
Hello,
Dr. Batman
Hello Doctor, Welcome!
Profile

Name: Batman
Email: batman@gotham.com
GASTROENTEROLOGY REVIEW
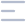
(Total Questions - 145)Q.1. A woman is complaining of burning retrosternal pain with normal ECG, what is the treatment?
Correct Answer : A
PPI because burning retrosternal pain is a classic sign of GERD, caused by stomach acid irritating the esophagus. PPIs reduce stomach acid, providing quick relief and allowing the esophagus to heal.
Incorrect options-
- H2 blockers reduce acid but are not as strong as PPIs.
- Antiemetics are used to treat vomiting.
- NSAIDs can irritate the stomach and worsen GERD.
Q.2. A 15-year-old male with a 3 day h/o yellow sclera, anorexia, and abdominal pain presents to you. His LFT: T. bilirubin = 253, Indirect = 98, ALT = 878, AST = 1005. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Infective hepatitis (Hep A) is of an acute onset with patient's yellow sclera, abdominal pain, anorexia, and markedly elevated liver enzymes to more than 10 folds- are classic signs of hepatitis.
Incorrect options-
- Gilbert disease- bilirubin is increased with normal liver enzymes.
- Obstructive jaundice- the indirect bilirubin would be normal and the direct would increase.
- Acute pancreatitis- serum amylase and lipase are the main diagnostic test.
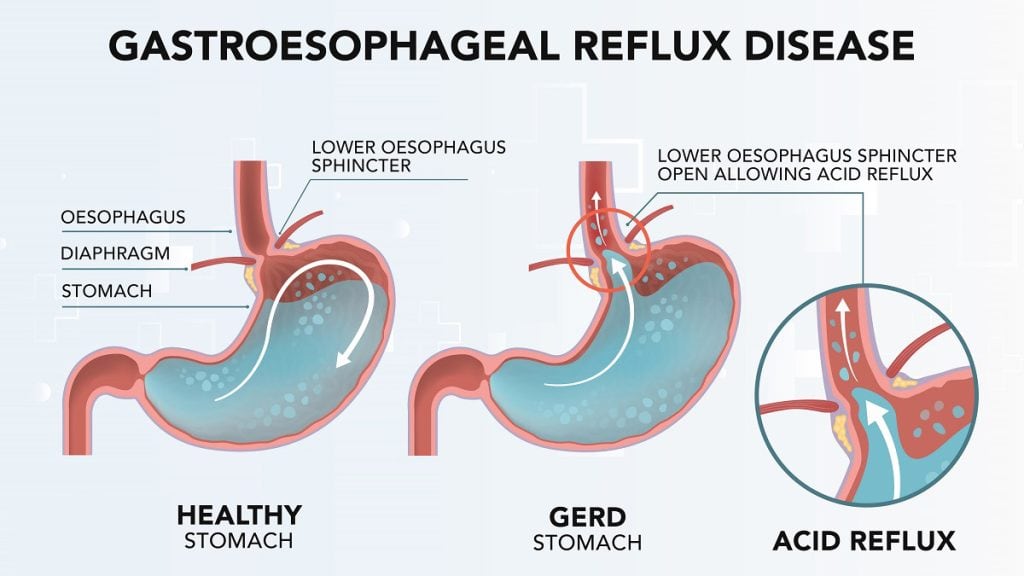
Q.3. A middle-age woman presented with upper abdominal pain, which increases on taking breaths. On examination her temperature is 39*C, and has right hypochondrial tenderness. Her investigations: Bilirubin & ALT - normal, WBC 12.9. What is the next step in investigation?
Correct Answer : B
Murphy's sign is present in the patient which is suggestive of Acute cholecystitis. By signs and symptoms most commonly this is acute cholecystitis and sonography is a sensitive and specific modality for diagnosis.
Q.4. Gastric lavage can be performed to wash all of the following, except?

Correct Answer : A
Drain cleaner is a sulphuric acid and its ingestion causes GI perforation and ARDS so no use of gastric lavage.
Incorrect options-
- Vitamin D, Diazepam, Aspirin can be safely removed with lavage if needed.
Q.5. Which of the following method is rapid and best for complete gastric evacuation?
Correct Answer : D
Activated charcoal as it binds toxins in the stomach, preventing absorption, and works quickly and effectively.
Incorrect options-
- Gastric lavage is less effective and has risks of aspiration.
- Induced vomiting is not recommended and safe.
- Syrup is irrelevant for toxins.
Q.6. A patient presents with vomiting, diarrhea and has moderate dehydration. How will you treat him?
Correct Answer : A
ORS only because it replaces lost fluids and electrolytes, rehydrating the body effectively during diarrhea and vomiting.
Incorrect options-
- Medications such as loperamide, anticholinergic, and adsorbents are not recommended for dehydration because of questionable efficacy and potential adverse effects.
Q.7. A drug addict swallowed open safety pins 5 hours back, he later presented to the ER, his X ray showed foreign body in the intestine. Which of the following is the best management?
Correct Answer : C
Admit and do serial abdominal X-rays and examination because swallowed safety pins can cause serious damage. Monitoring ensures early detection of complications like perforation.
Incorrect option-
- Immediate surgery is only needed if complication arises.
- Discharge with follow-up is too risky.
- Catharsis can worsen damage by speeding pin movement.
There is a chance that safety pins pass without any significant damage to the GI tract but caution must be taken and the patient is under observation by serial X-rays. If a patient develops signs of perforation immediate surgery is crucial.
Q.8. A patient with hepatosplenomegaly, skin bruises and cervical mass presents at your clinic, what is the initial investigation?
Correct Answer : A
The presenting symptoms are likely to occur in leukemic patients, bone marrow biopsy is one of the initial and gold standard investigation to diagnose these conditions by analyzing blood cell production and detecting abnormal cells.
Incorrect options-
- CT abdomen can show organ enlargement but doesn't confirm blood cancer.
- Spleen or liver biopsy is less infomative for blood disorders.
Q.9. Which of the following is an indication of surgery in Crohn’s disease?
Correct Answer : A
Most patients with Crohn's disease ultimately require one or more operations in their lifetime.
Operative indications are the same no matter where the disease manifests itself and include:
- Failure of medical therapy
- Obstruction, fistula, abscess, or hemorrhage
- Growth Retardation (in the pediatric population)
- Perforation ,
- Carcinoma
- Extraintestinal manifestations.
Q.10. A 40-year-old patient who is known to have Crohn's disease, came with fever, hip and back pain, occult blood test is positive & brown stool. On Examination, soft abdomen, normal bowel sounds, normal range of motion of hip. What is the best radiological investigation?
Correct Answer : B
The correct answer is abdominal CT because the symptoms- fever, hip and back pain, occult blood in stool, and brown stool is suggestive of Crohn's complication like an abscess or fistula. A CT can provide detailed image to detect these issues.
Incorrect option-
- Abdominal US is less sensitive for abscesses or fistulas.
- Hip CT only shows hip not abdomen.
- IV venogram focuses on veins and is irrelevant.
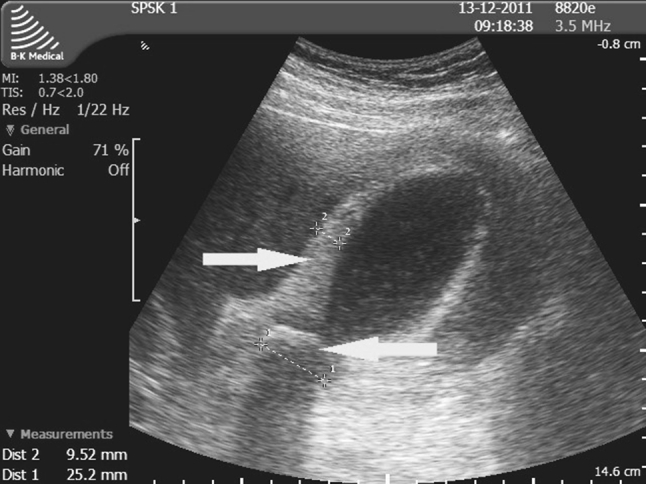
Q.11. Initial investigation in small bowel obstruction is?
Correct Answer : A
Erect abdominal X-ray because it shows air-fluid levels, a key sign of small bowel obstruction. It's quick, simple, and effective for initial diagnosis.
Incorrect options-
- CT scan is more detailed but not the first line test.
- MRI is too complex and costly.
- Colonoscopy is irrelevant for diagnosing small bowel obstruction.
Q.12. In which group you will do lower endoscopy for patients with iron deficiency anemia with no benign cause?
