
Hello,
Dr. Batman
Hello Doctor, Welcome!
Profile

Name: Batman
Email: batman@gotham.com
ENDOCRINOLOGY REVIEW
(Total Questions - 97)Q.1. The patient is a known case of type 2 DM on insulin. His blood sugar levels are as follows: in the morning= 285 mg/dl, at 3 pm= 165 mg/dl, at dinner time= 95 mg/dl. What will be your management plan?
Correct Answer : A
The elevated fasting blood glucose of [285 mg/dl] indicates insufficient basal insulin coverage overnight. Increasing the evening dose of long-acting insulin will improve overnight glucose control and reduce morning hyperglycemia.
Reference: American Diabetes Association [ADA] Standards of care 2024 - Insulin management for fasting hyperglycemia.
Q.2. A patient known case of IDDM, presented with DKA, K+= 6 mmol/L and blood sugar= 350 mg/dl. What treatment will you provide?
Correct Answer : B
The primary treatment for DKA includes :
1- IV fluids- to correct dehydration. [3 'I'OF DKA - Impaired insulin give IV fluid and Insulin]
2-Insulin- Administer IV insulin to lower blood glucose levels and stop ketone production [K+ levels must be monitored as insulin can shift K+ intracellularly, risking hypokalemia].
NOTE-Sodium bicarbonate is to be used only in cases of severe acidosis (pH < 6.9).
Reference: ADA Guidelines 2024
Q.3. The patient has increased foot size [39 to 41.5] accompanied by enlargement of hands and joints. Which hormone is responsible?
Correct Answer : D
The patient's enlarged hands, feet, and joints suggest acromegaly, which is caused by an excess of Growth Hormone [GH] in adults, typically due to a pituitary adenoma. This increase in growth hormone elevates IGF-1 levels, resulting in the enlargement of soft tissues and bones.
Incorrect Options-
- thyroid hormones control metabolism not the growth of hands and feet
- prolactin hormone mainly involves milk production, not changes in extremity size.
- ACTH stimulates cortisol production linked to stress and Cushing's syndrome, not acromegaly.
Reference: Melmed, S., et al. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology, [14th] ed.
Q.4. What is the underlying pathophysiological mechanism that leads to the development of diabetic ketoacidosis [DKA]?
Correct Answer : A
Insulin deficiency→lack of insulin→prevents glucose from entering into cells [high blood sugar levels]→ fat breakdown occurs because cells cannot utilize glucose →release of fatty acid into bloodstream→in liver fatty acids are converted into ketones by process of ketogenesis→metabolic acidosis→symptoms
Q.5. A female patient presents with a whitish discharge from the nipple. Investigation reveal a pituitary adenoma. Which hormone is most likely responsible for this symptom?
Correct Answer : A
Prolactin is produced by the pituitary gland and is responsible for milk production. A pituitary adenoma can cause elevated prolactin levels, leading to galactorrhea.
Incorrect Options:
FSH, LH, and GnRH are not related to the symptom.
Q.6. What is the most likely diagnosis for a patient presenting with following TFT report: T4 high, Free T3 high, TSH low.
Correct Answer : D
Thyrotoxicosis refers to a condition where there is an excess of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream, in the scenario, the thyroid function test [TFT] shows high T3 and T4 levels with low TSH, which is consistent with hyperthyroidism. The low TSH level occurs due to a negative feedback mechanism from the elevated thyroid hormones in the pituitary gland.
Incorrect Options -
- Immune thyroiditis eg. Hashimoto's thyroidits usually presents as hypothyroidism.
- Goitre can occur in both hyperthyroid and hypothyroid.
- Hypothyroidism presents with low T3 and T4 levels along with high TSH
Q.7. What is the treatment of choice for a young male presenting with unilateral gynecomastia?
Correct Answer : C
Unilateral gynecomastia in young males, often seen during puberty, typically resolves spontaneously as hormone levels stabilize. This self-resolution typically occurs within 6 months to 2 years.
Incorrect options-
- Discontinue soy products and other potential hormonal disruptors-limited evidence linking soy or other disruptors to gynecomastia.
- Compression garments provide cosmetic improvement or comfort, not a first-line treatment.
- Surgical intervention is needed only if the condition persists or causes significant psychological distress.
Q.8. A 42-year old patient presents with thyroid mass. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Correct Answer : A
FNAC [fine needle aspiration cytology] is the gold standard for evaluating thyroid nodules and masses. It helps in guiding further management by determining whether the mass is benign or malignant.
Incorrect Options-
- CT scan- considered in cases where invasion or local metastasis is suspected, but it is not the first-line diagnostic tool.
- x-ray doesn't provide detailed information about thyroid tissue.
- Total thyroidectomy -treatment option, especially if malignancy is confirmed, A biopsy is typically needed before deciding on surgery
Q.9. A patient with hypothyroidism, currently on levothyroxine therapy, presents with anorexia, dry cough ,dyspnea & left ventricular dysfunction. Laboratory results show normal TSH & T4 levels, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia and elevated parathyroid hormone [PTH] levels. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Secondary hyperparathyroidism [a common complication of CKD] results in impaired phosphate excretion leading to hyperphosphatemia and hypocalcemia due to the formation of calcium phosphate complexes →stimulation of parathyroid gland→inreased level of PTH →secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Incorrect Options-
- Primary hypoparathyroidism- PTH-low + hypocalcemia+ hyperphosphatemia
- Hypopiuitarism-not associated with calcium phosphate imbalances
- Uncontrolled hyperthyroidism-elevated T3,T4 and suppressed TSH levels
Q.10. A patient with Type 2 DM, currently on conservative management presents with complaints of weight gain and polyuria. What would be the treatment of choice to address these symptoms?
