
Hello,
Dr. Batman
Hello Doctor, Welcome!
Profile

Name: Batman
Email: batman@gotham.com
DERMATOLOGY REVIEW
(Total Questions - 143)Q.1. Patient came with a history of tinea capitis, what is the treatment?
Correct Answer : B
Explanation: oral antifungal is considered to be the treatment of choice for tinea capitis , shampoo is being considered as an adjunct to oral treatment.
Q.2. Cold induced Urticaria, what is the treatment?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Patients with cold Urticaria should learn to protect themselves from a rapid drop in body temperature. Regular antihistamines are not generally effective. The antihistamine cyproheptadine (Periactin) has been found to be a useful treatment. The tricyclic antidepressant doxepin has also been found to be an effective blocker of histamine release. Finally, a medication called ketotifen, which keeps mast cells from releasing histamine, has also been used with success.
Q.3. A man went on vacation. He noticed a white patch in his chest which became clearer after getting a sun tan which was spread on his chest. what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Tineaversicolor (TIN-ee-uh vur-si-KUL-ur), also called pityriasis , is a common fungal infection of the skin. The fungus interferes with the normal pigmentation of the skin, resulting in small, discolored patches.
Q.4. A male with itching in groin area. On examination, he had erythematous lesions and some have clear centers, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Explanation: Jock itch (tineacruris) is a fungal infection that affects the skin of genitals, inner thighs and buttocks. Jock itch causes an itchy, red, often ring-shaped rash in these warm, moist areas of body.
Q.5. A patient presented with mid face pain, erythematous lesions and vesicles on periorbital area and forehead. The pain is at nose, and nose is erythematous. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Explanation: Symptoms typically include prodromal sensory phenomena along 1 or more skin dermatomes lasting 1-10 days (averaging 48 h), which usually are noted as pain or, rarely, paresthesias. Patchy erythema, occasionally accompanied by induration, appears in the dermatomal area of involvement.
Q.6. Which of the following drugs causes angioedema?
Correct Answer : B
Q.7. What is the Treatment of comedones?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Retinoid medications are derivatives of Vitamin A and the treatment of choice for comedonal acne, or whiteheads and blackheads. They work by increasing skin cell turnover promoting the extrusion of the plugged material in the follicle. They also prevent the formation of new comedones. All of the retinoids must be prescribed by a healthcare provider
Q.8. What is the treatment of non-inflammatory acne?
Correct Answer : A
Treatment of comedones: Topical retinoid
Treatment of papules or pustules: Topical benzoyl, peroxide plus topical antibiotics, mainly clindamycin or
erythromycin.
In severe cases, intralesional steroid injection or oral antibiotics, such as tetracycline or erythromycin
may be added.
Q.9. Which is the treatment of papules or pustules?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Antibiotics: Antibiotics can be effective in treating most inflammatory acne (papules and pustules). They work by decreasing inflammation caused by bacteria and other irritating chemicals present in the sebaceous follicle.
Antibiotics may be combined with benzoyl peroxide, which is contained in over-the-counter medications, to form a topical solution that can be obtained with a doctor's prescription.
Q.10. What is the treatment of acne in severe cases?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Cystic acne, or nodulocystic acne, is the most severe form of acne vulgaris. Deep, inflamed
breakouts develop on the face and/or other areas of the body. The blemishes themselves can become
large; some may measure up to several centimeters across. Some common treatments for nodulocystic
acne include:
1) Oral antibiotics
2) Isotretinoin
3) Oral contraceptives - for women
4) Surgical excision and drainage - A doctor makes a small incision in the skin and extracts the infected
material.
5) Intralesional corticosteroid injections - Medication is injected directly into the lesion to reduce
inflammation and shrink the blemish.
Q.11. A 7 days old male baby was brought in OPD due to white papules on his face. How will you manage?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Milia are tiny white bumps or small cysts on the skin that are almost always seen in newborn babies. In children, no treatment is needed.
Q.12. What is the diagnosis of nasal pain & rash?
Correct Answer : A
Q.13. Patient has pain around his nose and there are pustules, papules and telangiectasia lesions. What is the diagnosis?
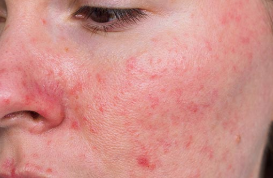
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that makes your face turn red and may cause swelling and skin sores that look like acne
Symptoms:
Redness of the face
Blushing or flushing easily
A lot of spider-like blood vessels (telangiectasia) in the face
Red nose (called a bulbous nose)
Acne-like skin sores that may ooze or crust
Burning or stinging feeling in the face
Irritated, bloodshot, watery eyes.
Q.14. A 15 years boy appear in OPD due to a patch in right lower leg. These patches are cleared-center circular lesions , with erythematous and raised margins. Picture is attached below. What is the probable diagnosis?
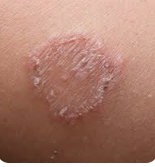
Correct Answer : B
Explanation: Tinea corporis Symptoms may include itching. The rash begins as a small area of red, raised spots and pimples. The rash slowly becomes ring-shaped, with a red-colored, raised border and a clearer center. The border may look scaly. The rash may occur on the arms, legs, face, or other exposed body areas.
Q.15. A mother brought her baby in OPD & was complaining of diaper rash. She used cornstarch, talc powder, zinc ointment & 3 different types of corticosteroids prescribed by different physicians but with no benefit. The rash was well demarcated & scaly with satellite lesions. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: They can commonly occur in body folds (axillae, groin, intergluteal space), genitals (vulva/vagina, penis), lips, and oral cavity. Candida lesions are red, tender, itchy, and have “satellite” lesions.