Correct Answer : C
Older men and postmenopausal women with iron deficiency anemia are routinely evaluated to exclude a gastrointestinal source of suspected internal bleeding.
Q.13. What is the contraindicated mechanism in a child who has swallowed bleach cleaner solution?
Correct Answer : A
Bleach cleaner is a strong alkali that causes GI perforation, aspiration pneumonia, and ARDS.
The best measure is to drink milk to normalize PH.
Q.14. Elderly women presents with diarrhea, high fever & chills, other physical examination is normal, no h/o back pain. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Viral infections have these systemic manifestations when affecting the GI tract, causing fever and chills.
Incorrect options-
- Pyelonephritis is excluded as there is no history of severe back pain.
- Bacterial gastroenteritis can cause similar features, but the fever and chills are typically less severe than in viral.
- IBS doesn't cause high fever or chills. It's more about chronic abdominal pain and bowel changes.
Q.15. A patient presented to the ER with diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, salivation, lacrimation and abdominal cramps. What do you suspect?
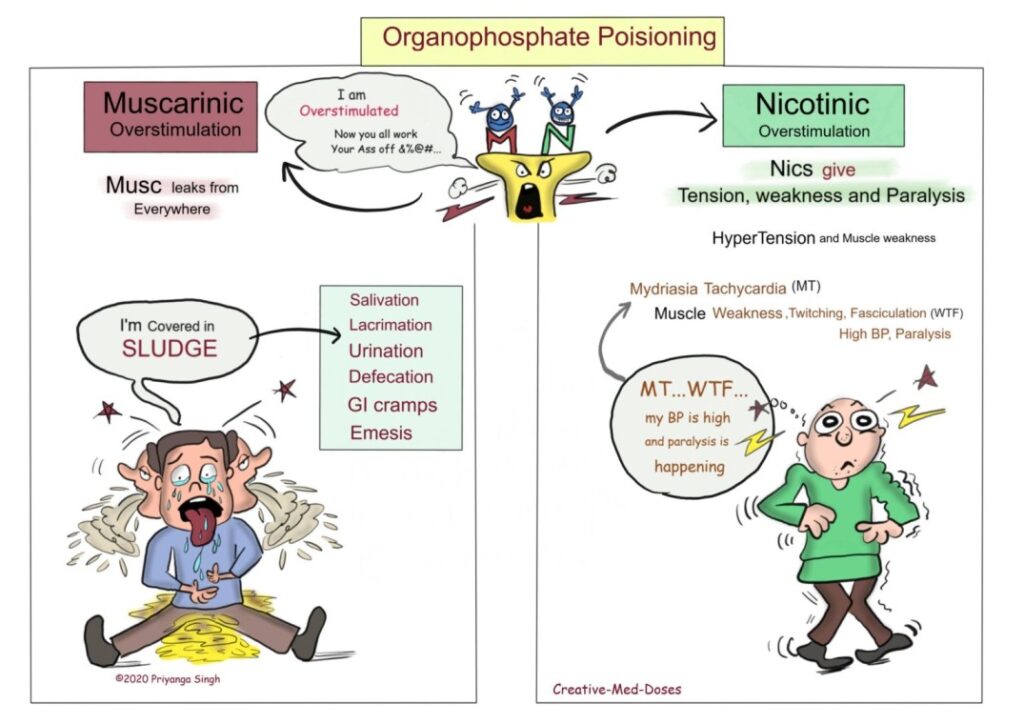
Correct Answer : A
OPC causes inhibition of acetylcholinesterase leading to the accumulation of acetylcholine in the body which cause -Salivation, lacrimation, urination, defecation, gastrointestinal motility, emesis, and miosis.
Q.16. What's the treatment for pseudomembranous colitis?
Correct Answer : B
Vancomycin is the first-line treatment for mild to moderate pseudomembranous colitis caused by Clostridium difficile.
Incorrect options-
- Metronidazole is no more the first line agent.
- Amoxicillin can worsen the condition by disrupting the gut flora.
- Clindamycin is associated with causing pseudomemranous colitis and should be avoided in treatment.
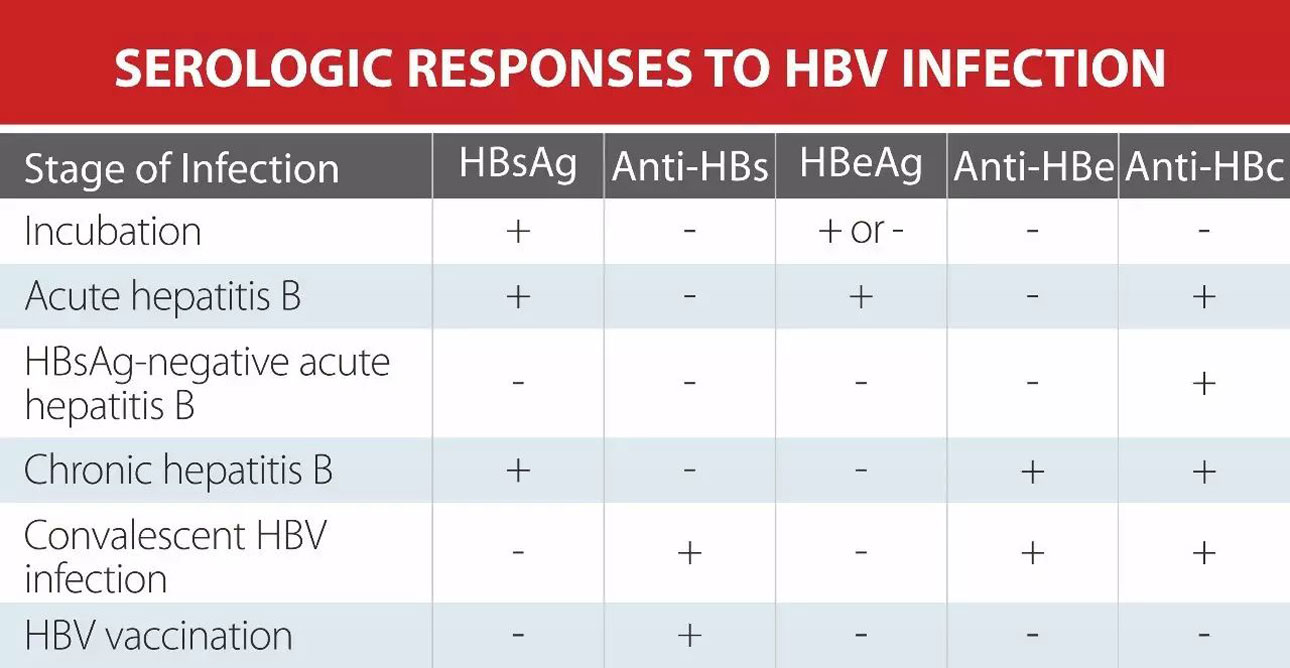
Q.17. A patient has HBsAB +ve, but the rest of the hepatitis profile was negative. What is the diagnosis?
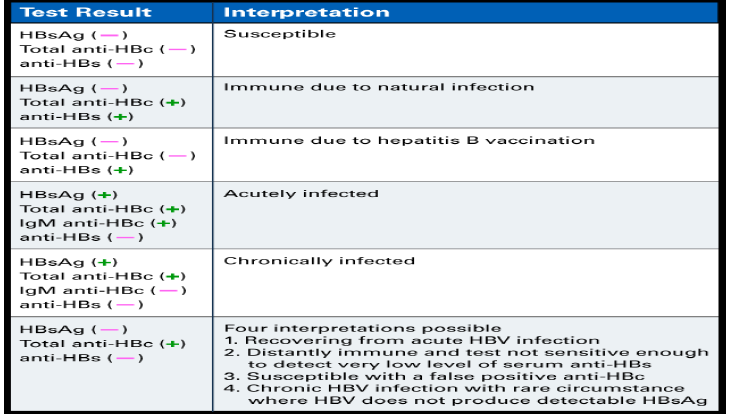
Correct Answer : A
Remember the chart below.
Q.18. A 24-year-old man presented with 4 month history of diarrhea with streaks of blood & mucous. Ulcerative colitis was confirmed by colonoscopy. The initial therapy for this patient is?
Correct Answer : D
Sulfasalazine is the first-line treatment for mild to moderate ulcerative colitis, it is thought to be an anti-inflammatory drug that is essentially providing topical relief inside the intestine.
Q.19. Which of the following organisms can cause invasion of the intestinal mucosa, regional lymph node and bacteremia?
Correct Answer : A
Salmonella can invade the intestinal lining, spread to lymph nodes, and enter the bloodstream, causing bacteremia.
Incorrect options-
- Shigella, Vibrio & E. coli do not invade beyond the lamina propria into the mesenteric lymph nodes or reach the bloodstream .