Correct Answer : B
Metformin is the first line of treatment for Type 2 dm. It helps improve insulin sensitivity, the patient's symptoms of weight gain and polyuria suggest that current management [likely with insulin] is not optimal, and metformin can address both symptoms.
Q.11. A 34-year-old female patient presents with terminal hair in a male pattern distribution and has female genitalia. What is the likely underlying process?
Correct Answer : B
Androgen oversecretion leads to hirsutism which is the male pattern hair distribution due to increased androgen activity.
Incorrect Options-
- Prolactin oversecretion -galactorrhea
- FSH oversecretion -follicular development in ovaries
- Testosterone oversecretion - a type of androgen oversecretion and is therefore the less preferred option in the given scenario.
Q.12. A female patient presented with symptoms of hyperthyroidism, including a tender neck swelling & discomfort. Her lab results showed a low TSH & elevated T4 levels. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Subacute thyroiditis-inflammation of thyroid gland.
Triggering factor-viral infection.
Clinical features- neck pain, tenderness, T4-high, TSH-low.
Incorrect Options-
- Thyroid nodule- asymptomatic + no hormonal imbalance.
- Graves disease- neck pain absent + hyperthyroidism+ diffuse goiter
- Hypothyroidism- T4-low+ TSH-high
Q.13. Which of the following electrolyte imbalance is commonly associated with primary hyperaldosteronism?
Correct Answer : C
Primary hyperaldosteronism→excessive aldosterone→increased- Na+ retention,K+ excretion through kidneys→Hypokalemia. [hypeRaldosteRetentionOfNa+ism]
Incorrect Options-
- Hypernatremia may occur due to Na+ retention but is not a hallmark electrolyte disturbance.
- Hypomagnesemia- not a prominent feature.
- Hyperkalemia- not a feature.
Q.14. A patient presents with this clinical picture but doesn't have other manifestations like “organomegaly or lymphadenopathy” what is the likely diagnosis?
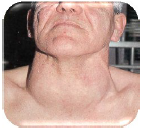
Correct Answer : B
A goiter is an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland, which may be seen as a swelling in the neck.
Incorrect Options-
As organomegaly and lympadenopathy are absent it points towards benign thyroid condition making these options incorrect.
- Lymphoma- painless lymphadenopathy, systemic symptoms.
- Throat cancer- hoarsness, dysphagia, localized pain, or lymph node involvement.
- Mononucleosis -generalized lymphadenopathy, fever, fatigue, splenomegaly
Q.15. Which of the following conditions can be associated with thyroid neoplasia?
Correct Answer : A
HT is strongly associated with development of thyroid neoplasia later in the life.
Q.16. A patient is experiencing symptoms like feeling irritable, tachycardia, night sweats, and their lab results show TSH: Normal, T4: High. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
The symptoms of irritability, tachycardia, night sweats, and lab results showing normal TSH and high T4 are typical features of Graves disease.
Incorrect Options-
- Hashimotos- high TSH+ low T4
- Secondary hypothyroidism- low T4+ low TSH
- Primary hypothyroidism- low T4+ high TSH
Q.17. An 8-year old boy comes to the clinic. His height matches that of a 6-year old, and his bone scan indicates a bone age of 5.5 years. The child has no significant dysmorphic features or systemic illness what could be the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Hypochondroplasia is a genetic condition involving a mutation in the FGFR3 gene, primarily affecting bone development, without significant metabolic disturbances.
Incorrect Options-
- Hypothyroidism- additional features like fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, and delayed milestones.
- Cushing Syndrome- short stature, central obesity, moon face, hypertension, purple striae.
- Addison's Disease- growth retardation not a feature.
Q.18. A 60-year-old male is complaining of decreased libido, difficulty ejaculating, and lab results show elevated FBS= 6.5 mmol, increased prolactin levels, but normal FSH and LH, normal testosterone levels. . What would be the next step in managing this case?
Correct Answer : D
As the question mentions a significant increase in prolactin levels it is suggestive of possible pituitary pathology. A CT of the head will help in evaluating the pituitary lesion.
Incorrect Options-
- DM, Normal FBG- does not explain the elevated prolactin levels or symptoms of decreased libido and difficulty ejaculating.
- Testosterone levels are mentioned to be normal in the question, so re-checking them won't provide additional diagnostic value.
Q.19. How would you treat a patient who presents with a single thyroid nodule that shows high iodine uptake?
Correct Answer : A
The preferred treatment is Radioiodine 131, as it targets and destroys the hyperfunctioning nodule selectively.
Q.20. A patient with thyrotoxicosis presents with all of the following symptoms, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
Thyrotoxicosis-
- excessive thyroid hormone→ increased metabolism→ increased gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis→hyperglycemia
- peripheral proximal myopathy and neuropathy occur due to prolonged metabolic disturbance.
Q.21. Which among the following thyroid hormone is considered the most biologically active form?