Q.16. A female patient presented with wheals over the skin with history of swollen lips. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Urticarial lesions are polymorphic, round, or irregularly shaped pruritic wheals that range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters
Angioedema, which can occur alone or with urticaria, is characterized by nonpitting, non-pruritic, well defined, edematous swelling that involves subcutaneous tissues (e.g., face, hands, buttocks, genitals), abdominal organs, or the upper airway (i.e., larynx).
Chronic urticaria: if more than 6 weeks Solar urticaria: due to sunlight
Cholinergic urticariae: due to a brief increase in body temperature.
Cold urticaria: due to exposure to cold.
Q.17. A child presented with a honeycomb crust lesion. The culture showed staphylococcus. aureus. What is the exact diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Impetigo A single or possibly many blisters filled with pus; easy to pop and -- when broken -- leave a reddish raw-looking base (in infants)Itching blister: Filled with yellow or honey-colored fluid oozing and crusting over. A culture of the skin or lesion usually grows the bacteria streptococcus or staphylococcus. The culture can help determine if MRSA is the cause because specific antibiotics are used to treat this infection
Q.18. On examination of newborn, the skin show papules and pustules over erythema base, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Explanation: The main symptom of erythema toxicumneonatorum is a rash of small, yellow-to-white colored papules surrounded by red skin. There may be a few or several papules. They usually appear on the face and middle of the body, but may also be seen on the upper arms and thighs. The rash can change rapidly, appearing and disappearing in different areas over hours to days.
Q.19. A patient presented with a 6 weeks history of itching & redness all over the body with wheals. Which type of urticaria this patient has?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Chronic hives, also known as urticaria, are batches of raised, red or white itchy welts (wheals) of various sizes that appear and disappear. While most cases of hives go away within a few weeks or less, for some people they are a long-term problem. Chronic hives are defined as hives that last more than six weeks or hives that go away but recur frequently.
Q.20. Which of the following reduces the risk of post-therapeutic neuralgia?
Correct Answer : C
Explanation: With postherpetic neuralgia, a complication of herpes zoster, pain may persist well after the resolution of the rash and can be highly debilitating. Herpes zoster is usually treated with orally administered acyclovir. Other antiviral medications include famciclovir and valacyclovir. The antiviral medications are most effective when started within 72 hours after the onset of the rash. The addition of an orally administered corticosteroid can provide modest benefits in reducing the pain of herpes zoster and the incidence of postherpetic neuralgia.
Q.21. A patient presents with colored pustules around his mouth. Laboratory testing reveals the presence of Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 (HSV-1). What is the treatment of choice for this condition?
Correct Answer : A
Medicines used to treat mouth sores include:
Acyclovir, Famciclovir & Valacyclovir.
Q.22. What is the treatment of scabies?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Permethrin cream and Malathion lotion are the two most widely used treatments for scabies.
Q.23. What is the treatment of herpes zoster in ophthalmic division?
Correct Answer : B
Explanation: Oral acyclovir (5 times/d) has been shown to shorten the duration of signs and symptoms,
as well as to reduce the incidence and severity of HZO complications. The use of oral corticosteroids has
been shown to reduce the duration of pain during the acute phase of the disease and to increase the
rate of cutaneous healing; Corticosteroids are recommended for HZO only for use in combination with
antiviral agents.
Q.24. A male patient presents with a vesicular rash on his forehead, which is indicative of Herpes Zoster (shingles). To prevent post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN), what is the most appropriate treatment?
Correct Answer : C
While corticosteroids can sometimes be used in conjunction with antivirals for Herpes Zoster to reduce inflammation and pain, steroids alone do not prevent post-herpetic neuralgia and should be used cautiously, especially in patients with immunocompromised states.
Q.25. A child presents with fever and malaise followed by the development of a rash. The rash starts as papules, then progresses to vesicles, and eventually crusts over. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
The described progression of the rash is characteristic of Chickenpox (Varicella), which is caused by the Varicella-zoster virus (VZV). The sequence of the rash beginning with papules, progressing to vesicles (fluid-filled blisters), and eventually forming crusts is a hallmark feature of chickenpox.
Q.26. A patient has 2 cm dome shaped mass at the dorsum of his hand. It’s covered by keratin. What’s the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Explanation: The classical keratoacanthoma has a raised margin and a central keratin-filled crater
Q.27. A male patient has hair loss that started at fronto-temporal area and progressed toward the vertex. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
In its most common form, androgenetic hair loss starts with an enlargement of the middle parting and the hair thinning out. The top of the head then gradually lights up, as part of a process that is irreversible if the person is not treated.
Q.28. A 30 year old male patient has hemorrhagic lesion in the mouth and papules at the face and back. He had shortness of breath, fever, cough and mediastinal mass, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: The tumors most often appear as bluish-red or purple bumps on the skin. They are reddish-purple because they are rich in blood vessels. The lesions may first appear on the feet or ankles, thighs, arms, hands, face, or any other part of the body. They also can appear on sites inside the body. Other symptoms may include: Bloody sputum &Shortness of breath.
