced by the patient.
Incorrect option-
- Peptic ulcer- While epigastric discomfort can indicate towards this, other symptoms of dizziness, falling down, and high heart rate are not associated with ulcers.
- GERD- Causes reflux, heart burn but not the above mentioned symptoms.
- Aortic stenosis- Typically doesn't present with above mentioned symptoms.
Q.28. A patient presents with orthostatic hypotension. What's the mechanism?
Correct Answer : A
Decreased volume of blood in vessels→ reduced cardiac output→ drop in BP when standing.
Q.29. What's the cause of sudden death in athlete?
Correct Answer : A
HOCM is a common cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes. In this condition heart muscle becomes abnormally thick, which can lead to obstruction of blood flow outside heart, leading to aryythmias during sternous exercise.
Q.30. Which of the following antihypertensive drugs is contraindicated for an uncontrolled diabetic patient?
Correct Answer : A
Hydrochlorothiazide is a thiazide diuretic which is based on the mechanism of removing fluid from the body which can lead to increase in blood gluscose levels making it unsuitable.
Q.31. A hypertensive patient presents with liver cirrhosis, lower limb oedema and ascites. What medication will you start?
Correct Answer : C
Spironolactone is the first-line treatment for ascites due to liver cirrhosis. It's a potassium sparing diuretic that counters the effects of aldosterone, which is elevated in cirrhosis. This reduces fluid retention effectively in patients with liver disease.
Q.32. A 69-year-old non diabetic with mild hypertension, and no history of coronary heart disease, what's the best drug in treatment?
Correct Answer : A
Thiazide diuretics are the drug of choice for mild HTN with no other additional comorbidities'.
Q.33. Which of the following decreases mortality after MI?
Correct Answer : A
Metaprolol is a beta blocker that reduces the heart rate and make it beat more steadily, lowering the risk of future complications.
Incorrect options-
- Nitroglycerine is mainly used for symptom relief.
- Thiazide are great for managing high BP.
- Morphine helps in managing pain and anxiety during the attack.
Q.34. A male patient with HTN is on medication, his BP is well controlled, the patient is having garlic water and he is convinced that it is the reason for BP control, what you'll do as his physician?
Correct Answer : A
If the patient's BP is well-controlled and they feel good using garlic water, there's no reason to stop it.
Q.35. A patient with rheumatic fever after untreated streptococcal infection after many years presented with mitral regurgitation, the cause of massive MR is dilatation of which of the following?
Correct Answer : D
Rheumatic fever can damage heart valves, the most common valve involved is the mitral valve. Damage to the mitral valve leads to mitral regurgitation, as the valve is not closing properly and allowing the blood to leak back into the left ventricle. The left venticle has to overcompensate for this leak causing it to enlarge due to hypertrophy.
Q.36. Regarding MI, all of the following statements are true, except?
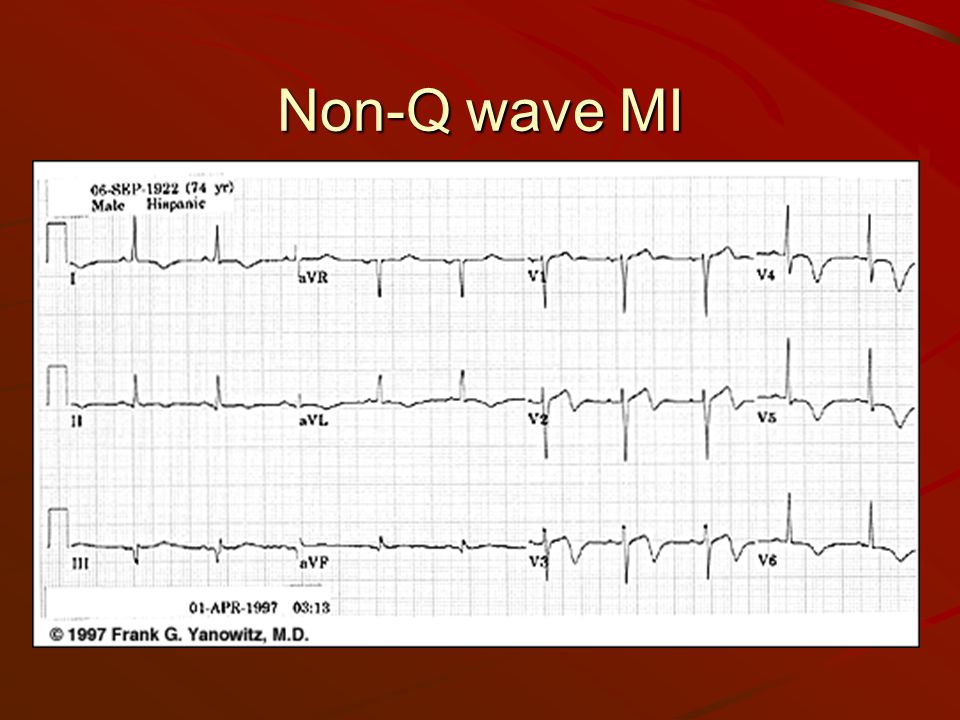
Correct Answer : C
While Q waves are a classic sign of a MI, especially in the early stages but sometimes the damage to the heart is not severe enough to create a Q wave.
Q.37. An adult presents with asystole, what will you give to the patient?
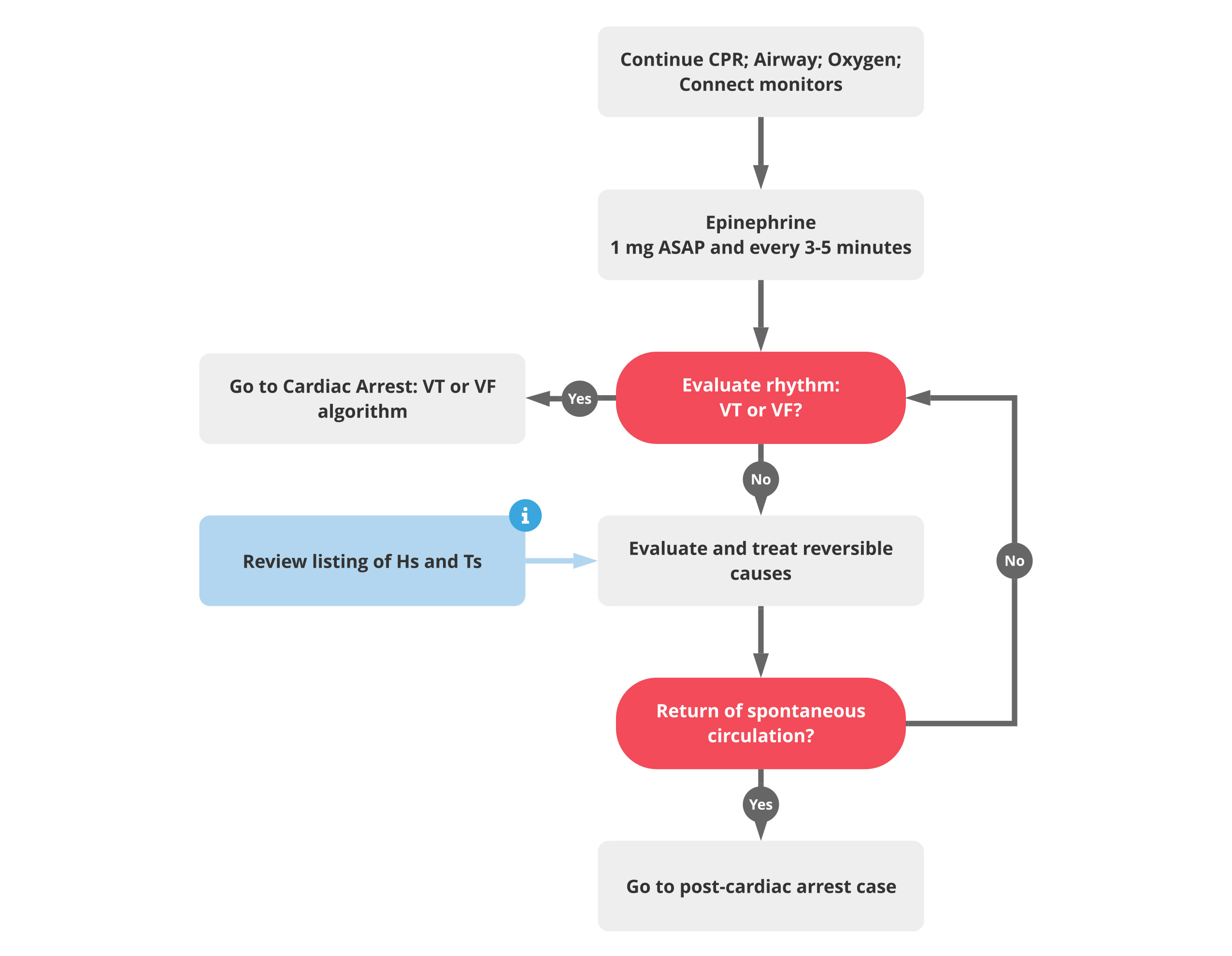
Correct Answer : A
Epinephrine also known as adrenaline is the only medication specifically recommended in the ACLS protocol for asystole.
- Dose- 1mg given I/V or via the ETT. This dose may be repeated every 3-5 min as needed.
Q.38. A patient who is a known case of diabetes and HTN presents with stroke. What is the pathophysiology of stroke?
Correct Answer : A
Atherosclerosis is the plaque buildup within blood vessel, narrowing it and making it harder for blood to flow. Diabetes and HTN are major risk factors for the development of atherosclerosis.
- Hypertension- Increased BP →stress on blood vessels→ endothelial damage→ inflammation →cholesterol deposition →Atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes- Increased blood glucose→ glycation of proteins →endothelial dysfunction→ plaque formation→ Atherosclerosis.
Q.39. A middle aged patient has acyanotic congenital heart disease, the X-ray shows ventricle enlargement and pulmonary hypertension, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
VSD is a common acyanotic heart condition. Ventricular enlargement is caused due to strain on the heart as increased amount of blood enters through the VSD. The extra blood is pumped into the lungs leading to high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries.
Incorrect options-
- ASD can cause similar findings but is comparatively less responsible for ventricular enlargement or pulmonary HTN.
- Truncus arteriosus usually presents with cyanosis.
- Pulmonary stenosis would cause the above mentioned symptoms significantly.
Q.40. A middle aged acyanotic male with CXR showing increase lung marking & enlarged pulmonary artery shadow, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
ASD is an acyanotic condition.
- Increased lung markings is suggestive of increased blood flow to lungs.
- Enlarged pulmonary artery shadow is due to increased blood flow to the lungs putting strain on the pulmonary arteries.
Q.41. Most common cause of secondary hypertension in female adolescent is ?
Correct Answer : C
The kidneys play a crucial role in regulating BP. When they are damaged, they can't filter blood properly, leading to buildup of fluids and an increase in BP.
Incorrect options-
- Cushing syndrome can cause HTN but is not a common cause among adolescents.
- Hyperthyroidism can cause HTN but is more likely to occur in older adults.
- Essential HTN also known as primary HTN is most common type of high BP.
Q.42. Commonest cause of secondary HTN in an 18 year old male?
Correct Answer : D
According to the age group;
- In pediatrics up to 18 years old it is renal parenchymal disease.
- In young adults it is thyroid disease.
- In middle age adults it is aldosteronism.
- In old adults > 65 it is atherosclerosis.
Q.43. Medical student had RTA , his systolic pressure is 70 mmHg, what you will do next in management ?
Correct Answer : A
In the given scenario the patient's systolic BP is low, our priority at the time is to restore fluid volume and increase the blood pressure. For achieving this we will use I/V fluids.
Q.44. A 55 year old complains of dyspnea, PND with past history of mitral valve disease, what's the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Mitral valve disease is commonly associated with left-sided heart faliure. When this valve is damaged, it can lead to backup of blood in the lungs, causing symptoms like dysnea and PND.
Q.45. What is the first sign of left side heart failure?
Correct Answer : B
Fluid build up in the lungs is the first sign of LHF, leading to dyspnea on exertion. Left-sided heart faliure impairs the ability of heart to pump blood effectively out of the left ventricle leading to buil-up of blood and fluid in lungs.
Incorrect answers-
- Orthopnea is shortness of breath on lying flat which is later sign of left-sided heart faliure.
- Pedal edema is sighn of righ-sided heart faliure.
- PND is defined as waking from sleep due to shortness of breath, it's a later sign of left-sided heart failure.
Q.46. Which of the following statement is true about oral anticoagulants?
Correct Answer : D
- Warfarin should not be given to pregnant lady, especially during the 1st and 3rd trimesters, as it crosses placenta as well as blood-brain barrier, it is usually difficult to reverse warfarin within a short time because it has a long half-life and works on vitamin K factors which take time to reverse.
- Barbiturates decrease the anticoagulant effect of warfarin.
Q.47. All of the following are features of rheumatic heart disease, except ?
Correct Answer : C
The Jones criteria require the presence of 2 major or 1 major and 2 minor criteria for the diagnosis of rheumatic fever.
The major diagnostic criteria include carditis, polyarthritis, chorea, subcutaneous nodules, and erythema marginatum. The minor diagnostic criteria include fever, arthralgia, prolonged PR interval on the ECG, elevated acute phase reactants “ESR”, presence of C-reactive protein, and leukocytosis.
Additional evidence of previous group A streptococcal pharyngitis is required to diagnose rheumatic fever. One of the following must be present: Positive throat culture or rapid streptococcal antigen test elevated or rising streptococcal antibody titer, history of previous rheumatic fever or rheumatic heart disease.
Q.48. A middle-aged male is involved in RTA, his RR is 30/min, heart sounds are muffled & the JVP is elevated, BP: 80/40 & a bruise over the sternum, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Cardiac tamponade (influenced by volume and rate of accumulation) includes the following features-
- Beck's triad (jugular venous distention, hypotension, and muffled heart sounds)
- Hypotension and tachycardia without elevated jugular venous distension if the associated hemorrhage is outside pericardial sac
- Pulsus paradoxus
- Cyanosis
- Varying degrees of consciousness
Q.49. In premature ventricular contracture (PVC), all are true, except ?
Correct Answer : A
PVCs in young, healthy patients without underlying structural heart disease are usually not associated with any increased rate of mortality. Antiarrhythmic therapy with flecainide and encainide has been shown to increase mortality. After MI, antiarrhythmic - Despite the suppression of ectopy- patients treated with encainide, flecainide, or moricizine had increased rates of sudden death and death from all causes. Amiodarone may be an exception, as it has been shown to reduce post-MI arrhythmia and death.
Q.50. Which one of the following is not true in patient with atrial fibrillation and stroke?
Correct Answer : A
Aspirin is commonly used blood thinner to reduce the risk of stroke in patients with AF. It's not accurate to say that aspirin is not true in patients with AF.
Q.51. ECG stress test is indicated in all of the following, except?
Correct Answer : A
Indications of stress test are:-
- 1) Diagnosis of CAD in patients with chest pain that is atypical for myocardial ischemia.
- 2) Assessment of functional capacity and prognosis of patients with known CAD.
- 3) Assessment of prognosis and functional capacity of patients with CAD soon after an uncomplicated myocardial infarction (before hospital discharge or early after discharge.