Correct Answer : B
T3 is the active form of thyroid hormone that directly influences metabolism and energy production in the body.
Q.22. A 45-year-old presented with polyuria, urine analysis showed glucose in their urine but no ketones, his FBS is 14mmol. What is the best course of management for this patient?
Correct Answer : D
In older patients, the first approach is by diet only, especially since he is not clearly into glucose toxicity. Tablet treatment for DM II is used in association with dietary treatment when diet alone fails, start with Metformin if no contraindications.
Q.23. Which among the following is an adverse effect of Metformin ?
Correct Answer : C
Metformin suppresses gluconeogenesis but is typically not associated with hyperglycemia or weight gain and cannot cause hypoglycemia on its own.
Q.24. A 30-year-old teacher complaints of excessive thirst and frequent urination, their physical examination is normal. You suspect DM and their FBS = 6.8 .what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Although the reading of FBS suggests impaired fasting glucose, this does not explain the symptoms (as patients with prediabetes are asymptomatic. So, DI is a reasonable answer.
In patients who present with symptoms of uncontrolled diabetes (eg, polyuria, polydipsia, nocturia, fatigue, weight loss) with a confirmatory random plasma glucose level of >200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/dl), diabetes can be diagnosed. In asymptomatic patients whose random serum glucose level suggests diabetes, fasting plasma glucose (FPG) concentration should be measured.
The oral glucose tolerance test no longer is recommended for the routine diagnosis of diabetes. An FPG level of >126 mg/dL (7mmol) on 2 separate occasions is diagnostic for diabetes.
An FPG level of 110-125 mg/dL (6.1 – 6.94 mmol) is considered impaired IFG. An FPG level of <110 mg/dL (6.1) is considered normal glucose tolerance, though blood glucose levels above >90 mg/dL (5mmol) may be associated with an increased risk for metabolic syndrome if other features are present.
Q.25. A 42-years-old female presented with 6 months history of malaise, nausea & vomiting, her lab results show- Na= 127 , K= 4.9, Urea= 15, creatinine= 135, HCO3= 13, glucose= 2.7 mmol/l. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Addison's disease- deficiency of cortisol and aldosterone.
- Features of hyponatremia and hyperkalemia due to aldosterone deficiency.
- Low bicarbonate and hypoglycemia due to cortisol deficiency.
- Elevated creatinine due to impaired renal function.
- malaise, nausea, and vomiting due to cortisol deficiency.
- fatigue and weakness due to electrolyte imbalance.
All of these features are characteristic of Addison's disease.
Q.26. Which of the following medication is used in the treatment of DKA?
Correct Answer : A
Short and intermediate-acting insulin is preferred to prevent hypoglycemia. Important measures in treating DKA include fluid and potassium replacement, along with identifying and treating any sources of infection.
Q.27. A 46-year-old man, a known case of diabetes for the last 5 months. He is maintained on Metformin 850 mg Po TID, diet controlled and used to walk daily for 30 minutes. On examination: unremarkable physical findings. Investigations show the following: FBS 7.4 mmol/L, 2hour PP -8.6 mmol/L, HbA1c 6.6% , Total Cholesterol 5.98 mmol/L, HDLC 0.92 mmol/L, LDLC 3.88 mmol/L, Triglycerides 2.84 mmol/L (0.34-2.27). Based on evidence, the following concerning his management is TRUE?
Correct Answer : C
In this case, since the patient's triglyceride level is elevated at 2.84 mmol/l, fibrates are the preferred medication. Fibrates are effective in reducing triglyceride levels and improving overall lipid profiles.
Q.28. A 76-year-old patient taking hypercalcemic drugs developed gout, which drug is most likely responsible for gout in this patient?
Correct Answer : B
Thiazide diuretics→reduced excretion of uric acid via kidneys→increased uric acid levels in blood→urate crystal formation→GOUT.
Q.29. Hyperprolactinemia is associated with all of the following EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : C
The diagnosis of hyperprolactinemia should be included in the differential for female patients presenting with oligomenorrhea, amenorrhea, galactorrhea, or infertility or for male patients presenting with sexual dysfunction. Once discovered, hyperprolactinemia has a broad differential that includes many normal physiologic conditions.
Pregnancy always should be excluded unless the patient is postmenopausal or has had a hysterectomy. In addition, hyperprolactinemia is a normal finding in the postpartum period. Other common conditions to exclude include a nonfasting sample, excessive exercise, a history of chest wall surgery or trauma, renal failure, and cirrhosis. Postictal patients also develop hyperprolactinemia within 1-2 hours after a seizure.
These conditions usually produce a prolactin level of less than 50 ng/mL. Hypothyroidism, an easily treated disorder, also may produce a similar prolactin level. Pregnancy, breastfeeding, mental stress, sleep, hypothyroidism, and Use of prescription drugs are the most common causes of hyperprolactinemia.
In men, the most common symptoms of hyperprolactinemia are decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, infertility, and Gynecomastia. If no obvious cause is identified or if a tumor is suspected, MRI should be performed.
Q.30. A patient came to the OPD, his BP is 160/100, he isn’t on any medication yet. Lab investigations show: Creatinine-(normal), Na- 145 (135-145), K- 3.2 (3.5-5.1), HCO3- 30 (22-30), what is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Patient with high Na+, low k+, and high bicarbonate → Primary hyperaldostronism
Q.31. Regarding the criteria for diagnosing diabetes mellitus, which of the following is not true?