Q.29. A 35 year old female came with complaints of development of rash all over the body except the face, after few weeks of unprotected sexual intercourse, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Typical presentation of secondary syphilis with a rash on the palms of the hands Reddish papules and nodules over much of the body due to secondary syphilis. Secondary syphilis occurs approximately four to ten weeks after the primary infection. While secondary disease is known for the many different ways it can manifest, symptoms most commonly involve the skin, mucous membranes, and lymph nodes. There may be a symmetrical, reddish-pink, non-itchy rash on the trunk and extremities, including the palms and soles
Q.30. A patient came in OPD with concerns of hypopigmented skin areas especially trunk and arms along with nerve thickenings. what is the probable diagnosis?

Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Leprosy is a disease that has been known since biblical times. It causes skin sores, nerve damage, and muscle weakness that gets worse over time.
Symptoms include:
Skin lesions that are lighter than your normal skin color.
Lesions have decreased sensation to touch, heat, or pain.
Lesions do not heal after several weeks to months.
Muscle weakness.
Numbness or lack of feeling in the hands, arms, feet, and legs.
Q.31. A patient presents with cystic nodules (acne) and scars. What is the best treatment option?
Correct Answer : A
For severe cystic acne with scarring, oral isotretinoin is the most effective treatment. It should be considered after other treatments (topical antibiotics, oral antibiotics, or topical retinoids) have failed.
Q.32. Acanthosis Nigricans associated with which of the following disease?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Acanthosis nigricans can be seen with obesity, PCOS, and other disorders associated with insulin resistance, a precursor to diabetes.
Q.33. An elderly male presents with back pain, and the initial examination is normal. After being prescribed steroids, he returns with a vesicular rash starting from his back and extending to his abdomen. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Shingles (Herpes Zoster) is a common condition in older adults, particularly after steroid use or other immunosuppressive treatments. It typically presents with pain followed by a vesicular rash that follows a dermatomal distribution. Early antiviral treatment can help reduce symptoms and prevent complications like post-herpetic neuralgia.
Q.34. A 6 year old male patient presented with diarrhea, dermatitis and dementia, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Pellagra is a condition of having too little niacin in the body and affects the normal the function of the nerves, digestive system, and skin. Pellagra may result in a number of symptoms. The symptoms can vary in intensity from person to person. Common symptoms of pellagra: You may experience pellagra symptoms daily or just once in a while. At times any of these common symptoms can be severe:
Abdominal cramping
Confused or delusional thinking
Depression
Diarrhea
Difficulty with memory, thinking, talking, comprehension, writing or reading
Headache
Loss of appetite, Weakness (loss of strength)
Malaise or lethargy
Mucus membrane inflammation
Nausea with or without vomiting
Skin lesions that are scaly and sore
Q.35. Regarding dermatomyositis, what is true?
Correct Answer : B
Explanation: The cause of dermatomyositis is unknown. Experts think it may be due to a viral infection of the muscles or a problem with the body's immune system. It can also sometimes occur in patients who have cancer of the abdomen, lung, or other body area.
Q.36. A patient with Dermatomyositis came in your OPD. What are the common symptoms of it?
Correct Answer : A
Symptoms including:
1) Difficulty swallowing
2) Muscle weakness, stiffness, or soreness
3) Purple or violet colored upper eyelids
4) Purple-red skin rash
5) Shortness of breath
Q.37. A 27 years old man has asymmetric oligoarthritis that involve bilateral Knee & elbow. He had painful oral ulcer for 10 years and mild abdominal pain, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Mouth. Painful mouth sores, identical to canker sores, are the most common sign of Behcet's disease.
Skin: Some people may develop acne-like sores on their bodies. Others may develop red, raised and
tender nodules on their skin, especially on the lower legs.
Genitalia sores
Eyes. Behcet's disease may cause inflammation in the eye — a condition called uveitis (u-ve-I-tis).
Joints. Joint swelling and pain often affect the knees in people with Behcet's disease. The ankles,
elbows, or wrists also may be involved. Signs and symptoms may last one to three weeks and go away
on their own.
Vascular system (Vasculitis).
Digestive system. Behcet's disease may cause a variety of signs and symptoms that affect the digestive
system, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, or bleeding.
Brain.. Behcet's disease may cause inflammation in the brain and nervous system that leads to
headache, fever, disorientation, poor balance, or stroke.
Q.38. Hair loss is a side effect of which of the following medications?
Correct Answer : C
Explanation: most COMMON side effects persist or become bothersome when using:
Valproic Acid: Constipation, diarrhea, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, increased or decreased appetite, mild hair loss; nausea; sore throat; stomach pain or upset; trouble sleeping; vomiting; weakness; weight gain.
Phenytoin: gingival hyperplasia, hirsutism, ataxia.
Carbamazepine: agranulocytosis, hepatotoxicity, aplastic anemia.
Na Valproate: transient hair loss.
Q.39. A patient presents with fever and warm, erythematous lesions over the face, desquamation of the hands and feet. On examination, his HR= 110bpm, blood pressure= 170/100 mm Hg and sO2=98%. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
The clinical scenario described strongly suggests Kawasaki Disease. Key features pointing to this diagnosis are:
- Desquamation of hands and feet: This is a classic feature of Kawasaki Disease and occurs after the acute phase, typically between 2-3 weeks into the illness.
- High blood pressure (170/110): Although Kawasaki Disease is primarily known for coronary artery inflammation and mucocutaneous involvement, hypertension can occur due to coronary artery involvement or kidney issues in severe cases.
- Symptoms of infection: Kawasaki Disease can present with fever and generalized signs of inflammation that may be confused with an infection.