Q.20. A patient presented with severe epigastric pain radiating to the back. He has past history of repeated epigastric pain. Social history: drinks alcohol. What’s the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Severe back pain with a history of chronic peptic ulcer is indicative of perforation also the patient hgas history of drinking alcohol which increases the risk. Perforation occurs when the ulcer erodes through the stomach or duodenal wall, causing sudden, intense pain.
Q.21. A female patient has clubbing, jaundice and pruritus. Lab results showed elevated liver enzymes (Alkaline phosphatase), high bilirubin, hyperlipidemia and positive antimitochondrial antibodies. What’s the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
PBC is an autoimmune disease that destroys bile canaliculi within the liver and leads to cholestasis and elevated liver enzymes. 9:1 (female to male). She is diagnosed by the Presence of AMA and ANA.
Incorrect options-
- PSC is more common in men and presents differently with less pruritis and AMA negativity.
- Autoimmune hepatitis doesn't show high ALP and AMA positivity.
- Cholecystitis causes abdominal pain, not systemic signs like clubbing or pruritis.
Q.22. A patient recently came from Pakistan after a business trip complaining of frequent bloody stool. What's the likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Travel to Pakistan [an endemic area] and frequent bloody stools are classic signs of amebic dysentry, caused by Entamoeba histolytica.
Q.23. What's true about erosive gastritis?
Correct Answer : B
Erosive gastritis involves rapid damage to the stomach lining, often occuring within 24 hours of the triggering injury, reflecting its acute nature.
Q.24. In a patient with acute abdomen, you will find which of the following?
Correct Answer : A
In acute abdomen, severe pain and peritonintis makes deep breathing painful, leading to rapid, shallow breaths to avoid moving diaphragm and abdominal muscles.
Q.25. About hepatitis B vaccination schedule for adult, which of the following is true?
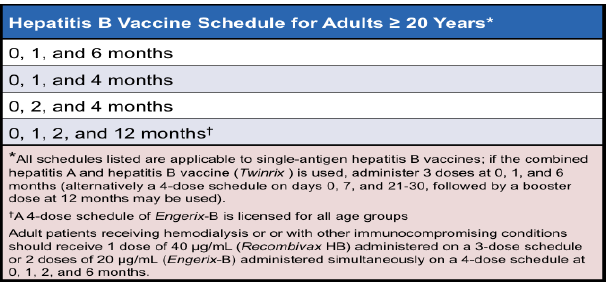
Correct Answer : A
Read the chart below.
Q.26. A patient took high dose of acetaminophen now presented with nausea & vomiting, investigation shows increase alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin, which organ is affected?
Correct Answer : C
Acetaminophen overdose primarily causes liver damage, reflected by elevated liver enzymes ALP and bilirubin.
Incorrect options-
- Brain- neurological effects can occur but liver is the primary concern.
- Pancreas- damage here raises amylase and lipase.
- Spleen- doesn't process bilirubin or produce ALP.
Q.27. An old patient presents with cramping abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and constipation but no tenderness, the most likely diagnosis is?
Correct Answer : C
Cramping abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and constipation without tenderness strongly indicate partial bowel obstruction.
Incorrect options-
- Diverticulitis usually presents as diarrhea, fever, pain, and tenderness.
- Colon cancer presents with bowel habit changes, blood in stool,or weight loss.
- Fistula formation often causes drainage, fever or other systemic symptoms.
Q.28. An old male patient came with fever, abdominal pain, diarrhea, loss of weight, and positive occult blood test. His lab show that infection with streptococcus bovis. What will you do next?
Correct Answer : D
Because there is a strong association between infections with S. bovis and colonic neoplasms and other lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, evaluation of the gastrointestinal tract with colonoscopy is important for patients with infections due to this organism.
Q.29. A patient came with chest pain, burning in character, retrosternal, increases when lying down, and increase after eating hot food. Clinical examination is normal, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Burning retrosternal chest pain that worsens after eating hot food or lying down is classic for GERD, caused by stomach acid irritating esophagus.
Incorrect options-
- MI pain is crushing or heavy often radiating to the jaw or arm.
- PUD causes upper abdominal pain, not retrosternal, and is unrelated to lying down.
- Esophagitis is similar but the symptoms in the question are strongly suggesting towards GERD.
Q.30. An adult patient with history of sickle cell anemia will be at a higher of?
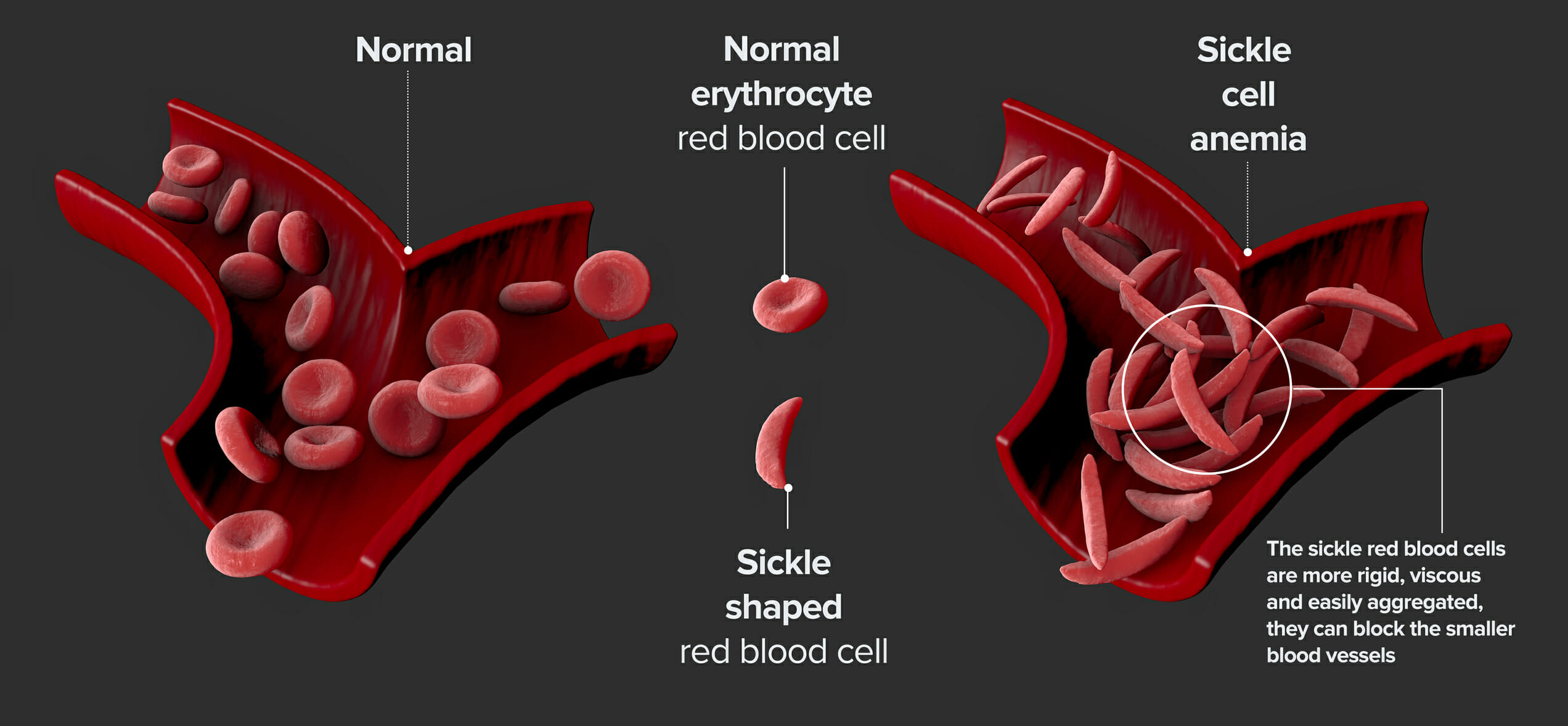
Correct Answer : A
Sickle cell anaemia causes the RBCs shape to become abnormal that can block the blood flow, leading to infarction in organs like spleen, lungs, and bones.
Q.31. A benign tumor of stomach constitutes about which of the following?
Correct Answer : A
Benign tumors of the stomach are not common and constitute only 5–10% of all stomach tumors. Benign tumors of Duodenum - 10-20%
Q.32. A 40-year-old patient with mild epigastric pain and nausea for 6 months, endoscopy shows loss of rugal folds. Biopsy shows infiltration of B lymphocytes, treated with antibiotics. What is the cause?