Correct Answer : D
Q.32. A 30-year-old male presented with polyuria, negative ketone in urine, and a random blood sugar of 280 mg/dl. What is the management?
Correct Answer : C
The patient is symptomatic - RBS -11.1→DX is DM type 2→ RX initially with diet, exercise, and decrease Weight for 6-8 weeks → further add Metformin.
Q.33. What is the surgical treatment of choice in patient presenting with enlarged cervical lymph node which on H/E showed thyroid tissue?
Correct Answer : B
Total thyroidectomy will prevent the further spread of disease as the primary source of thyroid tissue in the lymph node is removed.
Radical neck dissection removes all the lymph nodes in the neck and eliminates any remaining cancerous cells simultaneously reducing the risk of recurrence.
Other options may not adequately address the spread of the disease.
Q.34. A 46-year-old female came to the OPD with symptoms of hypothyroidism, including excessive fatigue, myxedema, and cold intolerance, now she suffers from difficulty in breathing, wheezing, her TSH= normal, T4= normal, S. Ca = decrease, phosphorus- elevated, PTH- low, ALP= normal, what is your diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Secondary hypoparathyroidism is typically due to damage or dysfunction of the parathyroid gland which might be associated with another condition, often an autoimmune disease such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis [in this scenario explaining the hypothyroidism features]. Low calcium and low PTH levels suggest secondary hypoparathyroidism. Elevated phosphorous and normal renal function are supportive of this diagnosis.
Q.35. What is the first step in managing acute hypercalcemia ?
Correct Answer : A
Hypercalcemia→elevated calcium in blood→ increase urinary calcium excretion→dehydration
- correcting the fluid deficit helps restore normal blood volume and kidney function essential for calcium excretion. Other measures [use of furosemide, mithramycin] can be considered once the fluid deficit is corrected.
Q.36. What is the targe Hba1c level for a Type 1 diabetic?
Correct Answer : C
HbA1c level for a type 1 diabetic is 6.5%.
HbA1c is a blood test that measures blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months.
Q.37. A 19-year-old athlete has gained 45 pounds in last 4 months. On examination, he is muscular, BP 138/89, what is the most likely cause?
Correct Answer : C
Anabolic steroids are synthetic substances. They can dramatically increase muscle mass, and strength in a short period, leading to rapid weight gain. The elevated BP could be a side effect of steroid use.
Incorrect Options-
While cocaine, alcohol, and smoking can contribute to weight gain, they are less likely to cause a rapid and significant increase in muscle mass.
Q.38. An adult presented with history of palpitation, sweating and neck discomfort for the past 10 days, his lab reports are as follows- CBC normal , ESR 80 , TSH 0.01, FT4 high, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Subacute thyroiditis is characterized by inflammation of the thyroid gland, leading to the release of thyroid hormone which manifests as symptoms of hyperthyroidism like palpitation and sweating. Elevated ESR is indicative of inflammation. Low TSH and high T4 indicate hyperthyroidism.
Q.39. A female came to the clinic with her 6 month old baby, she complaint of tremor, palpitations, and heat intolerance. Which of the following is most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Postpartum thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorder that occurs within first year after childbirth. It is characterized by transient or permanent thyroid dysfunction.
Often presents as 3 phases-
- Initial thyrotoxic phase→ hypothyroidism→ returns to euthyroidism. [However, all patients might not experience all 3 phases.]
Incorrect Options-
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis - typically presents as hypothyroidism.
- Hyperthyroidism- while the symptoms mentioned above are suggestive of hyperthyroidism, postpartum thyroiditis is a better option given the context of childbirth in the scenario.
- Subacute thyroiditis- painful thyroid gland with a recent history of viral infection.
Q.40. A chronic diabetic patient on insulin and metformin treatment has renal impairment. What’s your next step in management of this patient?
Correct Answer : A
Metformin- This medication tends to accumulate in the body of patients with renal impairment which increases the risk of lactic acidosis. Therefore stopping metformin is a crucial step in managing patients with renal impairment.
ACE inhibitors- These medications help lower BP and protect the kidney from proceeding to further damage.
Incorrect Options-
other options are not sufficient for the management and can increase the risk of damage to the kidneys and leave the patient at risk of lactic acidosis.
Q.41. What is the single best test to confirm Cushing's syndrome?
Correct Answer : C
Dexamethasone suppression test - This test measures the body's response to dexamethasone which is a synthetic glucocorticoid. In Cushing's syndrome, the adrenal glands produce excessive cortisol, this test helps determine the ability of dexamethasone to suppress cortisol production, a failure to suppress cortisol is indicative of Cushing's syndrome.
Incorrect Options-
- Plasma cortisol- less specific, elevates in other conditions as well.
- ACTH- although stimulates cortisol production, not the most reliable test for Cushing's.
- Prolactin- plays a role in lactation, not related to Cushing's.
Q.42. Which of the following is more common with type 2 DM than type 1 DM?
Correct Answer : C
Type 2 diabetes has a stronger association with genetic component as compared to type 1 diabetes.
Incorrect Options-
- Weight loss- More commonly associated with type 1 diabetes due to insulin deficiency and the body's inability to utilize glucose for energy production.