Q.40. Patient with symptoms of blepharitis and acne rosacea, what is the best treatment?
Correct Answer : A
Most eye doctors will prescribe long-acting tetracyclines such as doxycycline, which can be taken once or twice a day. Furthermore, doxycycline, unlike traditional tetracycline, can be taken with food and milk products without preventing absorption in the body
Q.41. For Folliculitis, what is the treatment?
Correct Answer : D
Explanation: Treatment; Hot, moist compresses may promote drainage of the affected follicles. Treatment may include antibiotics applied to the skin (mupirocin) or taken by mouth (dicloxacillin), or antifungal medications to control the infection
Q.42. Which is the most common association with acanthosis nigricans?
Correct Answer : D
Explanation: This occurs due to insulin spillover (from excessive production due to obesity or insulin resistance) into the skin which results in abnormal growth being observed.
The most common cause would be insulin resistance, usually from type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Q.43. A middle aged man having black spots on his thigh for years, it has started to become more black with bloody discharge since few months, what is the best management?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: The patient is having a malignant melanoma and the treatment is by excision.
Q.44. A 6-year-old child presents with multiple painful swellings on the dorsum of the hands, feet, fingers, and toes. His laboratory results show a hemoglobin level of 7 g/dL, and a peripheral blood smear reveals crescent-shaped red blood cells. What is the most appropriate long-term management for this child?
Correct Answer : B
Explanation: this patient has sickle cell anemia.
Q.45. A 50-year-old patient presents with bullous lesions on the foot. A biopsy shows subdermal lysis, and fluorescent staining reveals IgG deposition. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Bullous Pemphigoid (BP) presents with tense, subepidermal bullae, often in older adults, and is characterized by IgG deposition at the dermoepidermal junction.
Q.46. A 2-month-old infant presents with scaling lesions on the scalp and forehead. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Cradle cap (seborrheic dermatitis) is the most common diagnosis for scaling lesions on the scalp and forehead in infants, especially within the first few months of life.
Q.47. Henoch-Schonlein purpura affect which of the following?
Correct Answer : B
Explanation: Henoch-Schönleinpurpura is a small-vessel vasculitis in which complexes of immunoglobulin A (IgA) and complement component 3 (C3) are deposited on arterioles, capillaries, and venules.
Q.48. Regarding urticaria, all are true EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : C
Explanation: it is not always due to deposition of immune complex in the skin (right :due to increase permeability of capillaries).
Q.49. A 4 day old neonate presented in your OPD due to rash over the face & trunk. On examination, the rashes are small, yellow-to-white colored papules surrounded by red skin. What is the Diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Erythema toxicum may appear in 50 percent or more of all normal newborn infants. It usually appears in term infants between the ages of 3 days and 2 weeks. Its causes are unknown. The condition may be present in the first few hours of life, generally appears after the first day, and may last for several days. Although the condition is harmless, it can be of great concern to the new parent. Symptoms: The main symptom is a rash of small, yellow-to-white colored papules surrounded by red skin. There may be a few or several papules. They usually appear on the face and middle of the body, but may also be seen on the upper arms and thighs. The rash can change rapidly, appearing and disappearing in different areas over hours to days
Q.50. Peter was living in a cold climate for a long time and he noticed a brown scaly lesion on his chest, when he moved to warm area, the lesion became hypopigmented, although the rest of his body was tanned. what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.51. The following drugs can be used for acne treatment except?
Correct Answer : A
Q.52. Seborrheic Dermatitis caused by which of the following?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: treatment --> selenium sulfide or zinc pyrithione shampoos for the scalp, and topical antifungals and/or topical corticosteroids for other areas.
Q.53. A patient complaining of back pain and hypersensitive skin of the back. On examination, patient had rashes at the back. The tender lesions have a red base, and distributed in a belt-like pattern on the back, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Etiology: Varicella-zoster virus (dormant in dorsal root ganglion after childhood chickenpox).
Q.54. Blistering skin rash is a feature of the following except?
Correct Answer : D
Erythema multiforme: is an acute, self-limiting, inflammatory skin eruption. The rash is made of spots that are red, sometimes with blistered areas in the center. so named because of the "multiple forms" it appears in; Divided into two overlapping subgroups (EM minor and Stevens-Johnson syndrome “most often results from a medication like penicillin’s and sulfa drugs”)
Eczema herpiticum: A febrile condition caused by cutaneous dissemination of herpes virus type 1, occurring most commonly in children, consisting of a widespread eruption of vesicles rapidly becoming umbilicated pustules. Skin reactions are the most common adverse reactions to sulfa medications, ranging from various benign rashes to life-threatening Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Erythema nodosum: the formation of tender, red nodules on the front of the legs.
Q.55. Regarding scabies infestation, all are true except?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Scabies are caused by the mite S scabieivarhominis, an arthropod.
Humans can be affected by animal scabies. Transient pruritic papular or vesicular erythemic lesions may occur after 24 hours of exposure to an infested animal. The immediate itching protective mechanism can prevent the mite from burrowing Treatment options include either topical or total medications. Topical options include permethrin
cream, lindane, benzyl benzoate, crotamiton lotion, and cream, sulfur, and Tea tree oil. Oral options include ivermectin
Q.56. Regarding dysplastic nevus syndrome, all of the following are true except?
Correct Answer : B
Dysplastic nevi, also known as atypical moles, are unusual benign moles that may resemble melanoma.