- 4) Evaluation of patients with symptoms consistent with recurrent, exercise-induced cardiac arrhythmia.
- 5) Assessment of functional capacity of selected patients with congenital or valvular heart disease.
- 6) Evaluation of patients with rate-responsive pacemakers.
- 7) Evaluation of asymptomatic men > 40 years with special occupations (airline pilots, bus drivers, etc)
- 8) Evaluation of asymptomatic individuals > 40 years with two or more risk factors for CAD.
- 9) Evaluation of sedentary individuals (men 45 years and women 55 years) with two or more risk factors who plan to enter a vigorous exercise program.
- 10) Assessment of functional capacity and response to therapy in patients with IHD or heart failure.
- 11) Monitoring progress and safety in conjunction with rehabilitation after a cardiac event or surgical procedure.
Q.52. 5 days after MI, a patient developed SOB and crackles in both lungs. Most likely cause is ?
Correct Answer : B
After MI mitral valve can become weakened or rupture which leads to acute mitral regurgitation, where blood flows backwards from left ventricle to left atrium during systole. This leads fluid to backup into lungs leading to these symptoms.
Q.53. A woman developed DVT, what's the best management?
Correct Answer : A
- Bed rest helps in preventing pulmonary embolism by reducing the risk of clot dislogement.
- Heparin prevents clot from increasing in size.
- Warfarin taken longer to start working but provides long term protection against further clots.
Q.54. A 70-year-old male came with history of leg pain after walking, improved after resting, he notices loss of hair in the shaft of his leg and it appears shiny, what's the probable cause ?
Correct Answer : A
CLI is a condition in which there is a narrowing or blockage of the arteries in the legs, reducing the blood flow. This can cause claudication that worsens with activity and improves with rest. The loss of hair and shiny appearance of skin is due to poor blood circulation.
Incorrect options-
- DVT causes leg pain, swelling, redness and warmth in the affected limb due to precense of clot in deep vein.
- DIC presents with widespread bleeding and not as a isolated leg pain.
- Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of spinal canal that compresses nerves and causes leg pain, however it typically presents as back pain which then radiates to the legs, but other above mentioned symptoms are not present.
Q.55. A patient comes to the ER with weak rapid pulse, what is your next step?
Correct Answer : C
Waiting for resuscitation team ensures that the patient receives care from a group of trained people who can initiate an appropriate treatment.
Weak pulse is not an indication to start CPR.
Q.56. Which of the following medications is considered as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor?
Correct Answer : A
Simvastsin is a hypolipidemic drug used to control elevated cholesterol ‘hypercholesterolemia’
Q.57. An old patient with HTN & BPH presents to the clinic, what's the treatment?
Correct Answer : D
Alpha blockers relax the muscle in bladder neck and prostate, improving urine flow and relieving symptoms of BPH.
Q.58. A patient presents with anterior MI and multiple PVCs, what is the treatment for this arrhythmia?
Correct Answer : A
Amiodarone works by stabalizing the heart rhythm and reduces the risk of more dangerous arrythmias like ventricular tachycardia.
Incorrect options-
- No treatment might be required in some PVCs but in this scenario an anterior MI and multiple PVCs are dangerous and should be treated appropriately.
- Nifedipine is a calcium channel blocker that is used to treat high BP.
- Spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic used to treat heart faliure and high BP. Not effective in treating arrythmia.
Q.59. One of the signs of severe hypokalemia is?
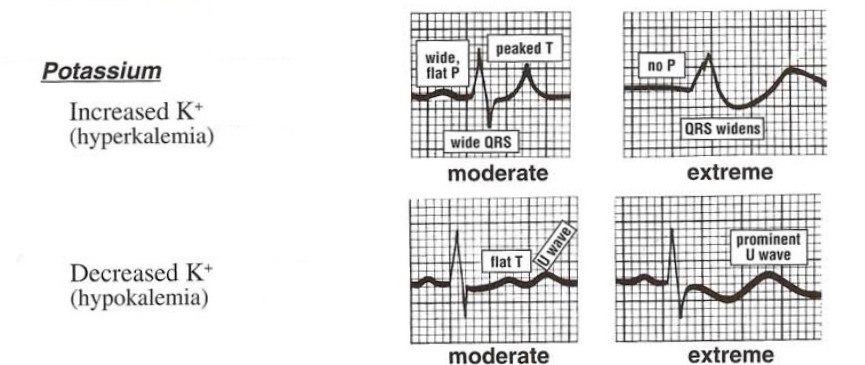
Correct Answer : D
Severe hypokalemia is defined as a level less than 2.5 mEq/L.
Severe hypokalemia is not linked with any symptoms but may cause:
- 1) Myalgia or muscle pain
- 2) Disturbed heart rhythm including ectopy
- 3) Serious arrhythmias (electrical faster or slower than normal)
Sequence of ECG changes in hypokalemia :
- Appearance of U-wave
- T-wave flattening; U-wave becomes more prominent; QU interval mistaken as prolonged QT interval
- T-wave starts inverting; U-wave is upright (looks like biphasic T-wave with proximal negative deflection and distal positive deflection)– but it is not a biphasic T-wave, rather they are 2 separate waves, i.e, inverted T wave and upright U wave.
- The entire ST segment going down: ST segment depression- looks like Roller-coaster pattern
Other ECG findings in hypokalemia: PR prolongation, BBBs, polymorphic VT.
[ECG changes in hyperkalemia: 1) Peak T wave & Loss of P wave 2) Wide QRS ( in severe cases) 3) PR prolong ( in severe cases)].
Q.60. A 31-year-old persons autopsy shows a bulky vegetation’s on aortic and mitral valves, what is the diagnosis?
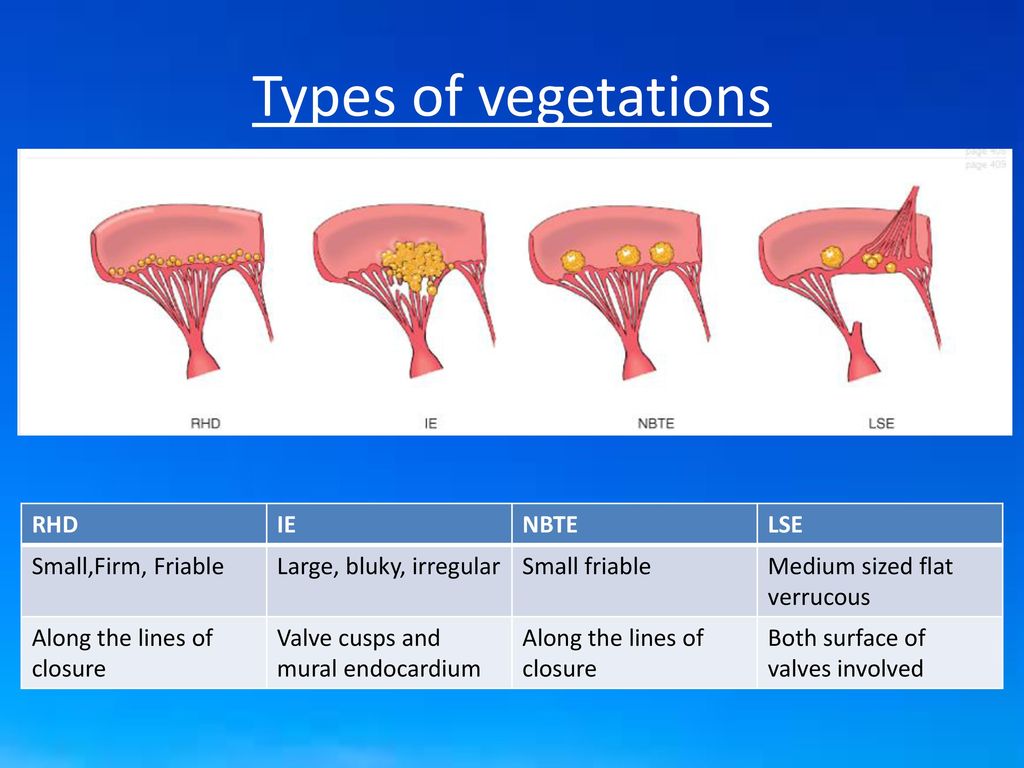
Correct Answer : A
Infective endocarditis is the infection of the inner lining of the heart and heart valves. It is often caused by bacteria or fungi that enter the blood stream and form colonies in heart valves forming vegetations.
Q.61. The effectiveness of ventilation during CPR is measured by?
Correct Answer : A
During CPR, effective ventilation means that air is sucessfully entering the lungs and expanding them. Chest rise is the most direct and visible sign.
Q.62. Which one of the following is a manifestation of hypokalemia?
Correct Answer : D
When potassium levels are low it can lead to muscle weakness, this in turn can affect the respiratory muscles leading to respiratory acidosis, where the body is unable to remove carbondioxide effectively causing a buildup of acid in blood.
Q.63. A 50-year-old patient, who is diagnosed with hypertension. He used to drink one glass of wine every day, he also has high Na and high K intake, his BMI is 30kg/m, what is the strongest risk factor for having hypertension in this patient?
Correct Answer : D
BMI 30 is indicative that the patient is obeses. Obesity is a major risk factor for HTN.
Incorrect options-
- Wine in less amount is unlikely to cause high BP.
- High Na intake is a well established risk factor for HTN. But the patient is also taking K+ which can help counterattack the effect of sodium on blood pressure.
Q.64. Premature ventricular contraction is due to?
Correct Answer : C
There are many causes of premature ventricular contractions, which include:
- 1) Heart attack, High blood pressure
- 2) Cardiomyopathy, including congestive heart failure, disease of heart valves such as mitral valve prolapse
- 3) Hypokalemia and hypomagnesaemia
- 4) Hypoxia for example, hypoxia occurs with lung diseases such as emphysema or COPD
- 5) Medications such as digoxin, aminophylline, tricyclic antidepressants& ephedrine containing, decongestant
- 6) Excessive intake of alcohol, excess caffeine intake
- 7) Stimulant drug use such as cocaine, and amphetamines
- 8) Myocarditis (heart muscle inflammation) and cardiac contusion (heart muscle injury)
- 9) Premature ventricular contractions also occur in healthy individuals without heart diseases.
Q.65. What is cardiac syncope?
Correct Answer : B
Cardiac syncope is a sudden breif loss of consiousness caused by a temporary decrease in blood flow to the brain. The characterstick feature of cardiac syncope is fast recovery.
Q.66. Patient with hypertrophic subaortic stenosis referred from dentist before doing dental procedure, what is true ?
Correct Answer : C
Patients with HOCM are not considered at high risk of infective endocarditis during routine dental procedure. Therefore, they typically do not require antibiotic prophylaxis before dental procedure.
Q.67. A female has narrow QRS on ECG, what is the contraindication for adenosine?
Correct Answer : A
Adenosine is a medication used to treat SVT. One of the contraindications of adenosine is LHF. Adenosine can cause a significant drop in BP which can further compromise blood flow in patients with LHF, worsening their symptoms and even causing cardiac arrest.
Q.68. A 15-year-old male patient complains of joint pain & fever for 1 week , difficulty in swallowing, his liver is 1 cm below the costal margin, and a pansystolic murmur. What's the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
RHD is the most likely diagnosis according to the given scenario.
Q.69. A patient on digoxin drug, started to visualize bright lights and other signs of visual disturbances. What has caused this?
Correct Answer : A
The patient is likely experiencing digoxin toxicity, which can cause visual disturbance.
Features of digoxin toxicity-
- Cardiac- Bradycardia, arrythmias
- GI- Nausea, vomitting
- CNS- Confusion, visual disturbance
- ECG- Prolonged PR, slooping depression in ST segment
Q.70. How does the heart get more blood?
Correct Answer : C
Stroke volume determines the amount of blood ejected with each heartbeat ensuring better perfusion of heart muscles.
Q.71. The best way of treating patient with BP= 130-139/80-85 mmHg is to?
Correct Answer : A
The best way to treat this patient is through weight reduction and physical activity. This lifestyle modification is essential for managing prehypertension, which is a condition where bloodpressure is higher than normal but not yet in the hypertensive range.
Q.72. A man presents with family history of CAD, his daily diet consists of eats 4 fruits, 4 vegetables, 8 breads , 4 meat and 4 diary products. What to do next?
Correct Answer : A
Meat and diary are high in unsaturated fats, and increase the risk of CAD. Reducing their intake can help lower cholesterol and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Q.73. A male patient who is a known case of hypercholesterolemia, BMI: 31, his investigations shows high total cholesterol, high LDL & high TG, of these investigations what is the most important risk factor for developing coronary artery disease?
Correct Answer : A
LDL cholesterol is often referred to as bad cholesterol. High LDL levels are a major risk factor for atherosclerosis.
Q.74. An adult presents with pulseless. On ECG, QRS are present as different shape complexes, what's the cause?
Correct Answer : B
The above mentioned features of pulselessness and different shape QRS complexes, indicates that the electrical activity is originating from different areas in heart suggesting disorganized electrical system. This pattern is commonly seen in ventricular dysfunction.
Q.75. A patient was brought by his son. He was pulseless and ECG showed ventricular tachycardia, BP 80/50, what is your next action?
Correct Answer : A
Pulse-less VT is treated by unsynchronized shock (not cardioversion) and CPR.
The first thing to be given is the shock, then CPR then drugs (epinephrine & amiodarone).
Q.76. A patient presents with severe chest pain for the past 2 hours along with sweating. His ECG shows ST segment depression 2-3 cm. Trop I is normal. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Angina with ST segment depression 1-2mm is a classic finding in ischemic heart block. The ST segment depression indicates that the heart is not getting enough blood flow.
Q.77. Which one of the following is a characteristic of syncope (vasovagal attack)?
Correct Answer : A
The defining characterstic of syncope is that it has an abrupt onset.
Incorrect options-
- Rapid recovery is present but irt is not typically the defining characterstic.
- When turn neck to one side is not a trigger for syncope to occur.
- Bradycardia can be a symptom but not a defining characterstic of syncope.
Q.78. A patient who is a known case of posterior MI presented with syncope. Examination showed cBatman (a) wave with tachycardia, unreadable BP & wide QRS complexes on ECG. The diagnosis is?
Correct Answer : A
As the patient has a history of MI, it can indiacate that the patients electrical system can get disrupted which can inturn lead to abnormal rhythms like re-enterant tachycardias. The precense of cBatman ''a'' wave wave suggests that the atria are contracting against a closed mitral valve, which is a sign of AV nodal re-enterant tachycardia.
Q.79. Which of the following indicate inferior wall MI (Inferior chest leads) in ECG?