- Gradual onset- Type 2 diabetes has a gradual onset whereas type 1 diabetes has a rapid onset.
- HLA DR3+-DR4- Associated with increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
Q.43. A patient presents with tremors, fever, palpitations, and has diagnosed as case of hyperthyroidism, what is your initial treatment?
Correct Answer : C
Beta-blockers provide rapid relief of symptoms and are safe and effective initial treatment for hyperthyroidism.
Incorrect Options-
- Surgery- not an initial treatment
- Radioiodine therapy- is not the best option for immediate and initial management.
- Propylthiouracil- it is a useful treatment but takes several weeks to yield effect, and it has potential side effects.
Q.44. A 23 year old patient presents with truncal obesity, easy bruising, hypertension, and a buffalo hump. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Cushing's syndrome- This condition is characterized by excessive production of cortisol regardless of source, leading to its characteristic symptoms which include truncal obesity, easy bruising, hypertension, and a buffalo hump.
Incorrect Options-
- Cushing's disease- excess cortisol production caused by a pituitary tumor.
- Addison's syndrome- This condition results in adrenal insufficiency, leading to low cortisol levels.
- Adrenal adenomas- These are benign tumors of the adrenal gland that can cause excess cortisol production leading to Cushing's syndrome, however, it is not the only cause of Cushing's syndrome.
Q.45. Which of the following is the treatment of choice for type 1 diabetes?
Correct Answer : D
Basal and bolus insulin therapy is a treatment approach that mimics the body's natural insulin production. Basal insulin provides a continuous level background insulin that covers the body's basal insulin needs, while bolus insulin is administered before meals to cover the extra insulin that is required to metabolize the carbohydrates in the meal, this approach provides the best insulin replacement therapy for patients with type 1 diabetes, helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Q.46. A well-known case of DM was presented to the ER with drowsiness, investigations showed: Blood sugar = 400 mg/dl, and a pH of = 7.05, what is your management?
Correct Answer : D
This is the most appropriate initial management in this scenario. The patient is presenting with severe hyperglycemia, and the pH indicates diabetic ketoacidosis. DKA can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. Normal saline helps to correct dehydration and electrolyte imbalance, which are the most crucial steps in managing DKA patients.
Q.47. A pregnant patient comes to the clinic with neck swelling and a multiple nodular, non-tender goiter, What is the next evaluation to be performed?
Correct Answer : D
The initial step is to assess thyroid function with TSH and T4 levels. If these are normal it is likely a benign goiter, and close monitoring or follow-up may be sufficient
Q.48. A 45-year-old patient presents with a neck swelling, a nodular goiter, a history of muscle weakness, cold intolerance , and hoarseness. What is your management plan?
Correct Answer : C
Thyroid lobectomy involves the removal of one lobe of the thyroid gland. It is a suitable option in this scenario as it will help remove the affected tissue and potentially improve the symptoms of thyroid dysfunction.
Q.49. A pregnant woman is experiencing symptoms of hyperthyroidism. Her TSH level is low, what is the next step in her care?
Correct Answer : A
Propylthiouracil [PTU] is considered the first-line treatment for hyperthyroidism during pregnancy.PTU is preferred over other antithyroid medications due to its lower risk of fetal complications.
Incorrect Options-
- Radioactive iodine - it is contraindicated during pregnancy unless necessary.
- Partial thyroidectomy- surgery is generally avoided during pregnancy.
- Complete thyroidectomy- contraindicated during pregnancy.
Q.50. A diabetic patient on medication was found unconscious with a blood sugar of 60, what is the most likely drug to cause this?
Correct Answer : A
Sulfonylureas→stimulate pancreas→release insulin→ can lead to severe hypoglycemia [when taken with other medications or when meals are skipped or delayed].
Q.51. A 40-years-old male presented with long hands and hepatomegaly, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Acromegaly- This is a condition characterized by excess production of growth hormone, leading to enlargement of bones and tissues.
Incorrect Options-
- Gigantism- it is also caused due to excess growth hormone but it occurs before the closure of the growth plate leading to its manifestation as excessive height. In acromegaly growth plates are closed so there is no significant increase in height.
- Hirsutism - excessive hair growth.
- Dwarfism - short stature.
Q.52. A 65-year-old diabetic patient is still experiencing hyperglycemia despite increasing their insulin dose, what is the problem with insulin in obese patients?
Correct Answer : D
A decrease in post-receptor action - refers to insulin resistance, which leads the body's cells to become less responsive to insulin. This is a common problem in obese patients with type 2 diabetes.
Q.53. A 32-year-old unmarried female has normal test results except FBS=142mg/dl. RBS=196mg/dl, what is the treatment?
Correct Answer : D
Weight control and lifestyle modification are the first line of treatment for prediabetes and early stage early-stage type 2 diabetes. Maintaining a healthy BMI can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of further progression.
Q.54. A 15-year-old diabetic patient comes to the clinic with abdominal pain, vomiting and sweet smell in their breath. What is the most likely cause of these symptoms?
Correct Answer : A
In a diabetic patient with abdominal pain, vomiting, and a sweet smell on their breath are the characteristic features of DKA. The combination of symptoms and the patient's diabetic status given in the scenario strongly suggests insulin mismanagement as the most likely cause.
Q.55. A 70-year-old diabetic Saudi male suddenly fell down, this could be due to?