Correct Answer : B
This is because H.pylori is a common cause of choronic gastritis, which can cause symptoms like mild epigastric pain and nausea. It leads to inflammation and damage to the stomach lining, seen in loss of rugal folds. The biopsy showing B lymphocytes further supports the diagnosis.
Incorrect options-
Salmonella, Klebsiella, and Streptococcus are less likely as they cause other types of infections, not choronic gastritis.
Q.33. After having dinner 4 members of a family had vomiting & diarrhea soon after, what is the causative organism?
Correct Answer : B
In Staphylococcal food poisoning onset is generally 30 minutes to 8 hours after eating contaminated food. The symptoms are short-lived usually lasting for a few hours.
Incorrect options-
- Salmonella, onset comes later than 8 hrs.
- C.difficile is linked to antibiotic use.
- Legionella causes pneumonia not food poisoning.
Q.34. Vitamin C deficiency will affect which of the following?
Correct Answer : A
Vitamin C is crucial for producing collagen, which supports skin, bones, and blood vessles. A deficiency leads to scurvy , causing symptoms like bleeding gums and poor wound healing.
Q.35. A patient presents with perianal pain, which increases during night and lasts for few minutes. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Proctalgia Fugax most often occurs in the middle of the night and lasts from seconds to minutes. It's thought to be due to pelvic floor muscle spasms.
Incorrect options-
Ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease and Diverticulitis usually cause persistent pain and other symptoms like diarrhea or abdominal issues, making them less likely option in this case.
Q.36. A young patient came with peptic ulcer, which of the following is not the cause?
Correct Answer : A
Sepsis is typically not associated with peptic ulcers.
Incorrect options-
Delayed gastric emptying, TCA, and Aspirin use can all contribute to peptic ulcers.
Q.37. A drug abuser, showed RNA virus. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
HBV and HCV are transmitted parenterally, HCV is an RNA virus and HBV is a DNA virus.
Incorrect options-
- HBV is a DNA virus.
- HEV spreads through contaminated food and water.
- HDV requires HBV to replicate.
Q.38. An old patient with positive occult blood in stool, which of the following investigation should be performed?
Correct Answer : A
Colonoscopy is the gold standard investigation for detecting colorectal cancer and polyps, especially in older patients with positive occult blood test. Colonoscopy allows for direct visualization and removal of any growths.
Risk of colonic malignancy increases in older age especially when with positive occult blood test.
Incorrect option-
- CT, Ultrasound, and MRI are less effective in diagnosing colorectal cancer and are not the first choice in this scenario.
Q.39. A patient presents with cirrhosis, ascites, and lower limb edema. What is the best medication to start with?
Correct Answer : B
Spironolactone ( K+ sparing drug) is the first-line treatment for ascites in cirrhosis, as it reduces fluid retention by blocking aldosterone, which helps with both ascites and edema.
Incorrect options-
- Thiazide causes hypokalemia and extracellular alkalosis and this is not tolerable by cirrhotic patients.
- Hydralazine is used in HTN.
- NSAIDs can worsen kidney function in cirrhosis.
Q.40. A young male who is a known case of sickle cell anemia presented with abdominal pain & joint pain. He is usually managed by hospitalization. What's the likely management?
Correct Answer : C
For sickle-cell pain crisis the focus is on supportive care.
- Hydration to prevent dehydration.
- Analgesia for pain relief, ranging from OTC pain relievers to stronger medications.
- Monitoring of vital signs and pain levels.
In patient management may be needed in severe cases, NSAIDs should be used cautiously, and opioids are reserved for severe pain due to their risks.
Q.41. A patient presents to you with celiac sprue, what should his diet include?
Correct Answer : C
Celiac sprue is triggered by gluten, so avoiding it is essential to prevent damage to the small intestine and promote healing.
Incorrect option-
- Carbohydrate-free, protein-free, and fat -free diets are not necessary for managing celiac sprue.
Q.42. What is the first sign of MgSO4 overdose?
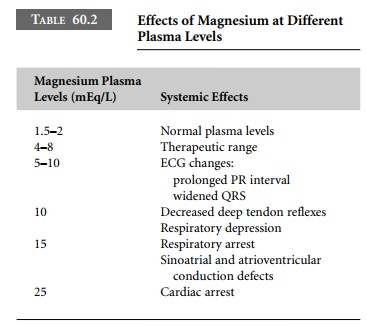
Correct Answer : A
This is the first sign of magnesium sulfate overdose, indicating neuromuscular blockade.
Incorrect options-
- Flaccid paralysis, respiratory faliure, and cardiac faliure are more severe and occur at higher serum levels.
Q.43. What is true about fetal alcohol syndrome?
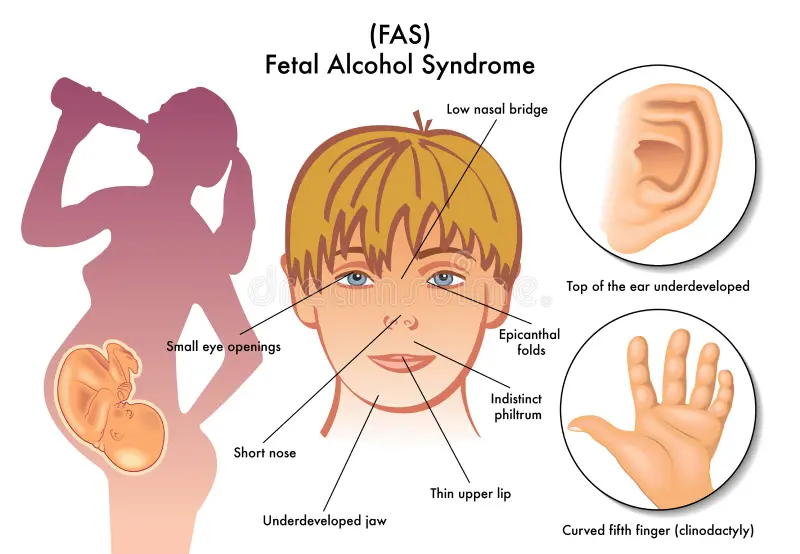
Correct Answer : A
Fetal alcohol syndrome is a pattern of mental and physical defects that can develop in a fetus in association with high levels of alcohol consumption during pregnancy.
Q.44. A patient with dysphagia to solid and liquid, has regurgitation. On barium there is non peristaltic dilatation of oesophagus, air-fluid level and tapering end. What is the diagnosis?
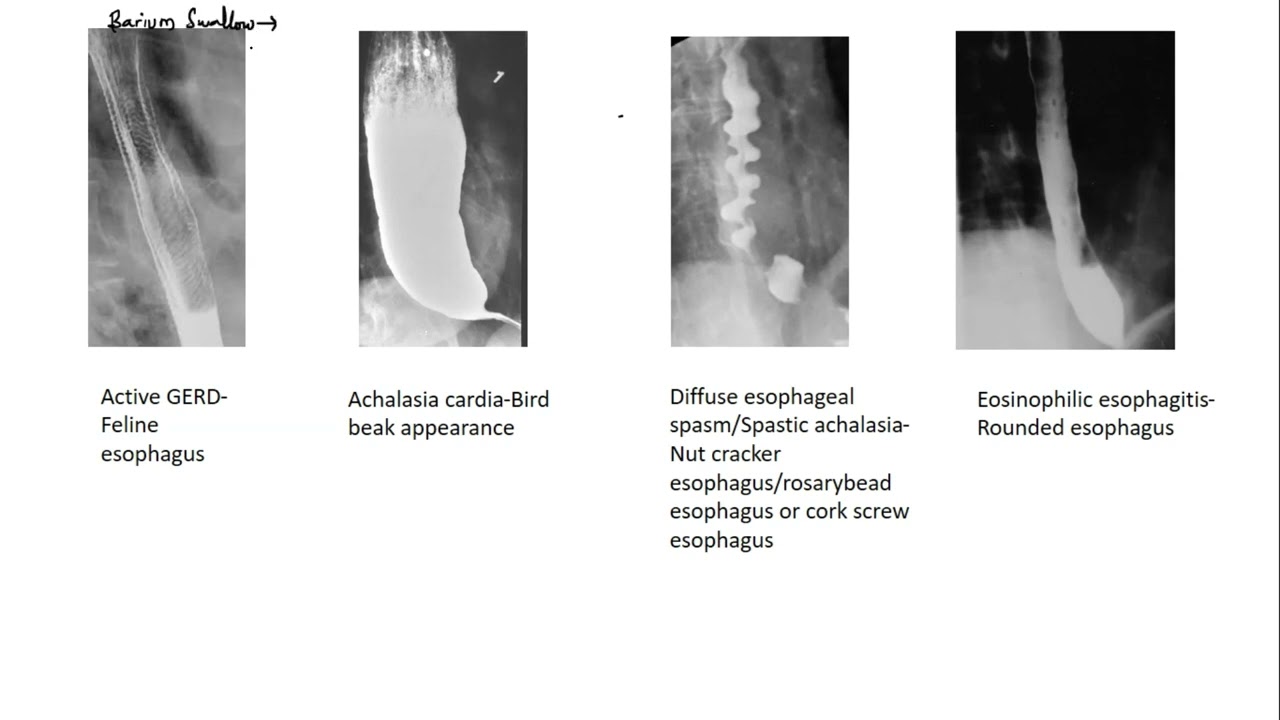
Correct Answer : B
Achalasia is a motility disorder which is characterized by incomplete LES relaxation, increased LES tone, and lack of peristalsis of the esophagus.