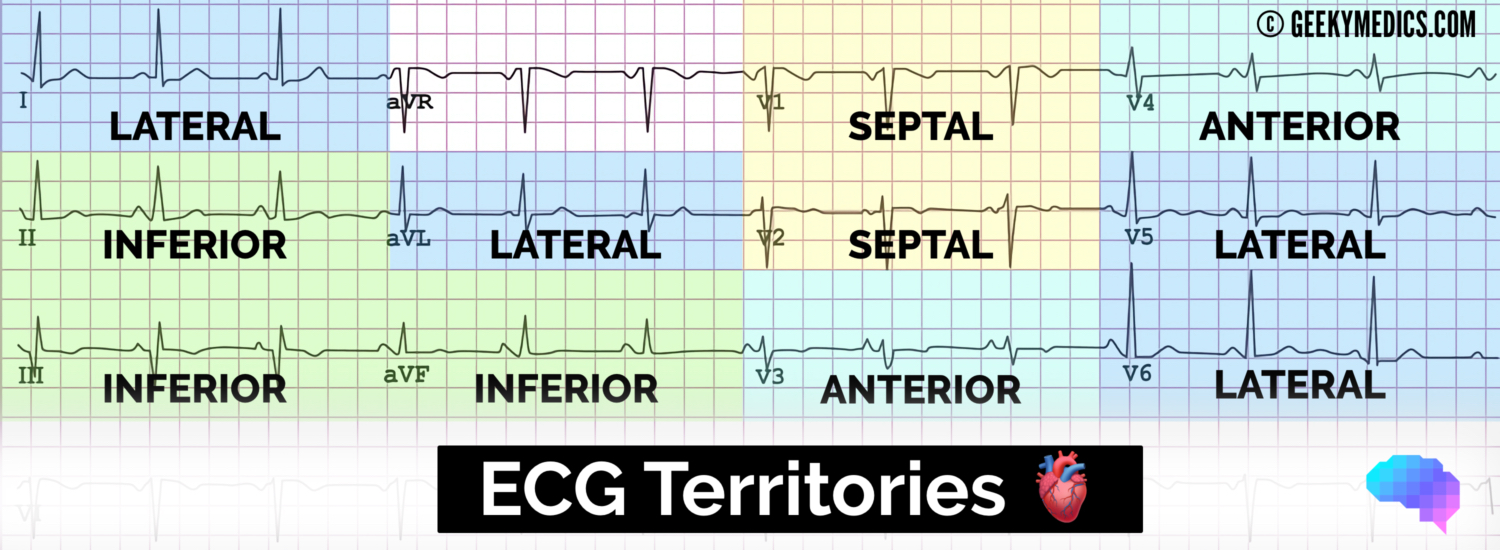
Correct Answer : A
These leads are specifically placed to record the readings of inferior portion of heart
Q.80. ECG shows ST elevation in the following leads V1, 2, 3, 4 & reciprocal changes in leads aVF & V2, what is the diagnosis?
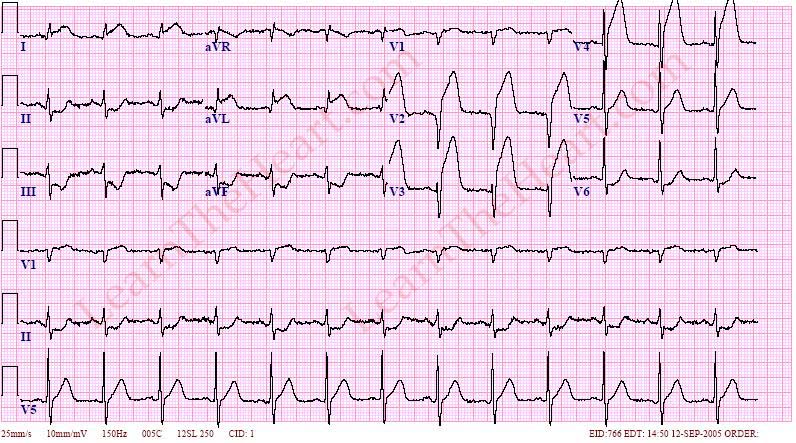
Correct Answer : B
ST elevation in leads V1-V4 is the hallmark of an anterior wall myocardial infarction. Reciprocal depression in the inferior leads is a common finding associated with anterior wall MI.
Q.81. A patient had chest pain and fainted, his ECG shows ST elevation and significant Q wave in V4 and ST depression in inferior leads, what's the diagnosis?
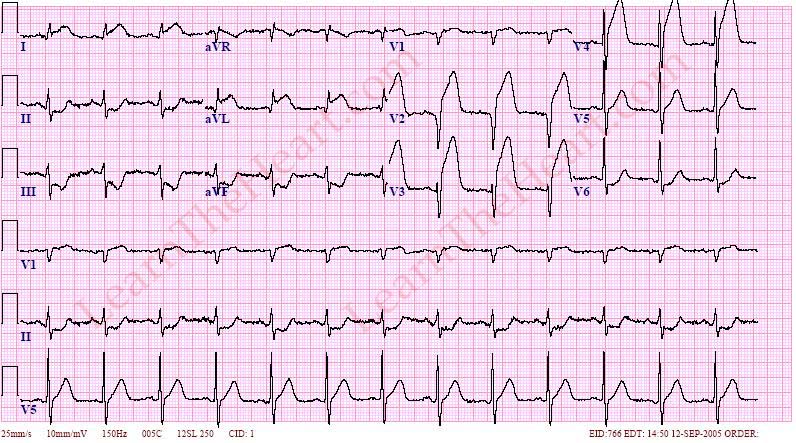
Correct Answer : A
The combination of ST elevation in V4 with a significant Q wave, and ST depression in the inferior leads strongly points towards an anterior wall MI.
Incorrect options-
- Inferior MI presents with ST depression in inferior leads but the precense of ST elevation and a significant Q wave makes it less likely.
- Pericarditis presents as diffuse ST segment elevation and PR segment depression.
- Posterior MI present as ST depression in V1-V4 [anterior leads] and reciprocal ST elevation in inferior leads.
Q.82. Best treatment for a woman with migraine and HTN?
Correct Answer : A
Propanolol is a beta-blocker that is effective in both preventing migraines and lowering blood preassure. It blocks the effects of adrenline which will effectively address both her migraine and hypertension.
Q.83. Warfarin is given to all the following, except?
Correct Answer : D
Warfarin is primarily used to prevent the formation of blood clots in people who are at an increased risk of stroke or heart attack. In the above mentioned option elderly male who has a normal heart has no risk of formation of blood clots so warfarin is not needed for this patient.
- All the other options have heart condition that can lead to clot formation.
Q.84. Which of the following will increase heart blood flow when there's increased load on heart?
Correct Answer : A
Coronary arteries supply blood to the cardiac muscle. When they dialate there is an increased flow of blood through them which will increase the oxygen and nutrient delivery to the cardiac muscle when there is an increased load on heart.
Q.85. Most common cause of chronic hypertension is?
Correct Answer : C
Interstitial renal disease is a disorder characterized by damage to the filtering units of kidney that leads to impairement in the kidneys ability of regulating BP, leading to choronic HTN.
Incorrect options-
- DM is a significant risk factor for causing HTN, but its not the most common cause.
- HTN is condition itself not cause.
- Amyloidosis can cause HTN but is less common as compared to interstitial renal disease.
Q.86. All are true about the best position for hearing murmurs, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
These murmurs are usually heard best during standing or sitting positions, as these positions increase the blood flow to heart, making the murmur more audible. The supine position may not be the best for hearing these type of murmurs.
Other options-
- Supine position is best to hear venous hum.
- AR murmurs are typically heard louder when the patient is in sitting position.
- Pericardial rub is best heard when the patient is sitting up and leaning forward.
Q.87. What is the important side effect of antihypertensive drugs in elderly patients?
Correct Answer : A
Hypotension is a major concern in elderly patients taking antihypertensive drugs. These drugs lead to hypotension and cause lightheadedness, dizziness, falls, and even unconsiousness.
Q.88. A patient comes with precordial pain, ECG shows: ST segment elevation, patient was given aspirin and nitrate, but no relief of pain, what next step will you do?
Correct Answer : A
Morphine is a strong pain reliever which will help relieving severe chest pain, also it helps in tackling the anxiety faced by the patient during this period and will improve the overall well-being of this patient. Administering morphine via the IV route ensures rapid onset of action, whcih is crucial in time-sensitive situation like this.
Q.89. A 60-year-old male presented with history of chest pain since 2 hours, ECG showed ST elevation on V1-V4 with multiple PVC & ventricular tachycardia. The management will be?
Correct Answer : D
Amiodarone is an antiarrhythmic medication that is widely used to treat and prevent dangerous heart rhythms like ventricular tachycardia. The scenario also mentions precense of ST segment elevation suggestive of MI which can also be a cause of the ventricular tachycardia. Amiodarone will help by stabilizing the heart rhythm and reduce the risk of further detoriation and complication.
Incorrect options-
- Digoxin is used to treat heart faliure not ventricular arrythmias.
- Lidocaine can be used, but is not the first-line treatment in the precense of ST segment elevation.
- Plavix and morphine are antiplatelet and pain relievers, both of which don't help in managing the abnormal rhythm.
Q.90. Which of the following statement is true about ventricular fibrillation?
Correct Answer : C
When the VF waves have a larger amplitude [>3mm] and are more irregular, it generally indicates that the VF is of recent onset. It indicates better chances of sucessful defibrillation because it is suggestive of some residual myocardial energy.
Treatment-
- Start CPR.
- Defibrillate [120-200J biphasic or 360J monophasic].
- Give epinephrine 1mg every 3-5 min.
- Give amiodarone 300mg, then 150mg if needed.
- Treat reversible causes [hypoxia, acidosis, thrombosis].
Q.91. A patient presents with diastolic blowing murmur which is best heard in the left sternal border and increases in squatting position. Which of the following condition is he suffering from?

Correct Answer : B
MS, AS, AR, MR all increased by squatting, diastolic murmur at apex is MS & at left sternal border is AR.
Q.92. A 35-year-old male has SOB, orthopnea, PND, nocturia and lower limb edema. What’s the most common cause of this condition in this patient?
Correct Answer : A
The above mentioned clinical features are strongly suggestive of heart faliure. Valvular heart disease is a common cause of heart faliure.
Q.93. A 35-year-old woman presented with exertional dyspnea. Precordial examination revealed loud S1 and rumbling mid diastolic murmur at apex. Possible complications of this condition can be all the following, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : C
All these are features of mitral stenosis. Atrial fibrillation occurs secondary to left atrial enlargement, the fibrillation increases the risk of thromboembolism. There’s more blood in the left atrium, so more is flowing back to the lungs causing pulmonary congestion and edema, when the lungs get congested they try to protect itself from this excess fluid by constricting the pulmonary arteries, so more constriction leads to more resistance and therefore results in pulmonary hypertension.
- The option left ventricular failure doesn’t occur. On the contrary, the LV is very relaxed since less blood is passing through the stenosed valve to the ventricle, so the requirements on the LV are less, the stress is less and ejection fraction is normal.
Q.94. A patient who is 20 year old comes with palpitations, ECG shows narrow QRS complexes and pulse is 300 bpm. Which of the following statement is true?
Correct Answer : A
The combination of narrow QRS complex and rapid pulse are strongly indicating towards atrial flutter. Atrial flutter is a rapid heart rhythm originating from atria. Amiodarone is an antiarrythmic medication that is effective in slowing down the rapid heart rate associated with atrial flutter.
Incorrect option-
Nifedipine is a calcium channel blocker which is mainly used for treating high BP. It can be used to slow the heart rate but is not the first-line treatment for atrial flutter.
Q.95. A patient presented with sudden cardiac arrest, the ECG showed no electrical activities with oscillation of QRS with different shapes. The underlying pathophysiology is?
Correct Answer : B
No electrical activity and QRS oscillation is a characterstic feature of pulseless electrical activity [PEA]. In this condition the heart's electrical function is still intact but the heart muscle is itself not contracting effectively to pump blood. This inability is a sign of ventricular dysfunction.
Q.96. Which of the following is the least likely to cause infective endocarditis?
Correct Answer : A
50% of infective endocarditis occurs on normal valves.
Predisposing cardiac lesions:
- 1) Aortic/mitral valve disease
- 2) IV drug users in tricuspid valves
- 3) Coarctation
- 4) PDA
- 5) VSD ( Fallot's tetrad included )
- 6) Prosthetic valves
Q.97. Sinus tachycardia and atrial flutter, how to differentiate between both?
Correct Answer : B
Carotid massage is the simplest non-invasive way to potentially distinguish between these two heart conditions.
Gently massaging the carotid artery stimulates the vagus nerve, which can slow the heart rate in atrial flutter. It can reveal the typical ''sawtooth'' rhythm on ECG, making it easier to tell apart from sinus tachycardia.
Q.98. What is the pathophysiology behind MI?
Correct Answer : A
MI occurs when blood flow to heart muscle is reduced or blocked due to plaque buildup and disruption in coronary arteries. This narrowing restricts oxygen supply, leading to heart muscle damage.
Q.99. A female patient with moderate AS had syncope in the gym while she was doing exercise. If the syncope was due to AS, what is the cause?
Correct Answer : A
Syncope from aortic valve stenosis is usually exertional. In the setting of heart failure, it increases the risk of death. In patients with syncope, the 3-year mortality rate is 50%, if the aortic valve is not replaced.
- One popular theory is that severe AS produces a nearly fixed cardiac output. When the patient exercises, their peripheral vascular resistance will decrease as the blood vessels of the skeletal muscles dilate to allow the muscles to receive more blood to allow them to do more work.
- This decrease in peripheral vascular resistance is normally compensated by an increase in the cardiac output. Since patients with severe AS cannot increase their cardiac output, the blood pressure falls and the patient will syncope due to decreased blood perfusion to the brain.
- A second theory as to why syncope may occur in AS is that during exercise, the high pressures generated in the hypertrophied LV cause a vasodepressor response, which causes a secondary peripheral vasodilation that, in turn, causes decreased blood flow to the brain.
- Indeed, in aortic stenosis, because of the fixed obstruction to blood flow out from the heart, it may be impossible for the heart to increase its output to offset peripheral vasodilation. A third mechanism may sometimes be operative. Due to the hypertrophy of the left ventricle in aortic stenosis, including the consequent inability of the coronary arteries to adequately supply blood to the myocardium (see "Angina" below), arrhythmias may develop. These can lead to syncope. Finally, in calcific aortic stenosis at least, the calcification in and around the aortic valve can progress and extend to involve the electrical conduction system of the heart. If that occurs, the result may be heart block a potentially lethal condition of which syncope may be a symptom.
Q.100. S3 occurs in all of the following, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : A
Physiological 3rd heart sound is a filling sound that results from rapid diastolic filling as occurs in healthy young adults, children, athletes, pregnancy, and fever.
Pathological 3rd heart sound is a mid-diastolic sound that results from reduced ventricular compliance and if it's associated with tachycardia, it is called gallop rhythm.
- Left ventricular S3 It's louder at the apex and expiration. It is a sign of left ventricular failure and may occur in AR, MR, VSD, and PDA.
- Right ventricular S3 It's louder at the left sternal edge and with inspiration. Occurs with right ventricular failure or constrictive pericarditis.
Q.101. A patient presented with carotid artery obstruction of 80%, what's the management ?
Correct Answer : A
[If the obstruction is more than 70 % go for surgery].
Carotid endarterectomy is a surgical procedure that removes the palque buildup from inside the carotid artery. This helps to restore normal blood flow to the brain and reduce the risk of stroke.
Q.102. A patient is a known case of coronary artery disease, presents with cardiac symptoms, ECG and enzymes normal, what's done next??
Correct Answer : A
[After symptoms subside].
An exercise stress test is a simple and non-invasive way to assess how the heart responds to physical exertion by monitoring ECG, heart rate, and blood pressure.
[NOTE- In this scenario even though the patient is a known case we want to perform the test to - Assess blood flow during exertion, stratify high risk patients who might need further evaluation, and decide between medical management or invasive procedures].