Correct Answer : B
The diagnosis is Non-ketotic hyperosmolar coma which can present with Hyper viscosity and increased risk of thrombosis and disturbed mental status. Neurological signs include focal signs such as sensory or motor impairments, focal seizures, or motor abnormalities including flaccidity, depressed reflexes, tremors, or fasciculations. Ultimately, if untreated, it will lead to death.
Q.56. A patient presents with constipation and is suspected of hypothyroidism. How would you confirm the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Normal process - Hypothalamus -→ TRH-→ Pituitary gland-→TSH-→thyroid gland-→production of high levels of T3 and T4-→ negative feedback -→ normal hormone levels.
Hypothyroidism- Hypothalamus- TRH - Pituitary gland- TSH-→thyroid gland→ Reduced production of T3, T4-→ no negative feedback mechanism→ excess TSH production to compensate for T3 and T4.
Low T3,T4 and High TSH⇒ Hypothyroidism
Therefore TSH is the most reliable test to confirm hypothyroidism.
Q.57. Which of the following medications should be avoided in diabetic nephropathy?
Correct Answer : D
Thiazides cause - hypovolemia, electrolyte imbalance [hypokalemia], and hyperuricemia⇒ impairing kidney function and exacerbating the damage.
Q.58. Which of the following indicates a benign thyroid lesion?
Correct Answer : B
Toxic nodules are benign in greater than 90% of cases with no underlying cancer.
Q.59. A patient with DM comes to you for checkup. Their blood sugar is well controlled, but their BP is 138/86, all other physical examinations including neurological examination shows no abnormality, he is on follow-up in ophthalmology clinic. What you will put in your plan to manage this patient?
Correct Answer : A
In patients with diabetes, the target blood pressure is lower than that in the general population. The goal is to achieve a BP of 130/90mmHg or lower. ACE inhibitors are the first line of treatment for hypertension in patients with diabetes as they do not compromise kidney function unlike the other drugs given in option. Moreover, they provide renal protection[ slowing down the progression of diabetic nephropathy, reducing albuminuria], cardiovascular protection-[decrease of heart failure and MI by reducing afterload], and cause a reduction in mortality.
Q.60. A female patient has hypothyroidism, her TSH level is high, pulse= normal, BP= normal, and she is currently taking thyroxine, what would you do next?
Correct Answer : B
In this scenario, the patient's TSH level is high indicating insufficient thyroid hormone replacement, for this the appropriate course of action is to increase the thyroxine dose and re-evaluate after 3 months.
Q.61. All of the following can cause hyperprolactinemia, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
Allopurinol is a medication used to treat gout. The mechanism of action by which the drug functions has no evidence of contribution to increasing prolactin levels.
Q.62. Which of the following is specific for DM1?
Correct Answer : A
HLA DR4 is a specific human leukocyte antigen associated with an increased risk of developing type 1 Diabetes Mellitus [DM1].
Incorrect Options-
- HLA B27- Ankylosing spondylitis.
- HLA DQ- Can be associated with Type1 DM[but HLA DR4 is more strongly linked].
Q.63. What is the difference between primary and secondary hyperaldosteronism?
Correct Answer : A
Primary: increased aldosterone due to a local cause in adrenals e.g. adrenal hyperplasia.
Secondary: increased activity of RAAS system. It is mainly due to high levels of renin e.g. Juxtaglomerular tumor.
Q.64. A 50-year-old with uncontrolled diabetes complains of black to brown nasal discharge. What the diagnoses?
Correct Answer : A
Diabetic patient -→uncontrolled blood sugar-→weakened immune system-→susceptible to infection.
Black or brown nasal discharge is a common symptom of mycosis.
Q.65. Which hormone affects bile acid & lowers cholesterol?
Correct Answer : A
Cholecystokinin[CCK] is a hormone that stimulates the gallbladder to contract and release bile into the small intestine, bile then aids in the digestion and absorption of fat, and it also contributes to the elimination of excess cholesterol from the body.
Incorrect Option-
- Statins- Medication to lower cholesterol, but does not directly affect bile acid levels.
- Bile- Substance produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder, not a hormone
- Vitamin D- no direct effect on bile acid and cholesterol levels
Q.66. In which scenario are thyroid nodules most likely benign?
Correct Answer : A
Multiple thyroid nodules are more likely to be benign compared to a single nodule, which has a higher risk of malignancy. However, all nodules should be evaluated to rule out malignancy.
Q.67. Thyroid carcinoma that has metastasized to cervical lymph nodes and biopsy shows well-differentiated thyroid tissues, what is the management?
Correct Answer : B
As the thyroid carcinoma is well differentiated with cervical lymph node metastasis, the standard treatment is a total thyroidectomy to remove the entire thyroid tissue and a modified neck dissection to improve the involved lymph nodes.
Q.68. What is the mechanism of Cushing's disease?
Correct Answer : A
Pituitary adenoma→increased ACTH→increased cortisol→no negative feedback mechanism →continued secretion of ACTH→Cushing's features.
Q.69. All of the following are signs of malignant thyroid, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : C
Multiple thyroid nodules are not always malignant. Other factors such as rapid growth, hard consistency, fixity difficulty in swallowing, and hoarseness are indicative of an underlying malignancy.
Incorrect Options-
- Irradiation to head and neck- A risk factor for thyroid cancer.