Q.45. A patient with nausea, vomiting and diarrhea developed postural hypotension. Where do you expect the fluid deficit?
Correct Answer : B
Vomitting and diarrhea mainly cause fluid loss from the extracellular compartment around the cells and in the blood. This can lead to low blood volume, causing postural hypotension.
Q.46. A patient was diagnosed with obstructive jaundice. What is the best method to diagnose common bile duct obstruction?
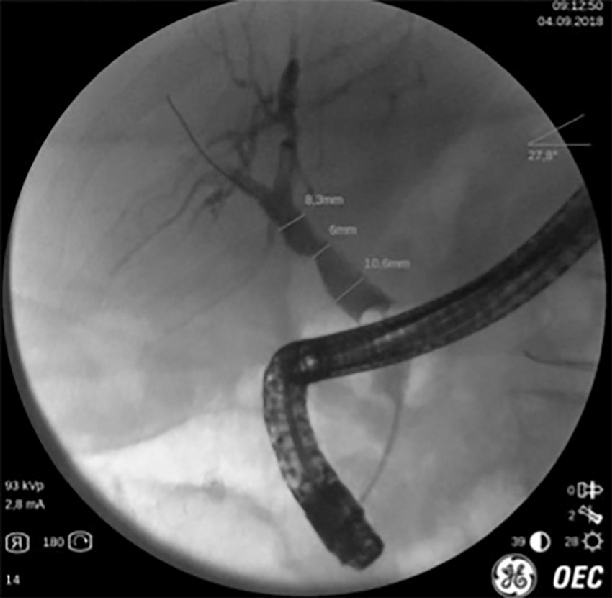
Correct Answer : A
The best method to diagnose common bile duct obstruction is ERCP. It allows direct visualization of the bile duct and pancreas and can also be used to treat obstruction, such as removing stones.
Q.47. A 25-year-old Saudi man presented with history of mild icterus, otherwise normal. Hepatitis screening : HBsAg +ve , HBeAg +ve, anti HBc Ab +ve . What is the diagnosis?
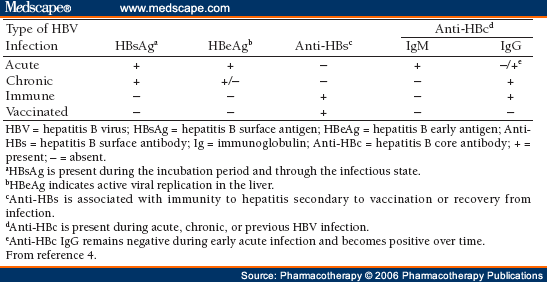
Correct Answer : A
The patient has HBsAg, HBeAg, and anti-HBc IgM,which are markers of active infection.
Q.48. A 23-year-old female presented with finding of hyperbilirubinemia, normal examination. Laboratory investigation shows total bilirubin= 3.1 , direct bilirubin= 0.4. The most likely diagnosis is?
Correct Answer : A
Gilbert's disease: asymptomatic, discovered incidentally, no treatment required, and a slight increase in unconjugated bilirubin.
Incorrect options-
- Crigler-Najjar syndrome1 can't survive adult life. Only type II survive.
- Duben Johnson syndrome & Rotor's disease: direct bilirubin (Q about indirect) Sclerosing cholangitis: 75% in men, pruritus & diagnosis by ERCP (MRCP).
Q.49. A 48-year-old female patient with abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and tenderness in right hypochondrial area. What's your diagnosis?
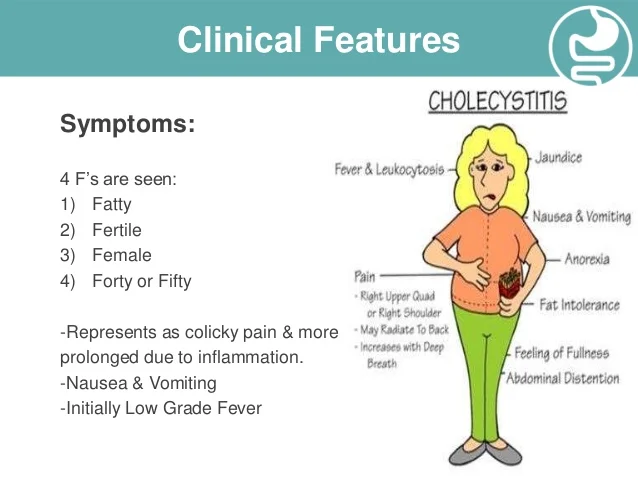
Correct Answer : A
The most likely diagnosis is acute cholecystitis, which is inflammation of the gallbladder typically caused by a blocked cystic duct, leading to RUQ pain, nausea, vomiting, and tenderness.
Q.50. A 50-year-old male with 2 years history of dysphagia, lump in the throat, excessive salivation, intermittent hoarseness & weight loss. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
The presenting symptoms are suggestive of malignancy (old age, weight loss, hoarseness, lump, dysphagia and excessive salivation).
Incorrect options-
- Achalasia, diffuse esophageal spasm, and scleroderma typically present differently .
Q.51. What is the most common cause of chronic diarrhea?
Correct Answer : A
The most common cause of choronic diarrhea is IBS. It is a functional disorder that causes abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits, but without underlying pathology.
Incorrect options-
- Crohn's, ulcerative colitis, and malabsorption can also cause choronic diarrhea byt are less common than IBS.
Q.52. Gastro Oesophageal Reflux Disease is best diagnosed by which of the following?
Correct Answer : D
The best method to diagnose GERD is history and upper GI endoscopy. While a detailed history of symptoms like heartburn and regurgitation is important, endoscopy helps in confirming the diagnosis and ruling out other potential causes by direct visualization of esophagus and stomach.
Q.53. A patient was diagnosed to have duodenal ulcer and was given ranitidine for 2 weeks, now he is diagnosed to have H. pylori. What is your choice of management?
Correct Answer : A
This triple therapy helps in eradicating the bacteria and healing the ulcer by combining a PPI with two antibiotics.
Q.54. All of the following are symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
Rome II criteria for IBS:
- At least 3 months (consecutive) of abdominal pain with 2 out of the following 3: Relief with defecation, change in the form of stool, or change in frequency of stool.
- Symptoms that support the diagnosis abnormal stool frequency, abnormal form, abnormal passage (straining, urgency, sense of incomplete defecation), passage of mucous, and bloating or feeling of distention.
- Absence of alarming features which are weight loss, nocturnal defecation, blood or pus in stool, fever, anemia, and abnormal gross findings on flexible sigmoidoscopy.
Q.55. A young patient complains of watery diarrhea, and abdominal pain, with a previous history of mucus diarrhea. Symptoms improve when he sleeps. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Most likely diagnosis is IBS. IBS causes abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits, and symptoms that often improve with sleep.
Q.56. Which of the following is protective against colon cancer?
Correct Answer : B
Fiber is protective against colon cancer. A high fiber diet helps promote regular bowel movements and reduce the time waste stays in colon, decreasing exposure to harmful toxins.
Q.57. Regarding H. Pylori eradication which of the following is true?
Correct Answer : C
Recommended treatment of H.pylori: eradication upon documentation of infection is controversial since most will not have peptic ulcer or cancer.
1st line - PPI+ clarithromycin + amoxicillin or metronidazole (3 drugs, twice daily for one week).
Q.58. A 70-year-old woman presented with 3 days history of perforated duodenal ulcer, she was febrile, semi comatose and dehydrated on admission. What is the management for this patient?
Correct Answer : C
For a perforated duodenal ulcer, the best approach is to insert NGT for suction, hydrate the patient, administer antibiotics, and perform laproscopic repair. This helps to decompress the stomach, treat infection, and surgically close the perforation.