Q.103. All of the following are treatment of chronic atrial fibrillation, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : A
In chronic atrial fibrillation, cardioversion is contra-indicated due to the risk of thrombus dislodgement.
- When AF is due to an acute precipitating event such as alcohol toxicity, chest infection, or hyperthyroidism, the provoking cause should be treated.
- Strategies for acute management of AF - ventricular rate control or cardioversion (+/- anticoagulation). Ventricular control rate is achieved by drugs that block the AV node, while cardioversion is achieved electrically with DC shock or medically with anti-arrhythmic.
In general, each patient deserves at least one cardioversion trial.
- If the patient is unstable and presents in shock, severe hypotension, pulmonary edema, or ongoing myocardial ischemia, DC cardioversion is a must.
- In less unstable patients or those at high risk for emboli due to cardioversion as in mitral stenosis, rate control is adopted (digoxin, b-blocker, or verapamil to reduce the ventricular rate. If it's unsuccessful then cardiovert the patient after anticoagulant him for 4 weeks.
Q.104. Treatment of unstable angina include all, EXCEPT ?
Correct Answer : D
- Hospitalization
- Strict bed rest
- Supplemental oxygen
- Sedation with benzodiazepine if there is anxiety.
- Systolic blood pressure is maintained at 100-120 mmHg and pulse should be lowered to 60/min.
- Heparin, antiplatelet, nitrates and b-blocker.
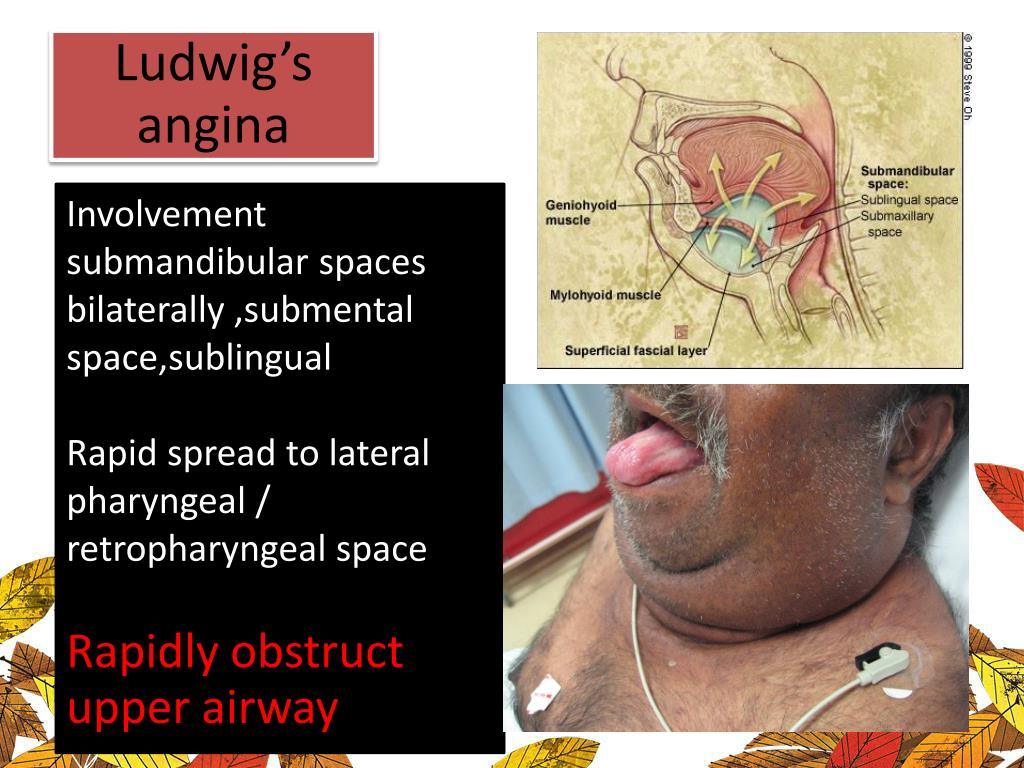
Q.105. What is the cause of death in Ludwig angina?
Correct Answer : B
Sudden asphyxiation is the most common cause of death in Ludwig angina. It is potentially life-threatening cellulitis or connective tissue infection, of the floor of the mouth, usually occurring in adults with concomitant dental infections and if left untreated, may obstruct the airways, necessitating tracheotomy.
Q.106. Each of the following murmurs will be elicited by the change of position, except?
Correct Answer : A
Innocent heart murmurs are harmless heart sounds that are common in children and young adults. They are often caused by turbulent blood flow through heart valves and are usually not associated with any underlying heart problems. These murmurs are often position independent.
Q.107. Old male comes with CHF & pulmonary edema, what is the best initial therapy?
Correct Answer : B
Furosemide is a powerful diuretic. In CHF heart struggles to pump blood leading to fluid buildup in the lungs causing pulmonary edema. Furosemide helps in quicly removing excess fluid thereby reducing the starin on the heart and improving breathing.
Q.108. A young patient came to ER with dyspnea and productive tinged blood frothy sputum, he is a known case of rheumatic heart disease, AF and his cheeks have dusky rash, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Mitral stenosis, often due to RHD, causes blood backup in the lungs, leading to dysnea, frothy blood-tinged sputum, and atrial fibrillation. The ''malar rash'' supports rheumatic origin.
Incorrect options-
- CHF is not the answer eventhough some features are overlapping as the scenario points to mitral stenosis.
- Endocarditis is less likely without history of infection.
- Pericarditis doesn't explain sputum or AF.
Q.109. Nitroglycerine causes all of the following, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : C
Nitroglycerine-
T1/2: 1-4 min.
Dose: 0.3-0.6 mg SL may be repeated 5 min for 15 min for acute attack.
Action: Increase coronary blood flow→ produce vasodilation→ decrease LVED vol. (preload)→decrease myocardial O2 consumption.
Therapeutic effect:
- 1) Relief or prevention of angina attack
- 2) Increase CO
- 3) Decrease BP
S/E of Nitroglycerine is Methemoglobinemia.
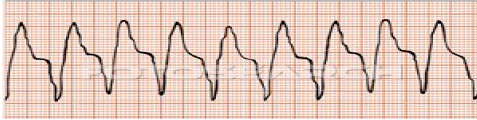
Q.110. Calcium channel blockers as nifedipine, verapamil and diltiazem are extremely useful in all of the following, except?
Correct Answer : D
Treatment of ventricular tachycardia depends on patient stability.
- Unstable patients: electrical cardioversion
- Stable patients: amiodarone, lidocaine, procainamide.
Q.111. In atrial fibrillation and stroke all are true, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : A
According to CHA2DS2-VASc score-
C = recent Congestive heart failure[1], H = Hypertension[1], A = Age>/=75[2], D = DM[1], S2: = stroke/ TIA [each scores 1],V=vascular disease[1], A= age-65-74[1], Sc= female sex[1].
- If score = 0 (AF with none of these) Aspirin
- If score = 1 Controversial (anticoagulation issue)
- If score >/=2 Warfarin
Q.112. An old man who has stable angina, all of the following are correct, except?
Correct Answer : D
Loss of consiousness is a serious symptom and is not typically associated with stable angina.
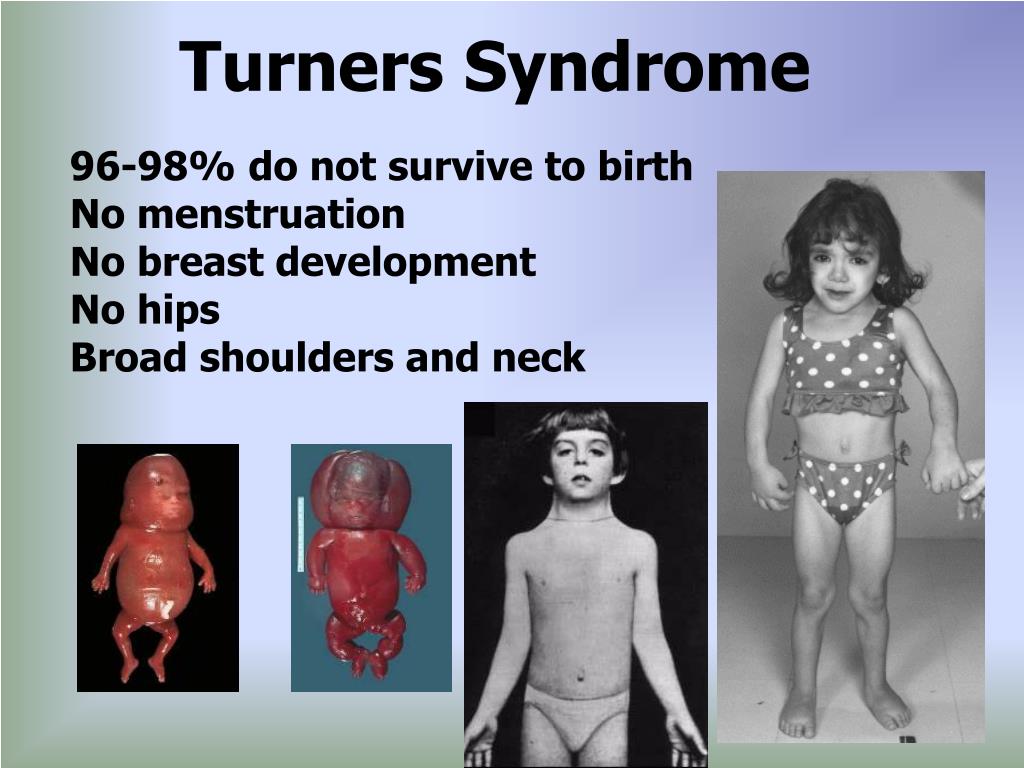
Q.113. Coarctation of the aorta is commonly associated with which of the following syndrome?
Correct Answer : B
Turner syndrome [45,X0] is a genetic condition affecting females, characterized by the abscence of X chromosome.
Features-
- Physical- Short starure, webbed neck, low hairline, wide-spaced nipple.
- Cardiac- Coarctation of aorta, bicuspid aortic valve.
- Reproductive- Primary amenorrhea, infertility, streak ovary.
- Renal- Horseshoe kidney.
- Endocrine- Hypothyroidism, osteoporosis.
- Other- Lymphedema at birth,learning difficulties.
Q.114. A 70-year-old male was brought to the ER with sudden onset of pain in his left lower limb. The pain was severe with numbness. He had acute myocardial infarction 2 weeks ago and was discharged 24 hours prior to his presentation. The left leg was cold and pale, right leg was normal. The most likely diagnosis is?
Correct Answer : B
An acute arterial embolus is a blood clot that forms likely in the heart due to recent MI and then lodges in a smaller artey in the leg. This blockage suddenly cuts off the supply to limb leading to severe pain, numbness, and potentially even tissue death.
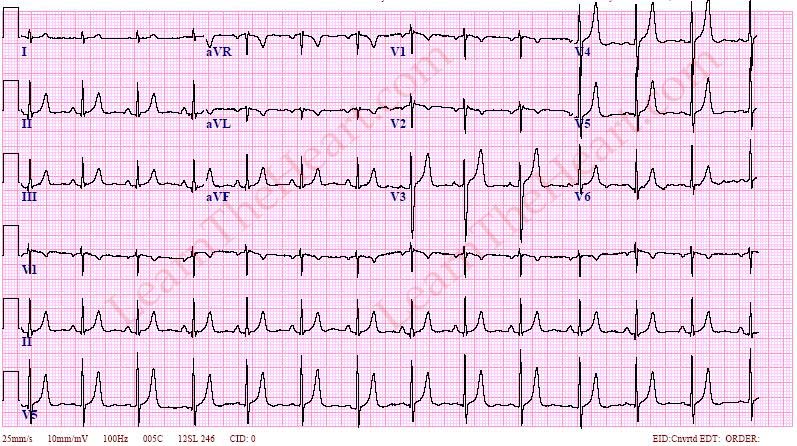
Q.115. Hyperkalemia is characterized by all of the following, except?
Correct Answer : D
Hyperkalemia is characterized by- tall peaked T-waves, wide QRS complex, and cardiac arrest if untreated
- Incorrect option-
- Chvostek sign is a sign of hypocalcemia (taping over facial nerve causes facial muscles to twitch).
Q.116. The antibiotic prophylaxis for endocarditis is?
Correct Answer : A
Amoxicillin is the most common antibiotic used for prophylaxis of endocarditis. It's taken usually one hour before the procedure to ensure it's in the blood stream when the procedure starts.
Q.117. A patient post MI presents with hemiparesis and drowsiness. What will your next step be?
Correct Answer : A
The features are strongly suggestive of stroke. It is caused by blood clot blocking the blood flow to brain. Heparin is an anticoagulant that activates antithrombin III, inhibiting thrombin and factor Xa, preventing clot formation.. Starting heparin quickly is a crucial step in managing stroke and improving outcome.
Q.118. A patient has hypercholesterolemia, what should he avoid?
Correct Answer : A
Organ meat like liver, kidney, and brain are very rich in cholesterol. People with hypercholesterolemia should therefore limit their intake.
Q.119. Difference between unstable and stable angina ?
Correct Answer : B
Unstable angina is characterized by chest pain that occurs at rest or with minimal exertion.
Q.120. A patient had rheumatic episode in the past, he developed mitral stenosis with orifice less than 1mm (severe stenosis). What will this lead to?
Correct Answer : A
Mitral stenosis causes increased pressure in the left atrium, leading to hypertrophy and dilation to handle the blood backup.
Q.121. A patient presented to ER with substernal chest pain. 3 months ago, the patient had complete done a physical examination, which was normal, his ECG was normal, only his LDL was high for which he started low fat diet and medication. What is the factor the doctor will take into considerations as a risk factor?
Correct Answer : D
The patient's current symptoms are most concerning at this point. The ER needs to focus on stabalizing the patient and determining the cause of chest pain. Past medical history is of no relevance and value at the movement.
Q.122. A drug that is contraindicated in hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM)?
Correct Answer : A
Digoxin is contraindicated as it increases the force of heart contractions, worsening obstruction and symptoms.
Incorrect option-
- Beta-blockers are the first-line treatment as they slow heart rate and improve blood flow.
- Alpha-blockers reduce the resistance of heart to pump against.
- Morphine is not contraindicated but has to be used with precaution.
Q.123. Fick method helps in determining cardiac output by?
Correct Answer : B
The fick method measures cardiac output by using oxygen saturation in blood to determine how much oxygen is delivered and consumed by tissues. It compares oxygen levels in arterial and venous blood to calculate oxygen consumption and cardiac output.
Q.124. A man who has had MI, you will check levels of which of the following enzyme?
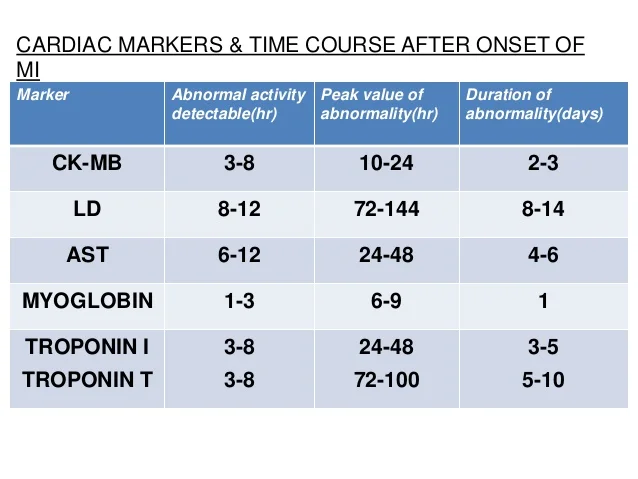
Correct Answer : A
CPK is an enzyme found primarily in heart, brain, and skeletal muscle. When there's damage to these tissues, such as heart attack, CPK levels in the blood rise.