Q.57. A patient presents with scaling along the hair margin, nasal folds, and behind the ears, accompanied by papules and irregular erythema. What is the most appropriate treatment?
Correct Answer : A
Q.58. Regarding Psoralen ultraviolet ray A (PUVA) , all of the following are true except?
Correct Answer : C
Psoralens should not be used by: Children under age 12, because the UV light therapy may cause cataracts, People who have diseases that make their skin more sensitive to sunlight (such as lupus), and Fertile men and women who do not use birth control. There is a small risk of birth defects., Pregnant women, because of possible effects on developing fetuses Side effects (short-term): Skin redness & itching, headache, nausea & Burns.The spread of psoriasis to skin that was not affected before (Koebner's response).
Side effects (long-term): Squamous cell carcinoma & Melanoma.
Q.59. Patient with eruptive purpuric rash, hepatosplenomegaly, Which is the causative agent?
Correct Answer : A
Q.60. A lady with 9 weeks history of elevated erythematous wheals overall her body, she also has lip swelling, no history of recent travel, food allergy, or drug ingestion, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Chronic urticaria: if more than 6 months
Solar urticaria: due to sunlight
Cholinergic urticaria: due to a brief increase in body temperature.
Cold urticaria: due to exposure to cold
Q.61. A patient with Acne presented in your OPD. she is taking retinoids for management of acne, what are the possible side effect?
Correct Answer : D
The side effects of retinoids are:
1) Dry skin, eyes, lips, hair & genitalia.
2) Sun sensitivity.
3) body ache&joint pain
4) decreased night vision
5) increased triglyceride levels
6) liver and kidney toxicity
7) Pseudo tumor cerebri
Q.62. An athlete who jogs on daily basis, presented with groin rash with erythema, what is the appropriate management?
Correct Answer : B
Q.63. A 42 years old man presented with sudden eruption of raised, itchy lesions all over the body with palm & foot. He can recall that he had sea-food at lunch. what is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Syphilis Is a sexually transmitted disease, & it is one of the infectious diseases, that has dermatological
manifestation: painless papule develops and soon breaks down to form a clean-based ulcer (chancre with
raised, indurated margins.
Erythema multiforme: most cases are related to drug ingestion and the majority of cases pertaining to antibiotics
(penicillin, sulfonamides), anticonvulsants (phenytoin, carbamazepine, Phenobarbital, lamotrigine), NSAID,
allopurinol, a minority of cases may be infection-related (mycoplasma pneumonia, herpes simplex) and involve
skin including perineum and genitals, and mucous membranes ( eyes, mouth, pharynx) It varies from a mild,
self-limited rash (E. multiforme minor) to a severe, life-threatening form (E. multiform major, or Stevens-
Johnson syndrome) that also involves mucous membranes. The skin form of E. multiforme, far more
common than the severe form, usually presents with mildly itchy, pink-red blotches, symmetrically
arranged and starting on the extremities
Erythema nodosum (red nodules) is an inflammation of the fat cells under the skin (panniculitis). It occurs
3-6 weeks after an event, either internal or external to the body initiates a hypersensitivity reaction in
subcutaneous fat and is frequently associated with fever, malaise, and joint pain and inflammation. It
presents as tender red nodules on the shins that are smooth and shiny.
Fixed drug eruptions are more common on the limbs than the trunk; the hands and feet “not necessarily
palms and soles”. Lesions may occur around the mouth or the eyes. The genitals or inside the mouth may
be involved in association with skin lesions or on their own, Can be caused by: acetaminophen,
sulfonamide antibiotics, tetracycline, Phenobarbital, and phenolphthalein.
Pityriasis rosea most often affects teenagers or young adults. In most cases, there are no other symptoms,
but in some cases, the rash follows a few days after an upper respiratory viral infection. Herpes viruses 6 and
7 have sometimes been associated with pityriasisrosea. It begins with one large (2-5cm), oval herald patch,
and smaller secondary multiple lesions appear within 1-2 weeks.
Q.64. 10 years old boy presented with a 5 days history of skin lesion which was scaly, circular and centrally pale lesions with raised erythematous borders. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.65. Referring the diagram, what is the diagnosis?

Correct Answer : D
Q.66. A hypertensive patient on hydralazine presents with sunburn. In addition to advising sun protection, what should be the next step in management?
Correct Answer : D
Q.67. A 32 years old patient come to you and is worried about one of his moles. Given history that his father had moles excisional biopsy done but now he has metastasis in lungs, bones and liver, what will come to your mind about malignant change of mole?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: The ABCDEs of melanoma are asymmetric, Irregular Border, Irregular Color, Diameter > 6 mm,
Evolution: changing or new lesion.
Q.68. A patient with a history of prolonged sun exposure near the sea presents with severe sunburn. The patient reports that they have already applied sun protection creams but they are still experiencing significant discomfort. They are now seeking treatment. On examination, there is erythema and scaling on the skin with no signs of blistering yet. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient's sunburn?
Correct Answer : A
Q.69. What is correct for erythema nodosum ?
Correct Answer : A
Q.70. Refer to the picture below, what is the causative organism of this condition?
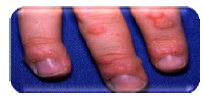
Correct Answer : A
Q.71. A child came in OPD with eczema flare up. He is on steroid inhaler. He has itching in the nasal cavity and that disturb his sleeping, What medication can be given to him?
Correct Answer : A
Q.72. Regarding Lichen planus, which is the most common site to develop infection?