- Fixity to tissues- Suggestive of local invasion, which is indicative of malignancy.
- Dysphagia- This can occur if there is compression over the esophagus or recurrent laryngeal nerve by a thyroid tumor.
Q.70. A pregnant woman presents to the clinic with complaints of tachycardia, irritability and multinodular goiter. Her TSH is less than 0.1 mmol. What is the treatment of choice?
Correct Answer : B
During pregnancy with hyperthyroidism, the treatment of choice is antithyroid drugs like propylthiouracil [PTU], or methimazole.
All other options mentioned above are generally avoided during pregnancy due to potential risks to the fetus.
Q.71. A man was recently diagnosed with DM I. When would you recommend an eye check-up?
Correct Answer : B
Diabetic retinopathy is one the most important complications of diabetes that can lead to impairment of vision, and vision loss. It typically develops slowly. For a newly diagnosed individual, an initial eye exam after 5 years is generally sufficient followed by an annual exam thereafter, to monitor for any changes.
Q.72. What is the treatment for chronic gout?
Correct Answer : A
Allopurinol is a medication commonly used to treat chronic gout.
Allopurinol→inhibits xanthine oxidase→ decreases uric acid production→decreased urate crystal formation→prevents gout.
Q.73. A 32-year-old patient was recently diagnosed with DM type II, he exercised for 8 weeks and his BMI changed from 32 to 31, what is the next step in his management?
Correct Answer : A
Exercise is a crucial component in the management of diabetes. It helps in controlling weight improving insulin sensitivity and has a positive impact on overall health and well-being. Since the patient has already shown positive results, continuing this regimen would be the best course of action in the management of this patient
Q.74. A female patient has wide-open eyes and tremors in her hands that do not diminish with intention. What investigation would you do?
Correct Answer : B
The patient's symptoms are suggestive of hyperthyroidism. Measuring T4 levels is a direct way to assess thyroid function and confirm the diagnosis
Q.75. A 50-year-old accountant, with sedentary lifestyle, a BMI 30, takes irregular meals, has early signs of atherosclerotic changes. What advice will you give them?
Correct Answer : D
As per the given scenario, the individual is living a sedentary life and has a high BMI. As the early signs of atherosclerosis have been identified, the most effective and immediate intervention is to start a regular exercise regimen. Exercise helps improve cardiovascular health, lower cholesterol levels, and control weight.
Q.76. A 43-year-old patient has elevated TSH, T3 and T4 levels, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
In secondary hyperthyroidism, the thyroid gland is overstimulated by the excessive TSH that is produced by the pituitary gland. This leads to elevated levels of both TSH and the thyroid hormones [T3, T4].
Q.77. What is the diagnosis based on the picture provided below?

Correct Answer : A
Autoimmune inflammation [stimulates fibroblast] and tissue swelling [accumulation of GAGs secreted by fibroblasts] in the orbit cause exophthalmos in Graves disease.
Q.78. A patient with DM and obesity plans to lose weight, what step can be taken to achieve this goal?
Correct Answer : C
This is the most suitable approach for a patient with DM and obesity.
Q.79. A patients lab results are as follows- Na-112mmol/l, S. osmolality- low, urine osmolality-500mOsm/kg, urine Na-45mmol/l. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
SIADH causes the body to retain water due to excess ADH, leading to hyponatremia, low serum osmolality, and concentrated urine [high urine osmolality].
Incorrect Options-
- Conn's syndrome- causes hypokalemia not hyponatremia.
- Cushing's syndrome -Leads to hypernatremia.
- Diabetes insipidus- Causes excessive urine output, thirst, with dilute urine[low urine osmolality].
Q.80. HbA1C values are used for which of the following?
Correct Answer : C
HbA1c measures average blood glucose over the past 2-3 months. It helps doctors assess how well diabetes is being managed and decide if any treatment changes are needed for better and long-term control.
Q.81. A patient presents with typical symptoms of hyperthyroidism. What’s the most effective and rapid way to relieve their symptoms?
Correct Answer : A
Propanolol rapidly relieves symptoms of hyperthyroidism like palpitations, tremors, and tachycardia by blocking beta-adrenergic receptors. It does not treat the cause but provides immediate relief.
Q.82. A healthy patient with a family history of DM type 2. What are the most important factors that increase their chance of developing DM?
Correct Answer : A
Both hypertension and obesity are major risk factors for type 2 diabetes. Obesity increases insulin resistance, while hypertension is associated with metabolic changes that worsen blood sugar control. Together, they significantly raise the chances of developing diabetes.
Q.83. Which of the following is the most related factor in diabetic retinopathy?
Correct Answer : A
The risk factors that increase diabetic retinopathy background are: HTN, Poor glucose control or long-case DM, raised level of fat ( cholesterol), renal disease, pregnancy (but not diabetes caused by pregnancy)
Q.84. What is the mechanism of action of Gliclazide?
Correct Answer : A
Lower blood glucose acutely by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas, an effect dependent upon functioning beta cells in the pancreatic islets.
Q.85. What is the treatment of choice for a patient with type 2 diabetes who is experiencing central nervous symptoms?
Correct Answer : B
The drug class of Biguanides is the first-line treatment of choice for type 2 diabetes. Other options are slower or inappropriate in addressing the underlying cause of type 2 diabetes with CNS symptoms effectively.