Q.125. Regarding murmur of mitral stenosis, which of the following murmur is true?
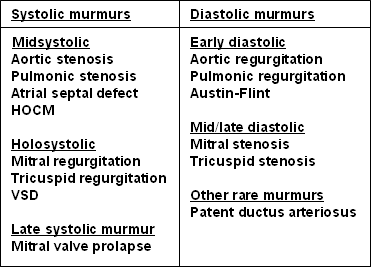
Correct Answer : C
Mitral stenosis is a mid-diastolic rumbling murmur that's low pitched and occurs as blood struggles to flow through the narrowed mitral valve during diastole.
Incorrect options-
- Holosystolic and pansystolic murmur occur during systole, not diastole.
- Mid-systolic - Mitral stenosis murmur is not systolic.
Q.126. What is correct about unstable angina ?
Correct Answer : B
Fifty percent of people with unstable angina will have evidence of myocardial necrosis based on elevated cardiac serum markers such as creatine kinase isoenzyme (CK)-MB and troponin T or I, and thus have a diagnosis of non-ST elevation myocardial infarction.
Q.127. A patient presents with history of AF and MI, what is the best prevention for stroke?
Correct Answer : A
Warfarin is the best prevention in the given scenario. It prevents stroke by inhibiting vitamin K- dependent clotting factors [II, VII, IX, X], reducing blood clot formation and embolism risk in atrial fibrillation.
Q.128. Which is the most common condition associated with endocarditis?
Correct Answer : D
Tetrology of fallot is associated with endocarditis because of the abnormnal blood flow patterns and the presence of a VSD in TOF can create areas of turbulence and increased pressure within the heart. These condition can damage the heart valves, making them more susceptible to bacterial infection, which leads to endocarditis.
Tetrology of fallot is a complex heart defect with four main features-
- VSD
- Pulmonary stenosis
- Overriding of aorta
- Right ventricular hypertrophy
Q.129. Which of the following describes RBBB?
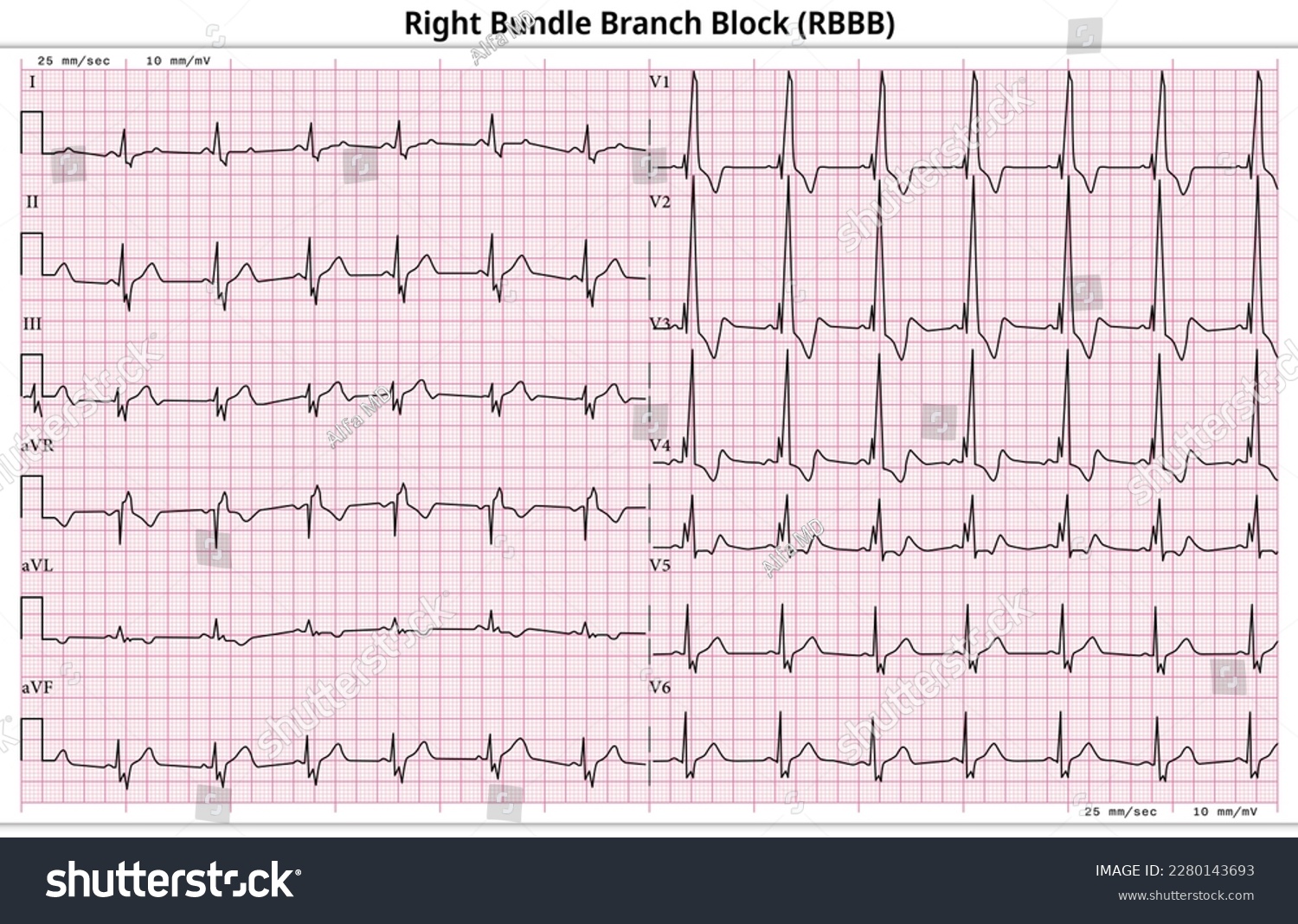
Correct Answer : A
In RBBB the ECG shows-
- Long S wave in lead V1- delayed right ventricle activation.
- Long R wave in lead V6- prolonged electrical signal due to delayed conduction.
Q.130. Drug used in treatment of CHF which decreases the mortality will be ?
Correct Answer : A
Beta-blockers reduce mortality in CHF by blocking adrenaline's effects, slowing heart rate, lowering BP, and decreasing heart strain. This improves heart function and prevents harmful cardiac remodeling over time.
Q.131. A patient is a known case of stable angina for 2 years, he came with c/o palpitation. The holter monitor showed 1.2mm ST depression for 1 to 2 minutes in 5-10 minutes. What is your diagnosis ?
Correct Answer : A
The ST depression seen on the Holter monitor indicates ischemia, even if no chest pain is present. MI occurs when the heart muscle doesn't get enough oxygenated blood.
Q.132. A patient on lisinopril c/o cough, what's the drug that has the same action without the side effects?
Correct Answer : A
- Lisinopril is an ACE inhibitor that lowers BP by blocking angiotensin I from converting to angiotensin II, a vasoconstrictor. It increases bradykinin, causing dry cough.
- Losartan is an ARB and blocks angiotensin II at its receptor itself, achieving the same BP lowering effect without affecting bradykinin, not leading to cough.
Incorrect options-
- Nifedipine, minoxidil and thiazide have a different mechanisms.
Q.133. Which of the following explains coronary artery disease the best?
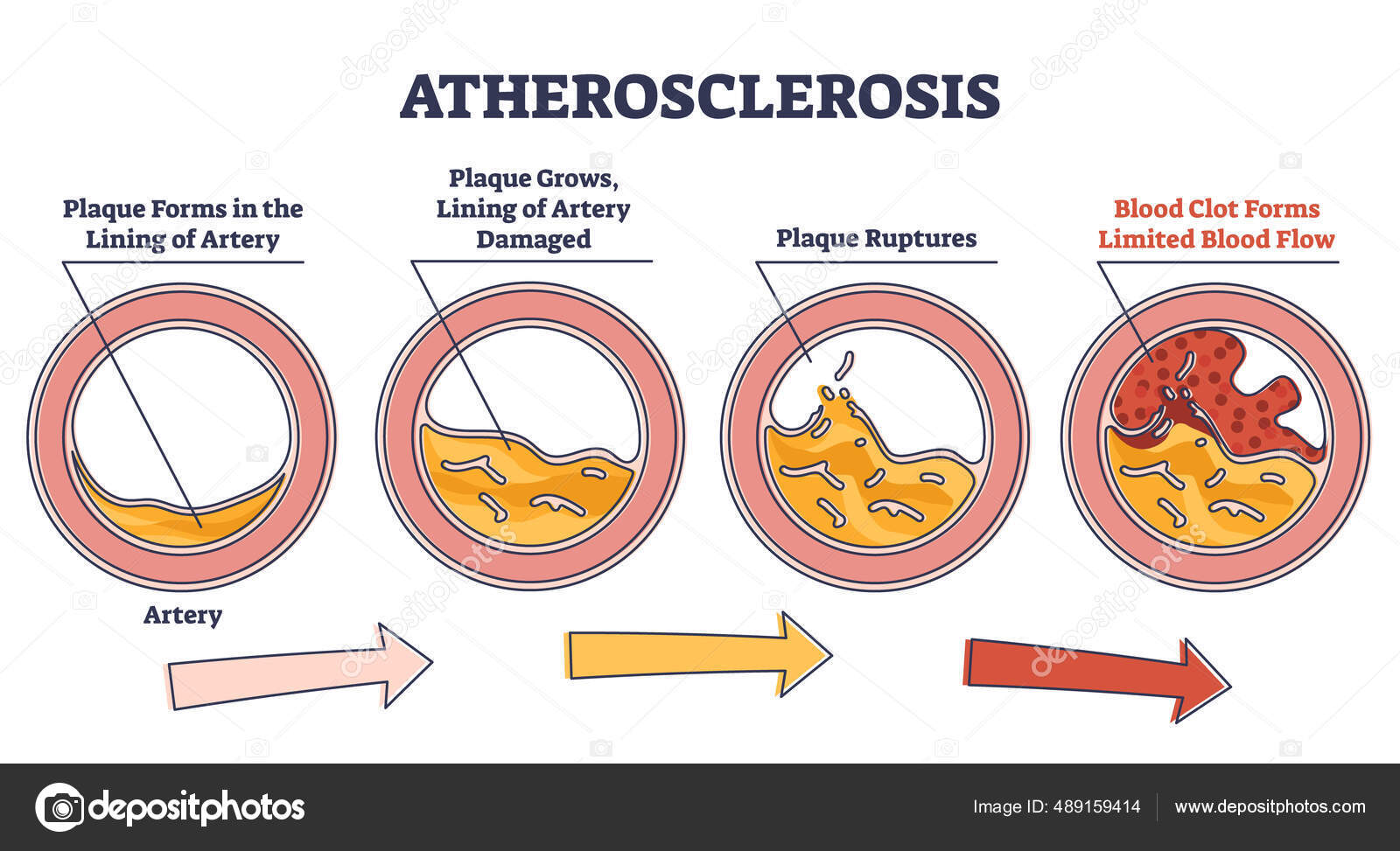
Correct Answer : C
Atherosclerosis is a process where plaque made of cholesterol, fat and other substances, builds up on the inner wall of arteries. This plaque formation narrows the arteries, restricing blood flow to heart.
Q.134. A 72-year-old carpenter lost one of his family member due to heart attack, he came to you to do some investigations. He is well and fit. He denies any history of chest pain or SOB. O/E everything is normal except mid systolic ejection murmur at left sternal area without radiation to carotid, what is your diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Aortic sclerosis is a common age-related condition where the aortic valve becomes thickened and stiffer. This makes it hard for the heart to pump blood out of the left ventricle, leading to a gradual decline in heart function. As the patient has a famliy history, age factor and no symptoms at the moment it is likely pointing towards aortic sclerosis.
Q.135. A patient comes with chest pain which radiates to the jaw, increases with exercise and decreases with rest, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Based on the symptoms the most likely diagnosis is stable angina.
Q.136. A patient with inferior MI had developed sudden SOB, what is the cause?
Correct Answer : B
After an inferior MI the papillary muscle that support the mitral valve can rupture. This leads to acute MR where blood leaks back to the left atrium during contraction, causing sudden shortness of breath.
Q.137. A patient has risk factor for developing infective endocarditis. He will be undergoing urology surgery. He is sensitive to penicillin. What you will give him?
Correct Answer : A
Since the patient in this scenario is allergic to penicillin alternative antibiotics are needed.
- IV vanomycin and IV gentamicin is a common choice for antibiotic prophylaxis in patients with penicillin allergy.
Q.138. A patient presents with a BP of 180/140mmHg, you want to lower the diastolic pressure, how should you lower the BP?
Correct Answer : A
A BP of 180/140mmHg is considered as hypertensive crisis, which is a medical emergency. The goal of treatment here is to rapidly reduce BP to prevent organ damage. We need to ensure a safe reduction as a rapid drop can be dangerous and lead to complication. Therefore the diastolic pressure should be reduced gradually 110-100 mmHg within 12 hours for the above mentioned scenario.
Q.139. Which of the following describes unstable angina ?
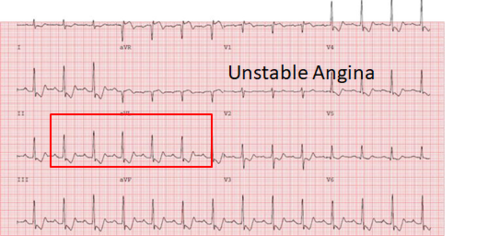
Correct Answer : B
Unstable angina is a condition in which the blood flow to heart is reduced, causing unpredictable chest pain, often at rest. It shows evidence of MI, such as ST-segment depression or T-wave inversion on an ECG.
Q.140. A patient came with gasping breaths, the pulse is not felt, what should you do?
Correct Answer : A
When patient has no pulse it is indicative of cardiac arrest. CPR is the immediate life saving intervention for cardiac arrest. It involves chest compression to circulate blood and rescue breaths to provide oxygen to the brain and other organs.
Incorrect options-
- Call resuscitation team- While calling resuscitation team is important, it should be done after initiating CPR.
- Admit to hospital- Necessary after sucessful resuscitation.
- Supply oxygen- Administered after CPR is initiated.
Q.141. Cause of Bundle branch block is?
Correct Answer : A
Causes of LBBB: 1) Aortic stenosis 2) Dilated cardiomyopathy 3) Acute myocardial infarction 4) Extensive coronary artery disease 5) Primary disease of the cardiac electrical conduction system 6) Long-standing hypertension leading to aortic root dilatation and subsequent aortic regurgitation.
Causes of RBBB : 1) Coronary artery disease 2) Myocarditis 3) ASD, VSD and Valvular heart disease 4) COPD & pulmonary embolus.
Q.142. A patient is 5 weeks post-MI, complaining of chest pain, fever and arthralgia. What's the condition?