Q.59. A 28-year-old lady presented with history of increased bowel motion in the last 8 months. About 3-4 motions/day associated with mucus. Examination was normal. Stool analysis showed cyst, yeast - nil. Mucus culture: no growth. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
The most likely diagnosis is IBD, given the chronic diarrhea with mucus and the absence of other causes. IBD, including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, often causes mucus in the stool.
Q.60. A 40-year-old man presented to the ER with 6 hour history of severe epigastric pain radiating to the back like a band, associated with nausea. No vomiting, diarrhea or fever. On examination the patient was in severe pain with epigastric tenderness. ECG was normal, serum amylase was 900u/l, AST and ALT are elevated to double normal. Which of the following is the least likely precipitating factor to this patient’s condition?
Correct Answer : B
Chronic active hepatitis is the least likely precipitating factor here. While it can raise liver enzymes, it typically doesn't cause an elevation in the serum amylase, which suggests pancreatic involvement.
Incorrect option-
- Hypercalcemia, chronic alcohol ingestion, cholelithiasis and hyperlipidemia are precipitating factors leading to acute pancreatitis
Q.61. Where is oesophagus located?
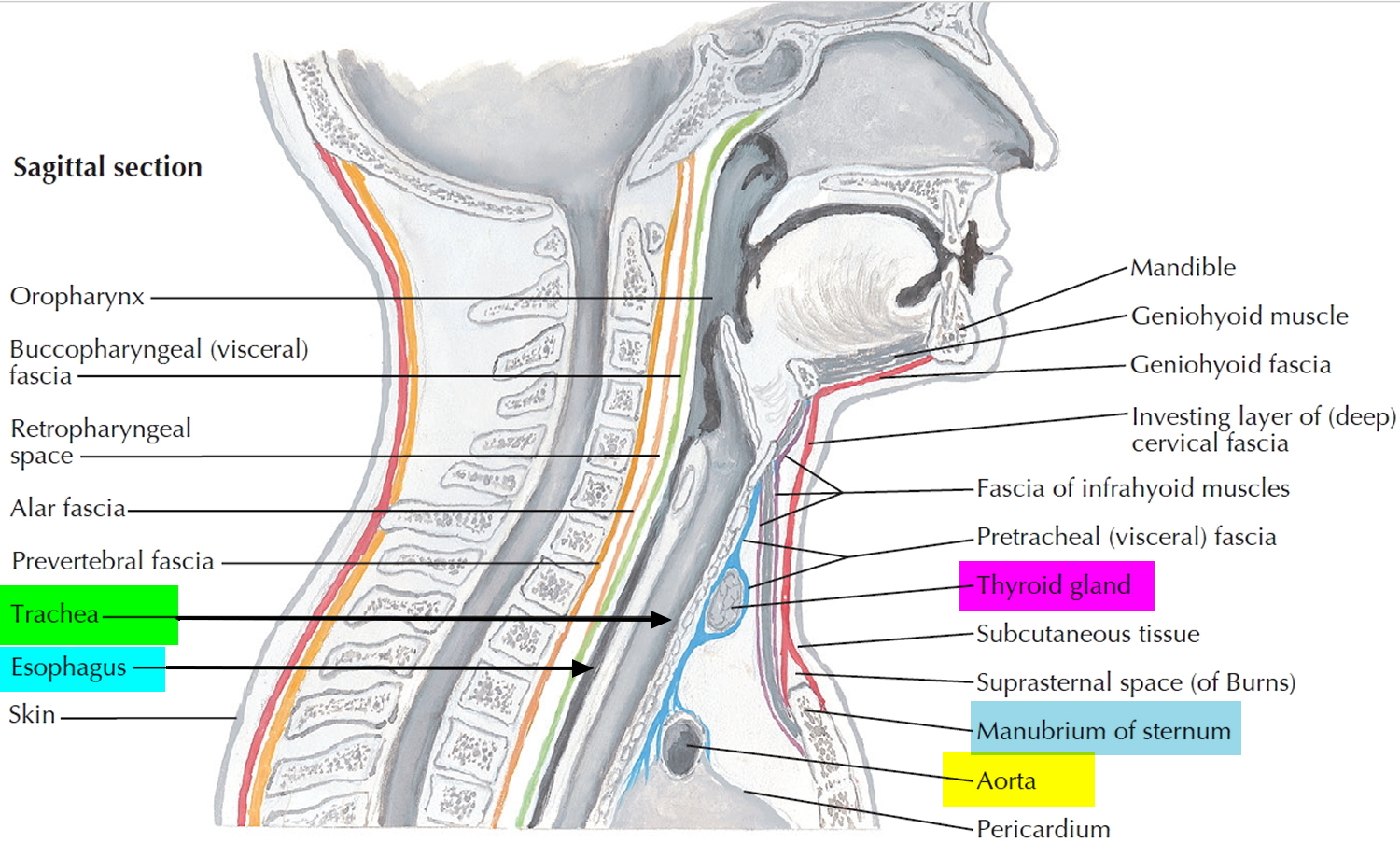
Correct Answer : A
Esophagus is located behind the trachea.
Q.62. The single feature which best distinguishes crohn’s disease from ulcerative colitis is?
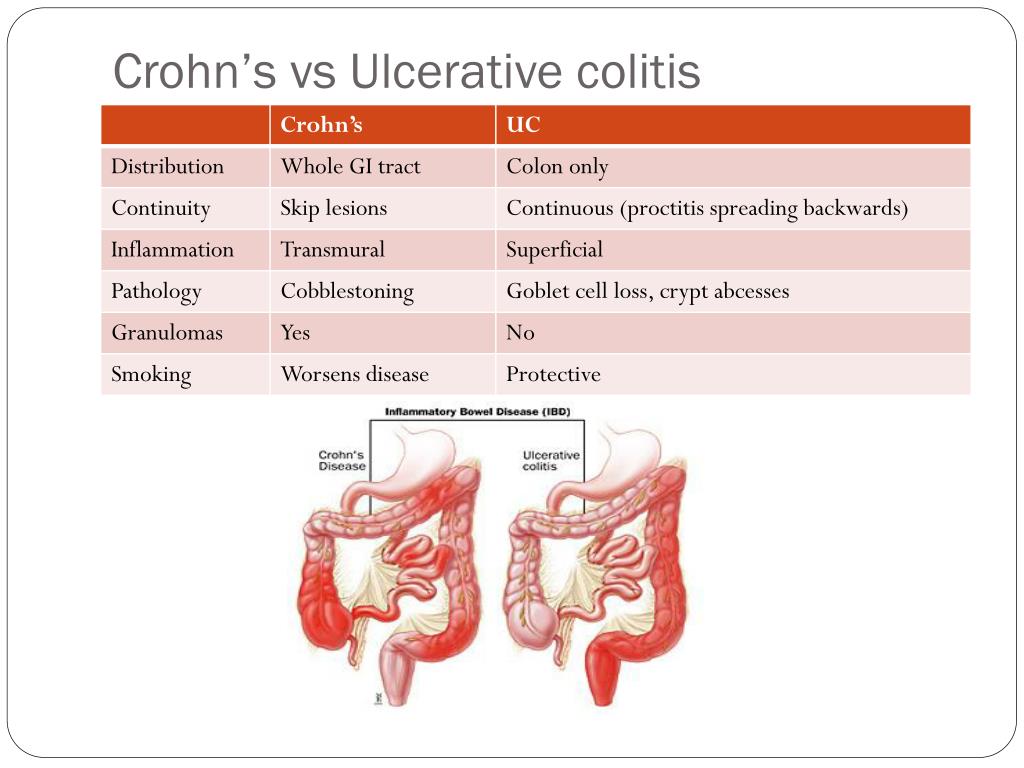
Correct Answer : D
The best distinguishing feature is non-casseting granuloma which is present in only 30 % of patients with CD however when it occurs this is definitively CD. The rest of the features can occur in either.
Q.63. What is the gold standard imaging for acute pancreatitis?
Correct Answer : A
CT scan is the gold standard for diagnosing acute pancreatitis. It provides detailed images to assess the pancreas, detect complications like fluid collection or necrosis, and guide treatment.
Q.64. An old patient with WBC-17000 and left iliac fossa tenderness and fever. What's the likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Old patient with the features of left side abdominal pain, fever, and high WBC is strongly indicative of diverticulitis. This condition involves inflammation or infection of the small pouches in the colon, often presenting with these symptoms.
Q.65. A 45-year-old man presented with anorexia, fatigue and upper abdominal pain for one week. On examination, he had tinge of jaundice and mildly enlarged tender liver. What's not included in the management?
Correct Answer : B
The case looks like acute hepatitis with acute history, fatigue, mild jaundice, and mild hepatomegaly. ERCP is not needed (not obstructive).