Q.86. A patient has DM and renal impairment. At what point will he start to experience symptoms of diabetic nephropathy?
Correct Answer : A
Symptoms of diabetic nephropathy often begin to appear approximately 5 years after the onset of diabetes, when microalbuminuria [30-300mg/day]develops this marks early-stage kidney damage.
Incorrect options-
10 years, 20 years,25 years
- Microalbuminuria- Albumin excretion of [30-300mg/day] can appear in 5-10 years after diabetes onset.
- Macroalbuminuria [overt nephropathy]- Albumin excretion .300mg/day can appear after 10-20 years of diabetes.
Q.87. All of the following favor DKA over AKA except?
Correct Answer : D
| DKA | AKA |
|---|---|
| high blood sugar | normal or low blood sugar |
|
low bicarbonate high potassium high anion gap metabolic acidosis |
low bicarbonate normal or low potassium low anion gap metabolic acidosis |
Q.88. A 43-year-old patient with h/o hypothyroidism is taking Thyroxine, TSH is high, what should you do?
Correct Answer : D
If the patient's TSH is high while on thyroxine therapy, it is indicative of under- replacement of thyroid hormone. The appropriate action is to increase the dose of thyroxine and recheck the levels after 6-8 weeks.
Q.89. What is Somogyi effect and dawn phenomenon?
Correct Answer : A
Somogyi and down phenomenon:
The dawn phenomenon: Early morning hyperglycemia due to increased secretion of GH. Increasing the dose of the night insulin treats it.
Treatment:
1) Increase evening physical activity
2) Increase the amount of protein to carbohydrates in the last meal of the day
3) Eat breakfast even though the dawn phenomenon is presented
4) Individual diet modification only if HbA1c is lower than 7%
5) Antidiabetic oral agent therapy only if HbA1c is lower than 7%
6) Use an insulin pump
7) Long-acting insulin analogs like glargine instead of NPH insulin.
The Somogyi effect: rebound hyperglycemia from late night or early morning hypoglycemia. Decreasing the dose of the night insulin treats it
Treatment: 1) Modify insulin dosage, Use an insulin pump
2) Long-acting insulin analogs like glargine instead of NPH insulin
3) More protein than carbohydrates in the last meal of the day
4) Go to bed with a higher level of plasma glucose than usual Brittle diabetes: A diabetic child with wide fluctuation in the glucose level & repeated attacks of DKA.
Honeymoon period: After the diagnosis of DM, marked reduction in insulin dose. It is due to an increase in the endogenous secretion of insulin by recently reactivated B-cells of the pancreas.
Q.90. All of the following are true regarding hypokalemia EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
Constipation is not a common symptom associated with hypokalemia.
Q.91. A patient with hypothyroidism on thyroxine has increase PTH, decreased calcium, normal Vit D, very high creatinine, presented with facial spasms when angle of jaw is tapped (Chvostek's sign), what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
The patient has chronic kidney failure-
- High creatinine, hypocalcemia, and secondary hyperparathyroidism.
- kidney damage reduces the activation of vitamin D -leading to low calcium.
- The tapping sign further confirms hypocalcemia.
- Normal vitamin D indicates the issue is with kidney function, not a deficiency.
Q.92. In a diabetic patient, what is the target glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c] level? (the standard is 5.5 -6.0%)?
Correct Answer : D
An HbA1c level between 6-7% is a good target for most people with diabetes, as it indicates good blood sugar control.This range helps balance effective management while reducing the risk of complications.
Q.93. Type 1 Diabetes is best maintained by which of the following?
Correct Answer : B
Short-acting insulin is the most appropriate choice for managing type 1 diabetes because it acts quickly and can be used to cover the insulin needs associated with meals.
Q.94. A 57-year-old patient came complaining of recent palpitations. His TFT showed high T4 , T3 and low TSH. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
The patient's symptoms of palpitations, along with high T4, T3, and low TSH levels, point towards an overactive thyroid. This condition is known as thyrotoxicosis.
Q.95. An obese patient was recently diagnosed with DM II. He is following a diabetic diet regimen and exercising regularly. When he came for his next visit his blood sugar was high and he had gained 5 kgs. He also complaint of thirst and hunger, what would be the treatment of choice?
Correct Answer : B
Metformin is the drug of choice for type 2 diabetes.
Q.96. A patient with DM II wears glasses, When should be the next follow up?
Correct Answer : B
- For a well-controlled type 2 diabetic patient with no complications, an annual follow-up is usually enough to monitor their health.
- more frequent visits, like every 6 or 7 months, are typically needed for poorly controlled cases or those with complications.
- A 5-year gap is too long for monitoring diabetes.
Q.97. A hypertensive patient comes with fatigue and weakness. He also mentions drinking a lot of water and c/o frequent urination. His bp is 180/100, renin and serum potassium was low, mild decrease in sodium level, what is the most likely cause for his symptoms?
Correct Answer : A
Conn's syndrome, or primary hyperaldosteronism is a condition that occurs when the adrenal glands produce too much aldosterone leading to several symptoms-
- Fatigue and weakness - Due to low K+.
- Frequent urination and thirst- Aldosterone causes Na+ and water retention.
- High BP- Aldosterone increases sodium retention raising blood volume and BP.
- Low renin and potassium- Aldosterone shuts down renin production, and potassium levels drop due to increased excretion.