Correct Answer : C
Lesions usually develop on flexural surfaces of the limbs, such as the wrists (see the image below). After a week or more, a generalized eruption develops with maximal spreading within 2-16 weeks.
Q.73. A child presents with localized hair loss in the temporal area. Upon microscopic examination of the scalp, there are findings consistent with broken hair shafts, inflammation around the hair follicles, and fungal spores. What is the most likely diagnosis?

Correct Answer : C
Q.74. Regarding Acne treatment, which topical antibiotic is commonly used?
Correct Answer : A
Q.75. A female has academic problems in school. She often pulls her hairs manually. Now she has bald patches. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.76. In reference to the attached picture of skin lesion that is purple, flat topped and polygonal papules, what is the diagnosis?
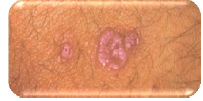
Correct Answer : A
Q.77. A male patient presents with a scaly, fine papular rash on the front of the scalp, nose, and retro-auricular area. What is the most appropriate treatment?
Correct Answer : D
The described rash, located on the scalp, nose, and retroauricular area, is consistent with seborrheic dermatitis, a common inflammatory condition characterized by scaly, fine papules, often seen in areas rich in sebaceous glands. Topical corticosteroids are commonly used to treat seborrheic dermatitis due to their anti-inflammatory properties.
Q.78. What is true for Xanthoma?
Correct Answer : D
Explanation: They are usually soft plaques that are located in the dermis at the inner aspect of the upper eyelid.
Q.79. A 12 year old child presented with atopic dermatitis, what are the treatment options other than cortisone?
Correct Answer : D
TREATMENT: Prophylactic measures include use of nondrying soaps, application of moisturizers, and avoidance of known triggers.
Treat with topical corticosteroids (avoid systemic steroids in light of their side effect profile), PUVA, and topical immunomodulators (e.g., tacrolimus, pimecrolimus).
Topical corticosteroids should not be used for longer than 2–3 weeks
Q.80. A Patient presented in an OPD with blepharitis, acne rosacea, but no keratitis. What is the best treatment option?
Correct Answer : C
Q.81. What is the most effective treatment for rosacea?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: if mention tetracycline choose it.
Treatment of Rosacea :
1) Oral tetracyclines& topical metronidazole or topical erythromycin or topical clindamycin.
2) For severe case: isotretinoin, surgical treatment for rhinophyma
Q.82. A 23 years old male patient presented in OPD with history of URTI then he developed ecchymosis, how you will manage this case?
Correct Answer : C
Q.83. A 35 year old smoker, presented in OPD due to tongue lesion. On examination, a irregular white patch is present on the tongue, what is the appropriate management?
Correct Answer : B
A biopsy should be done, and the lesion surgically excised if pre-cancerous changes or cancer is detected.
Q.84. A Patient who is a known case of ulcerative colitis came in OPD with complaint of erythematous rash at lower limbs, what is the most likely diagnosis?
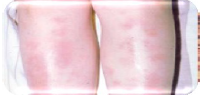
Correct Answer : A
Q.85. A 50 year old patient, known to have ulcerative colitis, presented with skin lesions around Tibia which are with irregular margins. Refer to the picture, what is most likely diagnosis?
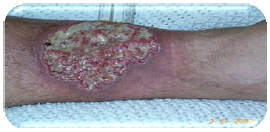
Correct Answer : A
Q.86. A child presented in ER with button-battery deep in ear canal. what to do next?
Correct Answer : B
Q.87. 45 years old male patient, who is a life-guard by profession, came in OPD with macular, painless lesion on face. There is a history of prolong, un-protected sun exposure. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
The patient's history of prolonged, unprotected sun exposure makes him susceptible to actinic keratosis (AK), which is a precancerous skin lesion often caused by chronic sun exposure. Macular lesions are typical for AK, and they are usually painless. They are more common in areas exposed to sunlight, such as the face, neck, ears, scalp, and backs of the hands
Q.88. All are true for black hairy tongue, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : B
Explanation: Black hairy tongue: Defective desquamation of the filiform papillae that results from a variety of precipitating factors (poor oral hygiene, use of medications e.g. broad-spectrum Abx& therapeutic radiation of the head & neck). All cases are characterized by hypertrophy and elongation of filiform papillae with a lack of desquamation. Seen more in those: tobacco use, heavy coffee or tea drinkers, HIV +ve. Rarely symptomatic. Rx: In many cases, simply BRUSHING THE TONGUE with a toothbrush or tongue scraper is sufficient. Medication: if due to candidiasis: Antifungal (Nystatin), Keratolytic agents (but irritant).
Q.89. A patient presents with a hyperkeratotic, scaly lesion over the extensor surfaces of the knee and elbow. What is the best approach to avoid exacerbation of the condition?
Correct Answer : C
The patient is most likely presenting with psoriasis, a chronic skin condition characterized by scaly, hyperkeratotic lesions that commonly occur on the extensor surfaces of the body, such as the knees and elbows. The best way to avoid exacerbation of psoriasis is to focus on regular moisturizing to reduce dryness and prevent scaling. Emollients help to restore the skin's barrier, prevent excessive dryness, and reduce irritation, which can trigger flare-ups.
Q.90. A 1 month old baby was brought in OPD with red macule & dilated capillary on the right side of the face, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
“Don’t choose milia or cavernous haemangioma”.
Q.91. A 10 year old presented in an OPD with erythematous, pruritic, scaly areas on face, flexure surfaces and scalp. Refer to the picture below, what is the most probable diagnosis?