Correct Answer : A
Dressler's syndrome is a secondary form of pericarditis that occurs in the setting of injury to the heart or the pericardium.
Q.143. What is the drug used in systolic dysfunction heart failure?
Correct Answer : C
ACEI are the first-line treatment as they-
- Lower BP
- Reduce heart workload
- Improve blood flow
- Decrease fluid retention
Q.144. An old patient, had MI complicated with ventricular tachycardia. She is receiving buspirone from that time. She came with fatigue, was normotensive & her pulse was 65bpm, what investigation must be done?
Correct Answer : C
Buspirone is an anti-anxiety medication that can cause liver related side effects, which may lead to fatigue. A liver function test is the most appropriate investigation in this case.
Q.145. An elderly patient who is a known case of AF came with abdominal pain and bloody stool. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
As the patient has AF there is an increased risk of blood clot formation. When a blood clot travels to arteries supplying intestines, it can cause blockage of the arterial supply to intestines causing tissue damage. This condition is called ischemic mesentery.
Symptoms of ischemic mesentery-
- Nausea/vomitting, severe abdominal pain and bloody stools.
Q.146. A patient having chest pain radiating to the back, decreased BP in left arm and absent left femoral pulse with left sided pleural effusion on CXR, left ventricular hypertrophy on ECG, most appropriate investigation is?
Correct Answer : A
The combination of these clinical features are strongly indicative of aortic dissection, which is a serious condition in which the inner layer of aorta tears allowing blood to flow between the layers of the vessel wall. Aortic angiogram is a diagnostic imaging test that uses X-rays and contrast dye to visualize the aorta and detect any tears or blockages. It is the most definitive test to diagnose aortic dissection.
Q.147. A 60-year-old patient has only HTN, which is the best drug to start with?
Correct Answer : C
These medications are often the first-line treatment of HTN, especially in older adults. They work by increasing urine output, lowering the amount of fluid in body thereby decreasing BP.
Q.148. A cardiac patient who is obese, has HTN with hyperlipidemia, a sedentary life style and unhealthy food habits. What are the 3 most correctable risk factors?
Correct Answer : C
Note: High cholesterol, unhealthy food &sedentary life are modifiable risk factors.
Q.149. A 15-year-old presents with palpitations and fatigue. Investigation showed right ventricular hypertrophy, right ventricular overload and right branch block, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
VSD causes a hole in the septum that seprates the ventricles of heart, leading to increased blood flow to the right side, causing right ventricular hypertrophy,overload, and RBBB on ECG.
Incorrect options-
- TGA will be immediately evident after birth.
- Coarctation of aorta is not associated with RVH.
- PDA increases blood floe to lung but will not lead to RVH.
Q.150. A patient with HTN is on diuretics, he developed painful big toe. What drug should not be prescribed to him?
Correct Answer : A
Hydrochlorothiazide is a thiazide diuretic which can worsen hyperuricemia and gout.
“ Hyperuricemia is a relatively common finding in patients treated with a loop or thiazide diuretic and may sometimes, lead to gouty arthritis”.
Q.151. Which of the following is true about pericarditis?
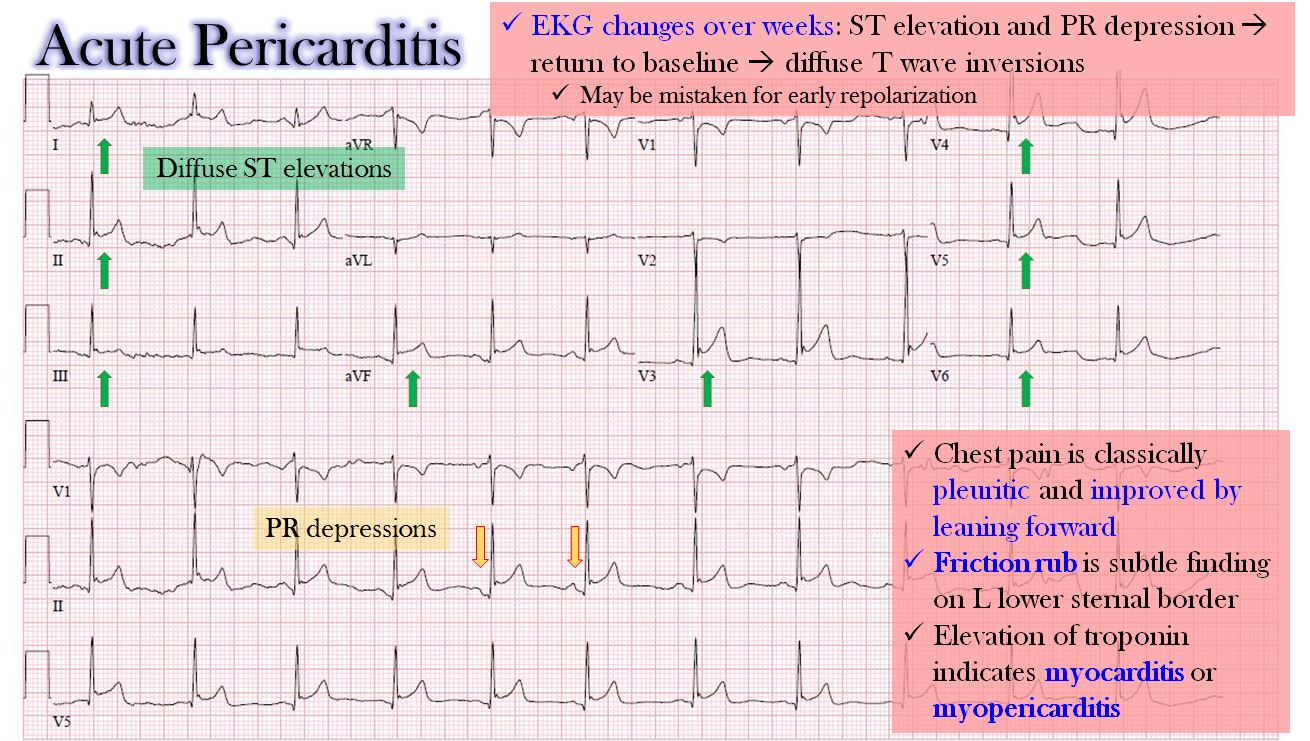
Correct Answer : A
Pericarditis patient presents with substernal pleuritic chest pain that is aggravated by lying down and relieved by leaning forward.
ECG - Low voltage diffuse ST segment elevation.
Q.152. A patient who is a k/c/o MI is on treatment. After 5 days, the patient develops shortness of breath + crepitation on both lungs. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
After an MI damage to papillary muscle can cause MR, leading to blood leaking backwards into the left atrium. Symptoms include SOB and lung crepitations due to pulmonary edema.
Incorrect options-
- Pulmonary embolism is less likely as there is no evidence of a clot.
- Pneumonia is not the correct option as the features are more indicative towards MR and not infection.
- AR is not typically a post MI complication.
Q.153. A patient 2 months post MI cannot sleep. What drug would you give him?
Correct Answer : A
Zolpidem is a short acting hypnotic. It works by enhancing the effect of GABA, which promotes sleep. It has a rapid onset of action and a short half-life.
[Long acting hypnotics can increase risk of accidents in a patient with MI].
Q.154. In a patient of MI, what is the inappropriate management?
Correct Answer : A
Ca channel blockers can lead to negative inotropy which can be life threatening. These medications can lead to hypotension which is dangerous in patients with MI who already may have low BP.
Q.155. A patient presented with chest pain for 2 hours with anterolateral lead showing ST elevation, there's no PCI facility in the hospital. What will you do next in terms of management?
Correct Answer : A
In absence of PCI facility, fibrinolytic therapy like Streptokinase is the next best option to restore blood flow to heart muscle.
Q.156. Which of the following is a MINOR criteria for rheumatic fever?
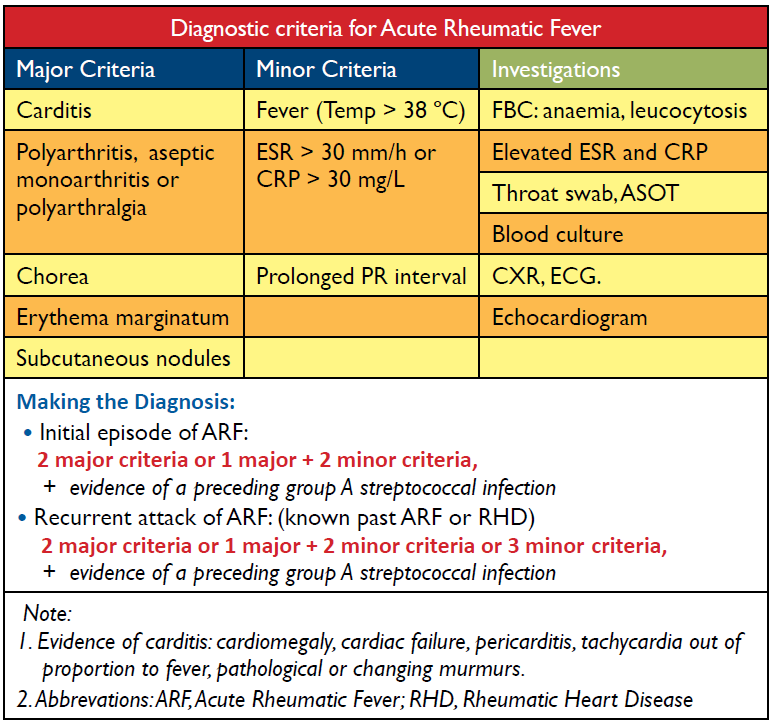
Correct Answer : D
Fever is considered a minor criteria as it's a common symptom in many illnesses, it's not specific to any one disease. However when combined with other minor or major criteria, it can help strengthen the diagnosis.
Q.157. A patient comes to ER with AF, BP 80/60mmHg, what is the management?
Correct Answer : A
In this scenario, the patient is presenting with AF and has a dangerously low BP - Syncronised cardioversion is the recommended treatment in this case as it delivers a timed electrical shock to heart, aiming to restore a normal heart rhythm. This can quickly improve BP and circulation.
Q.158. A patient was diagnosed with aortic stenosis, he is a teacher, while he was in his class he fainted, what is the cause?
Correct Answer : B
AS causes narrowing of the aortic valve which restricts the blood flow from the heart to the body. This can lead to hypotension, especially during exertion. When the teacher stood up to teach there was decreased blood flow to brain due to hypotension which led him to faint.
Q.159. A patient k/c/o CHF loved to eat outside 2-3 times weekly. What would you advise him?
Correct Answer : A
One of the precipitants of CHF in HF patients is a high salt diet. Therefore salt restriction is most important advise.
Q.160. A patient has been treated for endocarditis. What is the recurrence rate?
Correct Answer : A
The recurrence rate of endocarditis even after treatment is around 12%.
Q.161. A picture of JVP graph given. Patient had low volume pulse, low resting BP, no murmur, pedal oedema. What's the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
The above mentionesd sysmptoms are stongly suggestive of constrictive pericarditis, which is a condition in which the pericardium become thickened and scarred restricting the hearts ability to fill properly.
Incorrect options-
- TR typically presents with murmur and symptoms of right sided heart faliure
- TS presents with murmur and features of right sided heart faliure.
- Pulmonary HTN usually doesn't present with low volume pulse and no murmur.
Q.162. A 46-year-old male came to ER with abdominal pain which is not that severe. He is hyperlipidemic, smoker, hypertensive. No compliance to medication. Vitally stable, O/E he is tall obese patient, with mid-line abdominal tenderness. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Arotic aneurysm is characterized by pulsatile epigastric mass.
Q.163. A female patient who is a known case of rheumatic heart disease, she has diastolic murmur, complains of aphasia and hemiplegia, what will you do to find the etiology of this stroke?
Correct Answer : C
Rheumatic heart disease can lead to mitral stenosis,which can cause embolic strokes. ECHO identifies valve abnormalities and potential embolic sources.
Incorrect options-
- MR angiography assesses blood vessels not the heart valves.
- Non contrast CT rules out hemorrhagic stroke but doesn't assess valve disease.
- ECG evaluates electrical activity but not structural abnormalities.
Q.164. A normal adult started gymming; he had a brother who died after jogging, what could be the probable cause?
Correct Answer : C
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy causes thickening of cardiac muscle, making it harder to pump blood. Exercise can trigger suddent cardiac death in these individuals, especially with a family history.
Incorrect option-
- PDA, VSD, ASD these are all congenital deformaties that present in early life and rarely cause sudden death in adults during exercise.
Q.165. Which one of the following is a component of TOF?
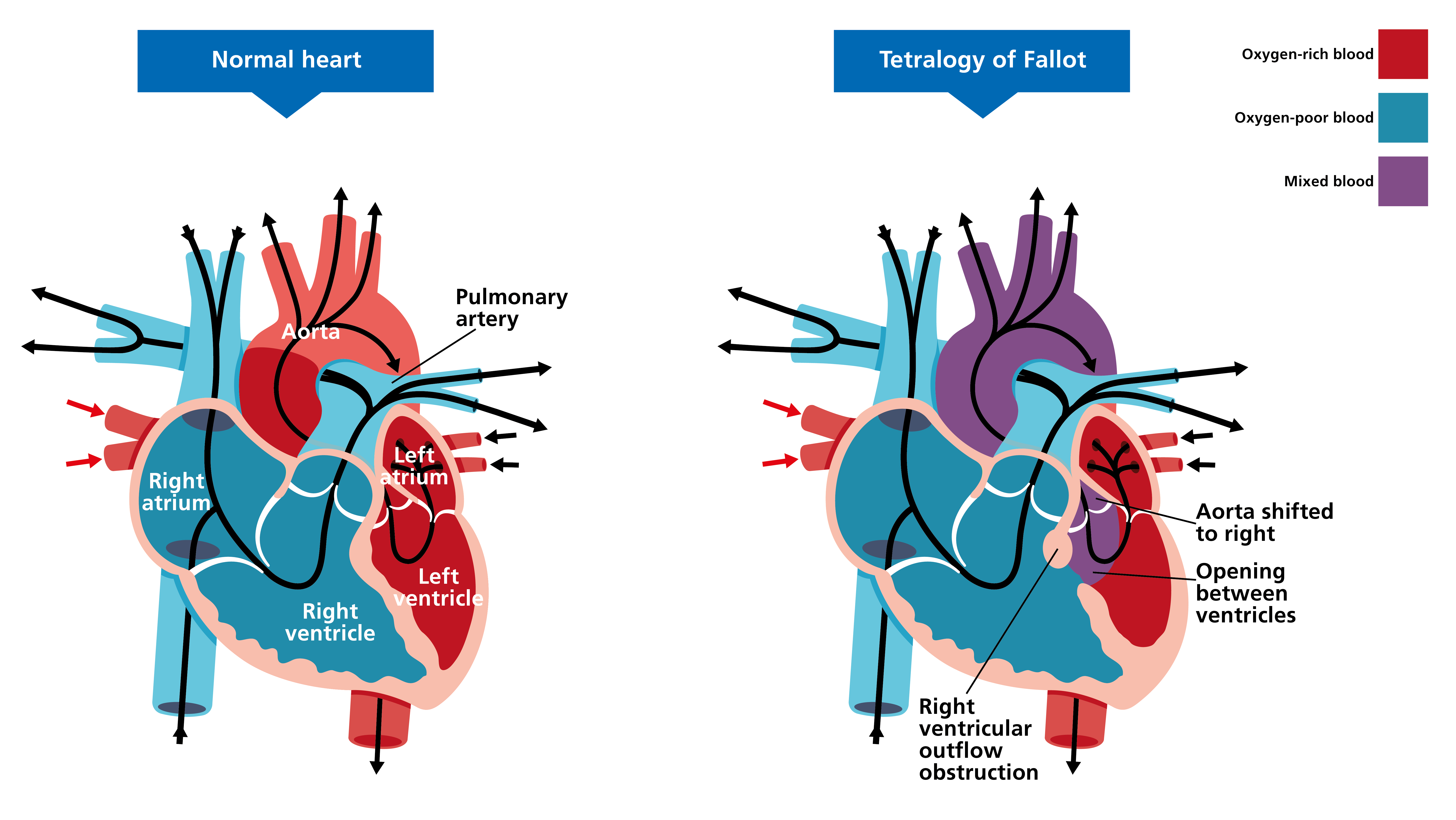
Correct Answer : B
TOF is a heart defect with 4 key features, and VSD is one of them.