- Investigations include - LFT, hepatitis markers, and US liver.
- Treatment is observation and follow-up.
Q.66. A 30-year-old man presented with upper abdominal pain and dyspepsia. Which of the following doesn’t support the diagnosis of peptic ulcer?
Correct Answer : C
The symptoms of peptic ulcer include pain, dyspepsia, heartburn, bleeding, and gastric outlet obstruction but don’t explain the presence of a mass.
Q.67. Which of the following type of Hepatitis is most commonly transferred by blood?
Correct Answer : C
HCV recently with PCR technology began to have a screening test, but transmission remains high as many infected individuals are carriers.
Incorrect options-
- HBV transmission by blood was common before effective screening tests and vaccines were available.
- HAV is transmitted via the enteral route.
Q.68. All of the following organisms cause diarrhea with invasion, except?
Correct Answer : D
Cholera is caused by Vibrio cholerae. It produces toxin that causes a profuse watery diarrhea by disrupting fluid and electrolyte transport in the intestinal cells. This mechanism involves secretory process rather than direct invasion.
Q.69. What do premalignant lesions have?
Correct Answer : B
Villous adenomas are high-risk precursors of colon cancer due to their finger like projections.
Q.70. A patient is diagnosed with hepatitis B, which of the following antigens appear in the window period?
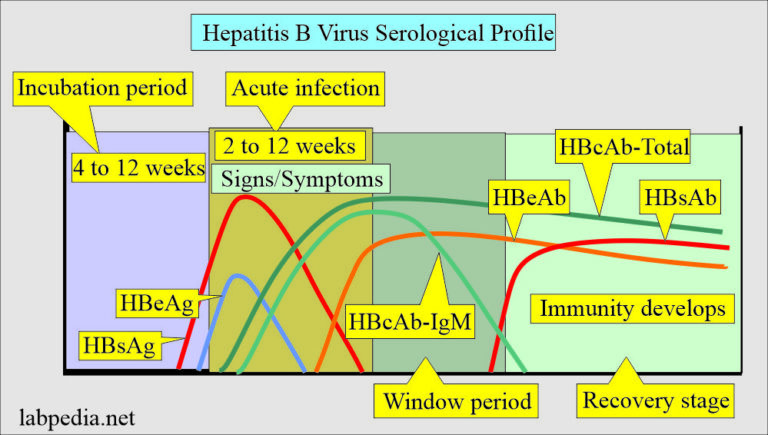
Correct Answer : D
IgM antibodies against HBcAg.
Q.71. What is the treatment for erosive gastritis?
Correct Answer : C
The treatment depends on the cause and severity. It can include medications like H2 blockers or PPI, antibiotics for infections, and lifestyle changes. Surgery such as gastrectomy, is rare and only considered in severe cases.
Q.72. Which of the following is true regarding Crohn’s disease?
Correct Answer : B
Crohn's disease can lead to several mechanical complications within the intestines, including obstruction, fistula, and abscesses.
Fistulas and obstruction in Crohn's need surgical repair.
Q.73. A man travelled to Indonesia and had some cold food. He is now having severe rice watery diarrhoea and is severely dehydrated. What is the likely causative organism?
Correct Answer : A
Rice watery diarrhea indicates cholera infection caused by Vibrio cholera and it’s endemic in Indonesia.
Q.74. A 60-year-old male patient is complaining of dysphagia to solid food. He is a known smoker and drinks alcohol, he has weight loss. What’s the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
This condition is strongly linked to smoking and alcohol consumption. Symptoms like progressive dysphagia starting with solids, significant weight loss, and the patient's risk factors point to oesophageal cancer.
Incorrect options-
- GERD typically presents with heartburn and chestpain, not seen here.
- Achalasia affects both solids and liquids.
- Esophagitis involves heartburn or chest pain.
Q.75. A 75-year-old female with 2 day history of MI is complaining of abdominal pain, vomiting, and bloody stool. X-ray shows abdominal distension with no fluid level, serum amylase is elevated. What is the Diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
The most likely diagnosis is ischemic colitis, as reduced blood flow after MI can cause abdominal pain, vomiting, bloody stool, and elevated serum amylase.
Incorrect options-
- Ulcerative colitis is a chronic condition not related to MI.
- Acute pancreatitis shows elevated amylase but X-ray findings are not present.
- Diverticulitis involves localized inflammation, which doesn't match with this scenario.
Q.76. Which of the following is true about gastric lavage?
Correct Answer : C
Gastric lavage with activated charcoal is most useful if given within 1 to 2 hours of ingestion. Lavage is effective only 1 hour after ingestion of any poison. After that it's ineffective
Q.77. Ibuprofen is contraindicated in patients with?
Correct Answer : A
It is contraindicated in peptic ulcers as ibuprofen, an NSAID, can irritate the gastric mucosa lining and worsen ulcers by reducing protective prostaglandins.
Incorrect option-
- Seizures- not contraindicated.
- Rheumatoid arthritis often requires NSAIDs for treatment.
- Fever- commonly used to lower fever.
Q.78. A patient presented with jaundice, three days later the color of jaundice changed to greenish. What is the cause?
Correct Answer : A
It is due to oxidation of bilirubin to biliverdin, as biliverdin is green in color and explains the jaundice turning green.
Incorrect options-
- Deoxygenation of bilirubin doesn't cause green color.
- Overeating green vagetables doesn't effect jaundice.
- Infection can cause jaundice but not a greenish tint.
Q.79. In irritable bowel syndrome, contraction and slow wave myoelectricity is seen in?
Correct Answer : A
In IBS, gut muscle contractions and altered slow wave myoelectricity can lead to slower bowel movements, causing constipation.
Incorrect options-
- Diarrhea is linked to faster gut activity, not slow wave patterns.
- Abdominal pain is not directly related to these changes.
- Peritonitis is not related to IBS.
Q.80. Kwashiokor disease is usually associated with which of the following?
Correct Answer : C
Kwashiorkor is caused by protein deficiency despite of adequate carbohydrate intake.
Q.81. A patient with peptic ulcer is using antacids, she presented with forceful vomiting of undigested food particles. What is the diagnosis?
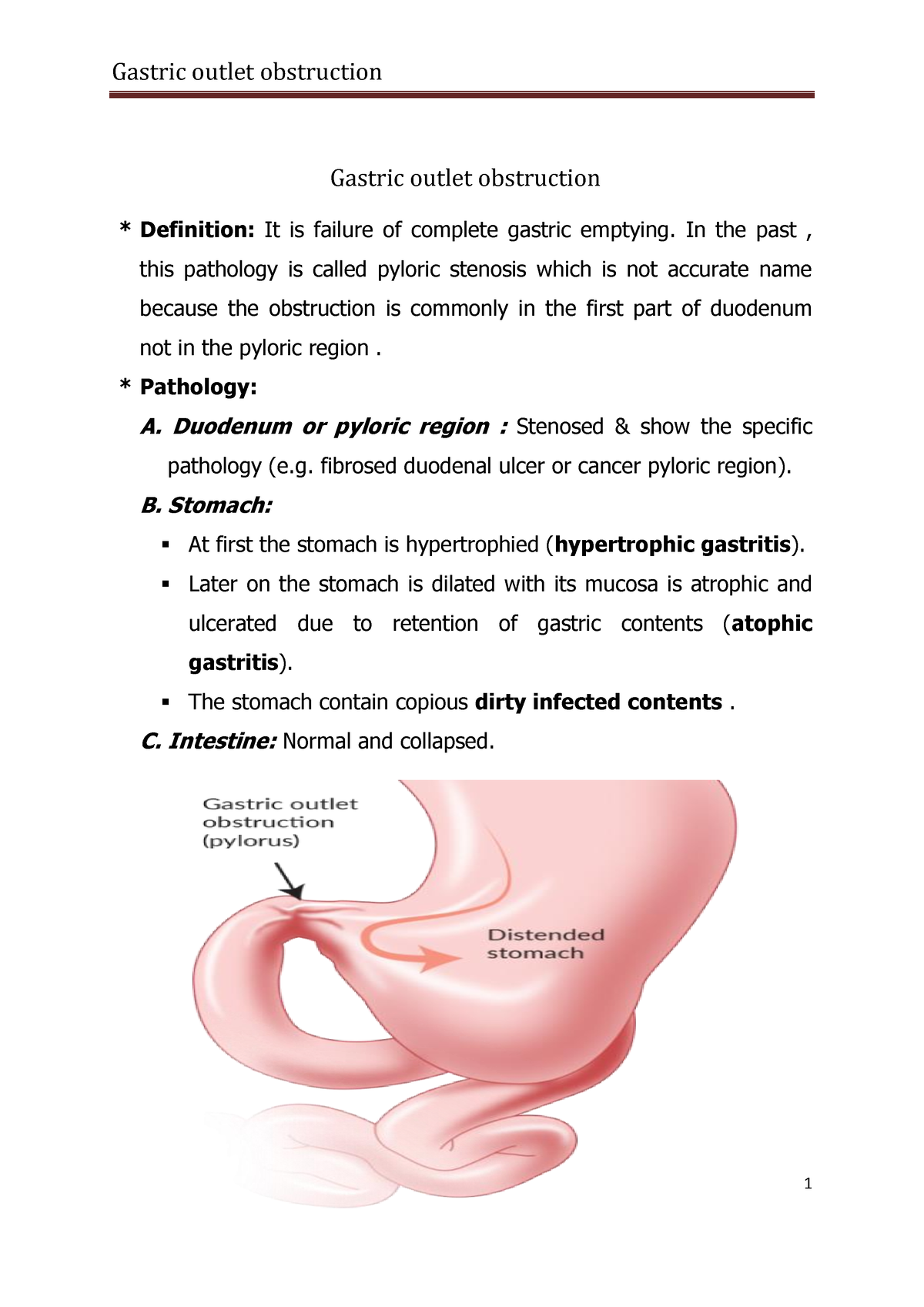
Correct Answer : A
Forceful vomiting of undigested food suggests a blockage where the stomach empties into the intestine, common in advanced peptic ulcers.