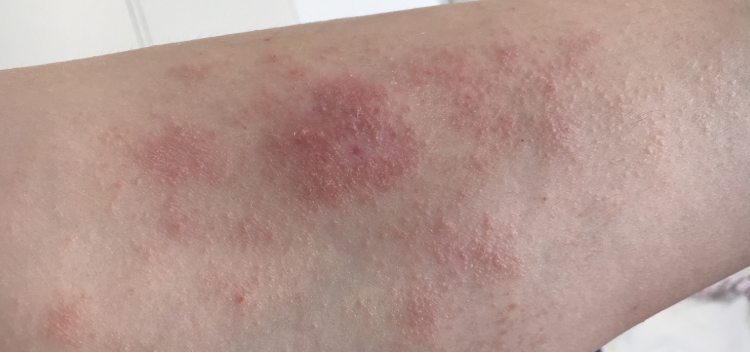
Correct Answer : A
Q.92. Which of the following is the type of acne that presents with pustules and yellowish-white discharge?
Correct Answer : A
Q.93. How will you manage a second degree burn on face and neck?
Correct Answer : A
Q.94. In reference to the picture below, A man presented in your OPD with the facial lesions which are erythematous , more prominent at this area, at angle of nose, chest and scalp The Lesions are scaly. What is the diagnosis?
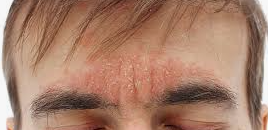
Correct Answer : C
Q.95. A picture of a child as shown in the picture below, He presented in your OPD with red rash on flexor surfaces, what is the diagnosis?
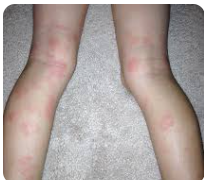
Correct Answer : A
Q.96. A child with round palpable red rash on his right leg, no pain or itching in these lesions, and they have been present for long time, What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.97. In which cases Laser therapy in derma ( PUVA) is used?
Correct Answer : D
Q.98. What is the goal of early management of inflammatory acne?
Correct Answer : A
Q.99. Pyoderma gangrenosum is treated by which of the following?
Correct Answer : A
Q.100. Cafe-au-lait confirms diagnosis of Neurofibromatosis as which of the following?
Correct Answer : B
Q.101. A female presented in OPD with Acne that is not responding to Steroid and antibiotics. You decided to give her retinol but before that what you will tell her about this medication?
Correct Answer : A
Q.102. A 7 year old male child who is a known case of asthma presented to you with complaint of red, itchy lesions of flexure skin surfaces, what is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.103. A 35-year-old female presents with a red, moist rash under her breasts. She mentions that the rash worsens with sweating and after washing, it remains moist. Examination reveals erythematous, well-demarcated patches with some maceration. What is the most appropriate treatment?
Correct Answer : B
The patient likely has intertrigo complicated by a Candida (fungal) infection, which is common in moist, warm areas like under the breasts. The presence of moisture and maceration suggests an overgrowth of Candida.
Q.104. A patient with family history of allergy has scaling skin and itching in face and anti-cubital fossa, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.105. Young female she have vulvar irritation she goes to her doctor and advise her to stop bubble bath ! She stopped but still she have this irritation. On examination, It was waxy with some things peaked what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Q.106. A young male patient presented in OPD with painful skin lesions. Picture of the lesion is shown below, they are mixture of vesicle, bulla and erythema at chest. What is the treatment for that condition?
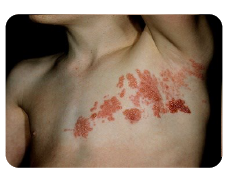
Correct Answer : C
This case is "herpes zoster”. Treatment of herpes zoster is antiviral and analgesic, Antiviral are (systemic) and includes: acyclovir, famciclovir.
Q.107. A 10 days old baby presented in OPD with vesicles on the face and honey comb crust. which of the following organism most likely to cause it?
Correct Answer : A
Q.108. Which is the classical characteristic for genital herpes?
Correct Answer : A
Q.109. A patient with cystic nodule (acne) and scars, what is the best treatment?
Correct Answer : A
Q.110. Recurrent swelling in the anal cleft with skin tract and recurrence, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.111. A prostitute with multiple sex partners presented in OPD with history of painless vaginal sore which healed and did not leave scar. O/E she has generalized lymphadenopathy. What is your diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.112. A 7 year old patient presented with history of fever and red, peeling rash at back of ears, on limbs and over body. What is the first line treatment?
Correct Answer : C
The diagnosis: scarlet fever: The cutaneous rash, lasts for 4-5 days, followed by fine desquamation, one of the most distinctive features of scarlet fever. The desquamation phase begins 7-10 days after the resolution of the rash, with flakes peeling from the face. Peeling from the palms and around the fingers occurs about a week later and can last up to a month or longer. The extent and duration of this phaseare directly related to the severity of the eruption Antibiotic therapy is the treatment of choice for scarlet fever: Penicillin remains the drug of choice (documented cases of penicillin-resistant group A streptococcal infections still do not exist). A first-generation cephalosporin may be an effective alternative, as long as the patient does not have any documented anaphylactic reactions to penicillin. If this is the case, erythromycin may be considered as an alternative.