Features of TOF-
- VSD
- Pulmonary stenosis
- overriding aorta
- Right ventricular hypertrophy
Q.166. A patient with rheumatic valvular disease, has a mitral orifice of 1 cm, what is the action to compensate that?
Correct Answer : A
In rheumatic valvular disease with a mitral orifice of 1 cm, the heart compensates by dilation of the left atrium with chamber hypertrophy. This happens because the left atrium has to work harder to push blood through the narrowed valve, causing it to enlarge and thicken.
Incorrect options-
- Ventricular changes [dilatation or contraction] occur later, not initially.
- The left atrium doesn't decrease contraction pressure- it needs to contract harder.
Q.167. A 60-year-old man presents with fatigue and progressive dyspnea. On echocardiography, he is diagnosed with mitral stenosis with valve area of 0.7 cm2. What is the next best step in her management?
Correct Answer : B
MS is classified as severe when the mitral valve area is </=1.0cm2. In this case the valve area is 0.7cm2 which is indicative of intervention.
Percutaneous mitral valvuloplasty is the preferred treatment for severe symptomatic MS in patient withot contraindication such as severe MR or left atrial thrombus.
Q.168. Which of the following medication is associated with QT prolongation?
Correct Answer : D
All can cause QT-interval prolongation
Q.169. A patient came with anterior wall MI + premature ventricular ectopy that indicates pulmonary edema, he was given digoxin + diuretics + after-load reducer, what to add next?
Correct Answer : A
The patient has had a anterior wall MI with PVCs and pulmonary edema, indicating the heart isn't pumping effectively. They are already on medications to strengthen the heart, reduce fluid buildup. The next best step is amiodarone, an antiarrythmic drug that stabilizes abnormal heart rhythms and prevents more serious complications.
Q.170. How does group A beta streptococci cause rheumatic heart disease?
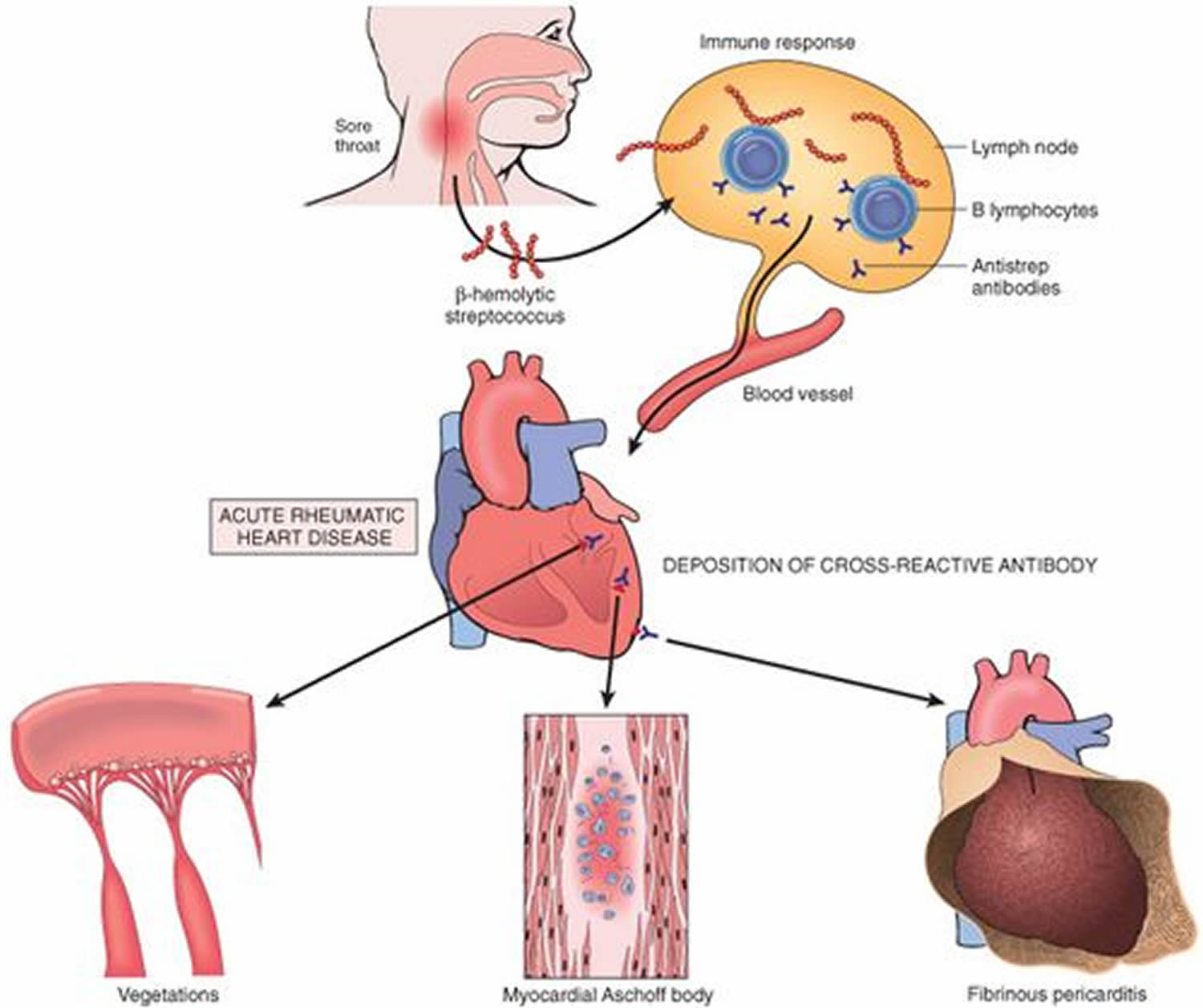
Correct Answer : A
RHD occurs after an infection with group A streptococcus, which typically causes tonsillitis or pharyngitis. The immune response to this throat infection can mistakenly attack the heart leading to damage.
Q.171. Pansystolic machinery murmur at left sternal border is?
Correct Answer : C
PDA is a condition in which the ductus arteriosus, a blood vessel connecting the aorta and pulmonary artery in a fetus, fails to close after birth. This abnormal blood flow creates continous, machinery like murmur that is often heard at the left sternal border.
Incorrect options-
- AS presents with ejection systolic murmur.
- MS presents with diastolic rumble murmur.
- MR presents with holosystolic murmur.
Q.172. A patient with heart failure and atrial fibrillation is on digoxin, what is the effect of digoxin?
Correct Answer : A
Digoxin is used in heart faliure and ventricular fibrillation to slow the ventricular rate. In AF, the atria beats rapidly and irregularly, which can cause the ventricles to pump too fast. By slowing the ventricular rate, digoxin reduces starin on the heart and improves its efficiency.
Q.173. Carvedilol is contraindicated in which of the following?
Correct Answer : B
Carvedilol is a beta-blocker and is contraindicated with diltiazem, a calcium channel blocker, because their combined action can cause severe bradycardia.
Q.174. Initial regulation of BP in vascular system occurs in which of the following?
Correct Answer : A
Arterioles are like control valves of the vascular system. They regulate blood pressure by constricting or dilating, which adjusts the blood flow and resistance. This makes them the key regulators in initial BP regulation.
Q.175. A patient presents to you with a history of hypertension, DM, he is a smoker as well. Which of the following are most important risk factors to deal with?
Correct Answer : A
- Obesity worsens HTN, and even small weight loss can lower BP.
- HTN is a major risk factor for heart attacks, strokes, and kidney disease.
So contolling these factors is crucial as they together have the most immediate and long-term benifits.
Q.176. A 40-year-old patient presented with history of syncope when he exercises or on rest, and chest pain. On Examination: There was ejection systolic murmur grade 2-4/6 on the lower left sternal border not radiating and increases when he lies down, nonspecific ST changes and there is left atrium enlargement. Which of the following is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Syncope on exertion/rest and chestpain are hallmark features of HCM.
Incorrect options-
- AS typically presents with murmur that radiates but doesn't change with change is position.
- Pulmonary stenosis affects the right heart and the murmur is heard at upper left sternal border.
- Constrictive cariomyopathy is more associated with signs of right heart faliure.
Q.177. In a patient with normal kidney function post MI, the troponin level will last for?
Correct Answer : C
Troponin appears 1-6 h after injury, peaks at 24 h, and may remain elevated for 7-10 d in STEMI.
Q.178. Which of the following is given as a prophylaxis for arrhythmia after MI?
Correct Answer : D
After MI metoprolol [beta-blocker] is commonly used to prevent future arrythmias by slowing the heart rate and reducing the strain on heart.
Q.179. Which of the following differentiates between sinus arrhythmia and atrial fibrillation?
Correct Answer : A
In sinus arrythmia, carotid massage slows the heart rate because the rhythm is still controlled by the sinus node.
In AF, the irregular rhythm is unaffected by carotid massage since its not controlled by the SA node.
Incorrect options-
- Temporal artery massage isn't relevant
- Amiodarone and Digoxin treat arrythmias but don't help in differentiating them.
Q.180. A 60-year-old man comes to your clinic with history of chest pain after meals and at night before sleeping, the best initial investigation is?
Correct Answer : C
A stress ECG is the best initial test. It helps assess wheather coronary artery disease is causing pain, especially since CAD is common in this age group.
Incorrect options-
- Barium study and UGID are for GIT related issues.
- CXR is useful for lung conditions, not for chest pain from potential heart problems.
Q.181. A patient presented with acute chest pain radiating to the back. The blood pressure is lower in the left arm compared to the right. The best diagnostic test is?
Correct Answer : C
This is a case of Aortic dissection. The confirmatory test is aortic angiography but it's invasive and done before surgery.
Trans-esophageal echocardiography (TEE) is very accurate with high sensitivity but they didn't specify the choices whether it's transthoracic or trans-esophageal.
Q.182. A patient presents with history of rheumatic fever. Few years later he developed mitral regurgitation. Long standing MR will result in dilation of which of the following?
Correct Answer : C
In long-standing MR, the left atrium becomes enlarged due to the extra blood flow it has to handle, as blood leaks backwards from the left ventricle.
Incorrect options-
- The right atrium and right ventricle aren't directly impacted by MR, and while the left ventricle might also enlarge, the primary effect is on the left atrium.
Q.183. A patient presented with SOB. He has Mitral stenosis (mitral valve area on echo is 1 cm2). The pathophysiology shows which of the following?
Correct Answer : A
In mitral stenosis, the mitral valve is narrowed, causing blood to backup into left atrium. This increased pressure in left atrium is transmitted to the lungs, raising pressure in the pulmonary veins and leading to pulmonary congestion. Over time, this causes the right ventricle to work harder, increasing right ventricular pressure and pulmonary vascular resistance.
Q.184. A MI patient presents to your clinic 3 weeks post attack, he is not able to get sleep. What medication should be given?
Correct Answer : B
Zolpidem is the best choice in case of this patient. It's a short acting sleep aid that works quickly, making it effective for short-term insomnia, which is common during recovery.
Q.185. A middle-age man (50 years) with family history of heart disease, active lifestyle, on self-induced diet with 50% fat, 35% protein and 15 % carbohydrates, his labs are as follows- elevated LDL, low HDL, elevated triglycerides and cholesterol, normal RFTs. What is the most accurate answer?
Correct Answer : B
Given the mans family history and elevated LDL levels, he is at increased risk of heart disease. While exercise and a healthy diet are important, statins are the most effective way to lowere LDL levels and reduce the risk of heart disease in this case.
Q.186. A male patient was advised to undergo ''Arterial Graft Bypass'' surgery at other clinic after having episode of pain in leg, now he is asymptomatic. He is a non-smoker, with elevated cholesterol and early atherosclerotic plaques on some descending aortal branches. What will you advise?
Correct Answer : B
For this patient with elevated LDL and cholesterol, taking medications like statins is the best step to prevent further arterial plaque formation and manage the risk of disease progression. Since the patient is asymptomatic, surgery like bypass grafting isn't needed.
Q.187. What is the most common congenital heart disease associated with rheumatic heart disease?
Correct Answer : B
RHD primarily affects heart valves but it can also be associated with certain congenital heart defects. Among these VSD is the most commonly linked congenital condition.
Q.188. Notching on the lower edges of fourth to the ninth ribs indicate enlarged intercostal arteries eroding the lower border of the ribs, it seen in which of the following case?
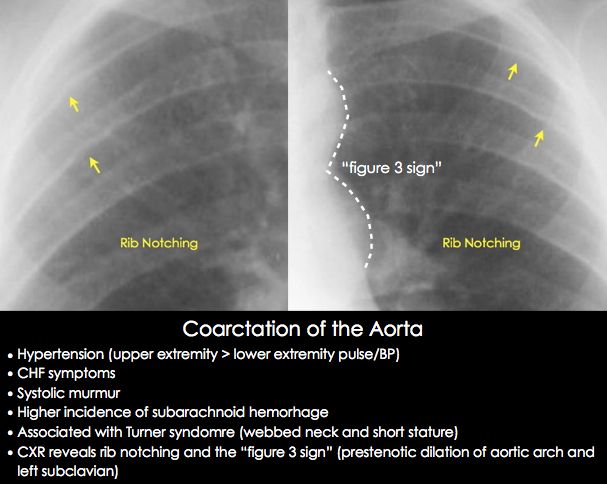
Correct Answer : A
This is a classic finding in coarctation of aorta, a condition where the aorta is narrowed, forcing blood to reroute through the intercostal arteries to bypass the blockage.
Q.189. A patient presents with frothy hemoptysis, and palpitation. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Frothy hemoptysis and palpitations are classic signs of MS. This condition occurs when the mitral valve is narrowed, causing blood to back up into the lungs. The resulting increased pressure leads to fluid leakage, causing frothy sputum and irregular heartbeats.
Q.190. A patient has DM2 and HTN. He is on CCB + Metformin + Glyburide + Statins, but still has high BP. What is your advice?
Correct Answer : A
ARBs are the best choice because they effectively lower the BP and offer protection to the kidney, which is particularly important in diabetic patients. ARBs also complement the existing medication without significant risk of side effects.
Incorrect options-
- Increasing CCB can cause side effects like dizziness or swelling.