Q.113. A 5-year-old child presents with intense itching and scaly rashes on the back of the knees, face, and anterior elbows. The rash has been persistent for months and worsens with dry weather. On examination, there is erythema, scaling, and lichenification in the affected areas. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Eczema: the earliest lesion affects anti-cubital and popliteal foss
Lesions are ill-defined as erythematous, scaly, patches and plaques
Q.114. A 30-year-old postpartum woman returns to work and notices brown discoloration on her face after sun exposure. The hyperpigmentation is symmetrically distributed over the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
A patchy brown or dark brown skin discoloration, that usually occurs on the face and may result from hormonal changes, generally found in sun-exposed areas.
Q.115. A child with high-grade fever and after 2 day he develop sore throat. On examination, there is congested throat and pharynx and white to yellowish papule on erythematous base in mouth and lip, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.116. A picture of Patients legs showing maculopapular rash. H/O red rah appearing on extensor surfaces. Rash is tender to palpate but does not blanch on pressure. What is the diagnosis?
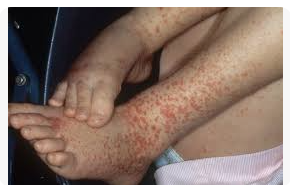
Correct Answer : A
Q.117. A Young male complains of generalized skin lesions and redness, before that there was a history of mouth and lips swelling for couple of days the its denied any history of traveling or unusual exposure, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.118. A 25-year-old male presents with scaly, hypopigmented macules on his chest and arms. He reports that the macules appear more prominent when exposed to sunlight. The lesions are mildly itchy. What is the most appropriate treatment?
Correct Answer : B
The presentation is suggestive of Tinea Versicolor (Pityriasis Versicolor), caused by Malassezia species, a superficial fungal infection.
Q.119. A 25 years old male complaining from scaly lesion in his chest , then they became hypopigmented since last 2 months in winter he spend his time near to the sea. The examination showed hypopigmented lesion over chest & arms, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.120. A old man presented with black macule on his back with irregular border and color variation, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.121. A 14 year old child came in OPD with eczema. He is already on 1% hydrocortisone, what other medication you can add?
Correct Answer : C
Q.122. A 55-year-old patient presents with tense bullae on the foot. Biopsy reveals epidermal lysis, and immunofluorescence shows IgG deposition along the basement membrane zone. What is the most likely diagnosis?
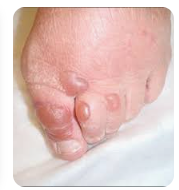
Correct Answer : A
Q.123. What is the most specific test for syphilis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.124. A 35-year-old male presents with hypopigmented macules on his skin with loss of sensation over the lesions and thickened peripheral nerves on examination. A skin smear for acid-fast bacilli (AFB) is negative. What is the most likely type of leprosy?
Correct Answer : A
Q.125. What is the treatment of psoriasis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.126. A patient with moderately severe acne vulgaris, what is the best treatment?
Correct Answer : A
Q.127. A 19 years old young male with good muscular body presented in your OPD due to bad mouth breath, he also complaints of acne. Which of the following could be a cause?
Correct Answer : A
Q.128. A 30 year old patient presented with vesicle in mouth with gingivitis and also painful vesicle at arm and leg, what is the most likely cause?
Correct Answer : A
Q.129. An infant has genital rash (the rash spares genital fold) and is not response to antibiotics, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.130. What is the use of antibiotic in acne?
Correct Answer : A
Q.131. A child presented with 2*2 cm hair loss at the temporal area. The clinical examination was normal, but microscopic examination of hairs around the area show clubbed and attenuated hairs, what is the diagnosis ?
Correct Answer : C
Trichotillomania (compulsive hair pulling) causes:
- Irregular patches of hair loss
- Hairs of varying lengths
- No signs of infection or inflammation
- Microscopy: broken, frayed, or attenuated (thin) hair shafts
Q.132. What is the treatment of tinea capitis?
Correct Answer : B
DOC of Tinea Capitis.
Q.133. During examination of a patient, you have noticed absence of eye lashes also the patient has thin scalp hair. what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Trichotillomania is a hair pulling disorder, that falls under anxiety spectrum. Patients have developed this habit of pulling hair all the time.
In Alopecia, eye lashes are usually not affected. If eye lashes are absent, it means patient is pulling them out.
Q.134. What is the best description of the lesion in herpes?
Correct Answer : A
Q.135. A 6 years old school going boy complain of itchy scalp and his 10 friends have the same problem what is your diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.136. A 12 years old female, non-pruritic annular eruption in the right foot for 8 months, looks pale and not scaling, no response to 6 weeks of miconazole, What is your diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Q.137. A picture of a patient with psoriasis is shown below. He ask you about how to decrease keratinization?
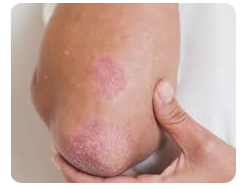
Correct Answer : D
Q.138. A patient presents with scaly lesions around the mouth and ear. What will you likely find during diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
The scaly lesions around the mouth and ear are suggestive of seborrheic dermatitis, a chronic inflammatory condition involving areas rich in sebaceous glands (e.g., scalp, nasolabial folds, and ears).
Q.139. What is the Side effect of Retin-A Gel in treatment of Acne?
Correct Answer : B
Q.140. All the following are treatment of scabies except?
Correct Answer : D
Q.141. A patient presents with a history of alopecia that started from the temporal area, then the occipital region, and has now reached the frontal region. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
The pattern of hair loss described—starting from the temporal and occipital areas, then spreading to the frontal region—suggests alopecia areata, an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks the hair follicles, causing hair loss.