- Thiazides may worsen blood sugar control.
- CCB is unnecessary as the patient is already on one.
Q.191. What drug improves survival in CHF patients?
Correct Answer : D
Drugs that improve the survival in CHF patients are ACE-I [enalapril] , it works by relaxing blood vessels, which reduce the strain on the heart and improves blood flow. This has been proven to significantly extend life expectancy in CHF patients.
Q.192. A patient with complain of reduced sleep along with persistent hypertension presents at your clinic. What is the cause of persistent HTN ?
Correct Answer : A
In this case sleep apnea is the likely cause of persistent HTN. This condition causes breathing interruptions during sleep, leading to poor rest and increase in stress hormones like cortisol, which can raise BP.
Q.193. A patient presents with chest pain radiating to the jaw and arm. Which condition is the patient suffering from most likely?
Correct Answer : A
The most likely cause of chest pain in this case is MI. This type of pain is known as angina, and occurs when the heart isn't getting enough oxygenated blood. The pain typically feels like tightness or pressure in the chest and can radiate to jaw, neck, or arms.
Incorrect options-
- Aortic dissection causes sharp, tearing chest pain that doesn't radiate to jaw or arm.
- Pancreatitis causes abdominal not chest pain that radiates to jaw or arm.
- CHF may cause chest pain, but it's usually a dull ache or pressure, not the classical radiating pain.
Q.194. A 55-year-old male, c/o angina and syncope on exertion, he has a normal ejection fraction, normal coronary arteries, there is only presence of calcified aortic valve with total area < .75 cm, the rest of examination and investigations are normal. What is your management?

Correct Answer : D
The only definitive treatment for aortic stenosis is aortic valve replacement. The development of symptoms due to aortic stenosis provides a clear indication for replacement. For patients who are not candidates for aortic replacement, percutaneous aortic balloon valvuloplasty may provide some symptom relief.
- Medical treatment (such as diuretic therapy) in aortic stenosis may provide temporary symptom relief but is generally not effective long term.In truly asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis, the issue of valve replacement is less clear.
The recommendations according to valvular heart disease guidelines for aortic valve replacement in patients with valvular aortic stenosis are summarized below, in Table 5. In most adults with symptomatic, severe aortic stenosis, aortic valve replacement is the surgical treatment of choice. If concomitant coronary disease is present, aortic valve replacement and coronary artery bypass graft(CABG) should be performed simultaneously.
Q.195. An old man presents with S/S of right sided heart failure, which one of these can cause the symptoms without any changes in the heart chambers (hypertrophy/dilation)?
Correct Answer : D
Constrictive pericarditis is a condition in which the pericardium becomes thickened and stiff, restricting the hearts ability to fill blood. This leads to right sided heart faliure symptoms like fluid build up and some shortness of breath, but without changes to the heart chambers themselves.
Q.196. A young patient presents with loss of consciousness lasting 4 minutes, no other symptoms are present. What's the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
The most likely diagnosis is fainting [syncope]. Fainting is a brief loss of consiousness caused due to sudden drop in blood flow to the brain. This can happen due to many reasons like dehydration, low blood glucose level, or emotional stress, and the episode lasts for a short time with no other symptoms.
Q.197. A patient comes with attack of Strep. throat, he had a history of previous attack (RF), what is his chance of getting RHD now?
Correct Answer : D
Rheumatic fever rarely develops before age 3 or after age 40 and is much less common than in developing countries, probably because antibiotics are widely used to treat streptococcal infections at an early stage. However, the incidence of rheumatic fever sometimes rises and falls in a particular area for unknown reasons. Overcrowded living conditions seem to increase the risk of rheumatic fever, and heredity seems to play a part. A child who has a streptococcal throat infection but is not treated has only a 0.4 to 3% chance of developing rheumatic fever. About half of the children who have had rheumatic fever develop it again after another streptococcal throat infection if it is not treated. Rheumatic fever follows streptococcal infections of the throat but not those of the skin (impetigo) or other areas of the body. The reasons are not known.
Q.198. Established diagnosis of shock must include which of the following?
Correct Answer : D
Shock occurs when the body's organs don't recieve enough blood flow, depriving them of oxygen and nutrients. Signs of this include confusion, low urine output, cold clammy skin, weak pulse, and rapid breathing.
Q.199. Regarding ischemic heart disease, which one of the following is true?
Correct Answer : C
High BP puts extra strain on heart and blood vessels, which can lead to atherosclerosis and reduce blood flow to the heart, increasing the risk of heart attacks.
Incorrect option-
- Incidence refers to the number of new cases.
- Prevalance refers to total number of existing cases of a disease at a specific point in time.
- Smoking is not related to IHD is an incorrect statement because it poses a significant risk for IHD development.
Q.200. When do we give aspirin + Clopidogrel?
Correct Answer : D
Aspirin and clopidogrel are both antiplatelet drugs that help prevent formation of blood clots. They are commonly given together after a procedure like cardiac catheterization, especially if a stent is placed, to reduce the risk of stent thrombosis.
Q.201. A female patient with MVP came for dental procedure, the dentist sent her to you for getting prophylaxis prior to the procedure. Physical examination was unremarkable, she said that she never had an echo earlier. What you will do?
Correct Answer : D
Mitral valve prolapse can increase the risk of complications like endocarditis, especially during dental procedures, due to bacteria entering the bloodstream. The echocardiogram helps assess the severity of MVP and determine if antibiotic prophylaxis is needed.
Q.202. A young patient came with essential HTN and history of high Na+ and K+ intake, obese >30, the most attributable cause for HTN is?
Correct Answer : C
More than 85% of essential HTN are with BMI >25
Q.203. The best anti HTN drug in patients with hyperaldosteronism & HTN is?
Correct Answer : A
Spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic and blocks the action of aldosterone which is responsible for increasing BP as it retains sodium and water. In hyperaldosteronism, where there's excess aldosterone,spironolactone helps lower BP.
Q.204. How does the heart pump more blood to the muscle?
Correct Answer : A
When the body needs more oxygen and nutrients, the coronary arteries dilate. This allows more blood to flow to the heart muscles, which helps it pump more blood to rest of the body.
Q.205. A patient with acute MI, presented with the rhythm strip of V-fib. What is the best treatment?
Correct Answer : A
Ventricular fibrillation is a serious and life threatening condition. The best treatment for this is DC shock, which resets the heart rhythm and allows it to pump effectively again.
Q.206. A patient with chest pain has T inversion and ST changes on ECG. What is the cause?
Correct Answer : A
T inversion and ST segment changes on ECG are common signs of MI.
Q.207. A 65-years-old male, known to have atrial fibrillation came complaining of recurrent attacks of head lightedness over the past 3 months. He used to take Digoxin but he had not used it for many years. His carotid examination was normal. Physical examination was normal apart from tachycardia. What would you consider to give this patient?
Correct Answer : B
Propranolol is a beta-blocker that helps slow the heart rate, which is important in managing AF. It can reduce symptoms like lighheadedness by controlling the irregular heart rhythms that cause these episodes.
Q.208. Which of the following is not a feature of normal ECG?
Correct Answer : A
In normal ECG P wave shows atrial depolarization, not repolarization. Depolarization is when the heart muscles contract, while repolarization is when they relax.
Q.209. A young male patient, who has normal findings on physical examination, his BP is 120/80 mmHg, RR 18 /min, HR 210bpm, no chest pain, no discomfort, no cyanosis, is complaining of palpitations, what is your next step?
Correct Answer : A
ECG is used to diagnose SVT.
Q.210. An old patient comes to ER with syncopal episodes, substernal chest pain and shortness of breath on exertion. His BP is 110/80, bibasilar rales, which auscultatory finding would explain his finding?
Correct Answer : A
This is a patient that has aortic stenosis because of the classic triad of (exertional dyspnea, chest pain, syncopal attacks).
Q.211. A female complains of palpitation, a 24hr holter shows occasional premature ventricular contractions and premature atrial contraction. Which of the following is the best management for this patient?
Correct Answer : D
If a patient has occasional premature beats without other symptoms or heart issues, these are usually harmless. The best approach is reassurance-no medication is needed.
Q.212. Death related to MI occurs in which of the following condition?
Correct Answer : C
Arrythmias are a common and serious complication of a heart attack. They disrupt the normal rhythm of heart, causing it to beat too fast, slow, or irregularly.
Q.213. Which parameter is needed for FICK formula to measure cardiac output?
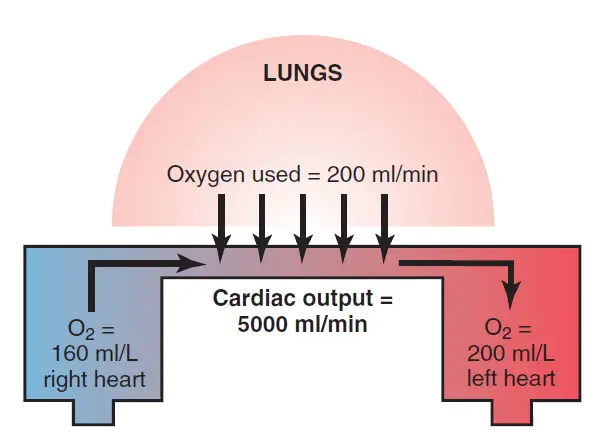
Correct Answer : D
The Fick principle measures CO using oxygen consumption. This refers to the amount of oxygen the body uses per minute, which is a key part of the calculation.
Q.214. Old patient came to ER complaining of tachycardia. Vital signs show: BP 80/50, PR 140. 2 strips of ECG attached; one of them is regular rhythm, narrow QRS complex and second one is irregular rhythm narrow QRS complex and P wave present. What is diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
The patient has a regular, fast heart rate and narrow QRS complex, which are hallmark features of SVT.
Q.215. A patient developed chest pain and sweating for 4 hours and was pulseless, there was an ECG attached, what is the diagnosis?
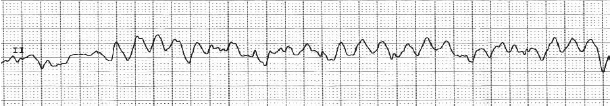
Correct Answer : A
VF is a life threatening heart rhythm where the heart's electrical activity becomes irregular preventing it from pumping blood. The patients symptoms include chest pain, sweating, and being pulseless stongly points VF.
Q.216. Which of the following can be considered as an appropriate investigation in a classic picture of heart failure?
Correct Answer : A
BNP is a hormone released by the heart when it's in stress, like in heart faliure. High BNP levels are strong indicator of heart faliure.
Incorrect options-
- ECG shows heart rhythm but doesn't directly diagnose heart faliure.
- Troponin indicates heart muscle damage, not heart faliure specifically.
- Chest X-ray can show signs of fluid in the lungs but isn't as reliable as BNP.
Q.217. About blood pressure, all of the following are true, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : C
Explanation: no circadian variation in BP
Q.218. Treatment for hypertensive crisis?
Correct Answer : C
Common Causes of Hypertensive Crisis -
1) Antihypertensive drug withdrawal (e.g., clonidine) 2) Autonomic hyperactivity 3) Collagen-vascular diseases 4) Drugs (e.g., cocaine, amphetamines) 5) Glomerulonephritis (acute) 6) Head trauma 7) Neoplasias (e.g., pheochromocytoma) 8) Pre eclampsia & eclampsia 9) Renovascular hypertension
Q.219. A 35-year-old patient with a history of RV and MS. Findings: Pan systolic murmur over the apex and diastolic rumbling murmur also over the apex. ECG: AF, ECHO: Dilated LV, LA, RA, pulmonary pre valve is thickened, calcified valve is < 0.7. What's the likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
- In mild mitral stenosis, the MVA is 1.5 to 2 cm2.
- In moderate stenosis it is 1 to 1.5 cm2.
- In severe stenosis, it is less than 1 cm2.
ESC/EACTS guidelines recommend percutaneous balloon commissurotomy in symptomatic patients with favorable characteristics, symptomatic patients with contraindications or high risk for surgery, symptomatic patients with unfavorable anatomy but without unfavorable clinical characteristics, and in asymptomatic patients without unfavorable characteristics and a high thromboembolic risk and/or a high risk of hemodynamic decompensation.
- Contraindications to percutaneous mitral commissurotomy include - mitral valve area >1.5 cm2, left atrial thrombus, more than mild mitral regurgitation, severe or bi-commissural calcification, absence of commissural fusion, severe concomitant aortic valve disease, or severe combined tricuspid stenosis and regurgitation, and concomitant coronary artery disease requiring bypass surgery If percutaneous balloon commissurotomy is not an option, patients should be referred for surgical repair or mitral valve replacement. Surgical correction of the mitral stenosis is indicated if embolization is recurrent, despite adequate anticoagulation therapy.
Q.220. Elderly patient known case of HTN and BPH. Which one of the following drug is potentially recommended in such case?
Correct Answer : B
It's an alpha-blocker that relaxes muscles in the prostate and bladder, easing urination for men with BPH. Plus, it also lowers BP, making it ideal for someone with BPH and HTN.
Q.221. All of the following causes secondary HTN, except?
Correct Answer : B
Addison’s disease causes postural hypotension.
Q.222. Diagnosis of infective endocarditis is?
Correct Answer : D
Duke’s criteria: Major blood culture criteria for IE include the following:
- Two blood cultures positive for organisms typically found in patients with IE
- Blood cultures persistently positive for one of these organisms, from cultures drawn more than 12 hours apart
- Three or more separate blood cultures were drawn at least 1 hour apart
Major echocardiographic criteria include the following:
- Echocardiogram positive for IE, documented by an oscillating intracardiac mass on a valve or on supporting structures, in the path of regurgitant jets, or on implanted material, in the absence of an alternative anatomic explanation.
- Myocardial abscess
- Development of partial dehiscence of a prosthetic valve
- New-onset valvular regurgitation
Minor criteria for IE include the following:
- Predisposing heart condition or intravenous drug use
- Fever of 38°C (100.4°F) or higher
- Vascular phenomenon, including major arterial emboli, septic pulmonary infarcts, mycotic aneurysm, intracranial hemorrhage, conjunctival hemorrhage, or Janeway lesions
- Immunologic phenomena such as glomerulonephritis, Osler nodes, Roth spots, and rheumatoid factor
- Positive blood culture results not meeting major criteria or serologic evidence of active infection with an organism consistent with IE
- Echocardiogram results consistent with IE but not meet major echocardiographic criteria.
A definitive clinical diagnosis can be made based on the following:
- 2 major criteria
- 1 major criterion and 3 minor criteria
- 5 minor criteria
Q.223. For coarctation of aorta all true, except?
Correct Answer : C
It produces a diastolic murmur, not a systolic murmur.
Q.224. An acyanotic middle aged man comes to you at the clinic, his X-ray shows prominent pulmonary arteries and vascular marking, most likely diagnosis is?
Correct Answer : B
Increased blood in right side of the heart, due to hole in atrial septum, will lead to classic findings described above.
Q.225. Which one of these drugs causes hypertensive crisis when stopped gradually?
Correct Answer : B
Clonidine lowers BP by activating brain receptors. Stopping it suddenly can cause rebound hypertension, leading to hypertensive crisis.
Incorrect options-
- Diltiazem,Beta-blockers, Alpha-blockers- These drugs lower BP but doesn't typically cause severe rebound HTN like clonidine.