Incorrect options-
- GERD causes acid reflux, not vomiting of undigested food.
- Esophagitis involves swallowing difficulty.
- Achalasia affects swallowing, not gastric emptying.
Q.82. Celiac disease severe form involves which part of intestine?
Correct Answer : A
Pathological abnormalities of celiac disease may include severe, mild, or moderate small bowel mucosal architectural abnormalities that are associated with both epithelial cell and lymphoid cell changes, including intraepithelial lymphocytosis. Architectural changes tend to be most severe in the duodenum and proximal jejunum and less severe, or absent, in the ileum.
Q.83. A patient with GERD is at risk of contracting which cancer?
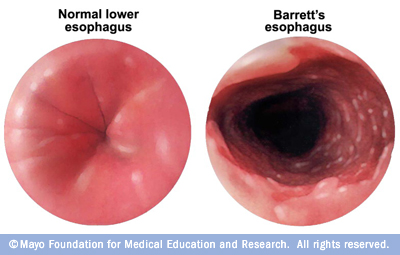
Correct Answer : A
The histology of the esophagus is columnar epithelium with persisting GERD it changes to squamous epithelium.
- Cancer of squamous epithelium is an adenocarcinoma.
Long term GERD can lead to Barrett's esophagus which is a premalignant condition that can then transform to adenocarcinoma.
Q.84. Which of the following is at high risk of developing colon cancer in young male?
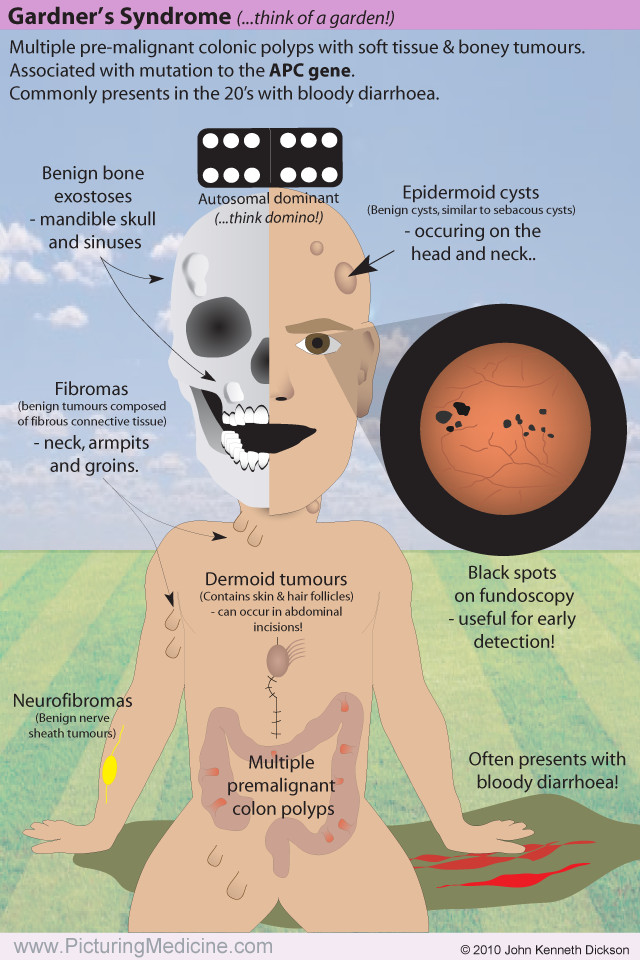
Correct Answer : C
Gardner syndrome is now known to be caused by mutation in the APC gene predisposing to colon cancer. It leads to multiple polyps in the colon, which can turn cancerous.
Q.85. All of the following are differentials of acute abdomen, except?
Correct Answer : B
As MI can cause referred abdominal pain, but it's not a primary cause of acute abdomen.
Incorrect options-
- Pleurisy can cause chest pain that can be mistaken for abdominal pain.
- Herpes zoster can present with abdominal pain.
- Polyarteritis nodosa is a rare condition that can cause abdominal pain due to inflammation of blood vessels.
Q.86. A man with history of alcohol consumption has which of the following?
Correct Answer : B
People with excessive alcohol intake and malnutrition are still at high risk of folic acid deficiency.
Q.87. What is the prophylaxis of cholera?
Correct Answer : A
- Handwashing, clean water, and proper sewage disposal are essential.
- Mass oral vaccination in outbreak areas reduces infection risk.
Q.88. A 6-month-old baby presented to the clinic with 2 days history of gastroenteritis. On examination: decreased skin turgor, depressed anterior fontanelle & sunken eyes. What's the estimate of degree of dehydration?
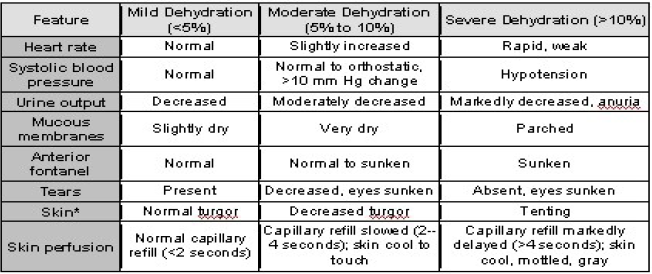
Correct Answer : C
All the mentioned features are indicative of moderate dehydration, which is around 10%.
Q.89. A 22-year-old male patient presented with recurrent diarrhea alternating with constipation, and abdominal pain that relieves after defecation, no blood in the stool, and no weight loss. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
These features are strongly indicative of IBS, a functional gastrointestinal disorder.
Incorrect options-
- Ulcerative colitis typically involves bloody diarrhea and weight loss.
- Crohn's disease can cause abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss but usually includes more severe symptoms.
- Malabsorption often cause weight loss and nutritional issues.
Q.90. A young healthy male has abdominal pain after playing basketball. Examination was normal except for left paraumbilical tenderness. What is the next step in management?
Correct Answer : C
As the symptoms suggest exertional abdominal pain, which typically resolves on its own after physical activity. Reassessing in 48 hours ensures any worsening symptoms are addressed early.
Q.91. Which of the following is a feature of chronic diarrhea?
Correct Answer : D
Metabolic alkalosis can occur in chronic diarrhea due to significant fluid and electrolyte loss, including bicarbonate.
Q.92. A teacher in school presented with 3 day history of jaundice & abdominal pain, 4 of her school students had the same illness. What is likely to be positive in this patient?
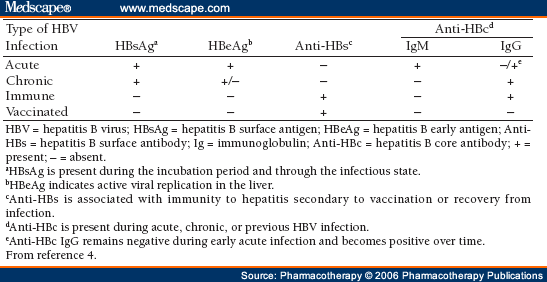
Correct Answer : B
The question points to an Hepatitis A outbreak as the teacher and students share similar symptoms, and Hepatitis A is highly contagious.
- Hepatitis A IgM is detectable during an active infection, indicating recent exposure.
Q.93. Which of the following features of ulcerative colitis distinguishes it from Crohn’s disease ?
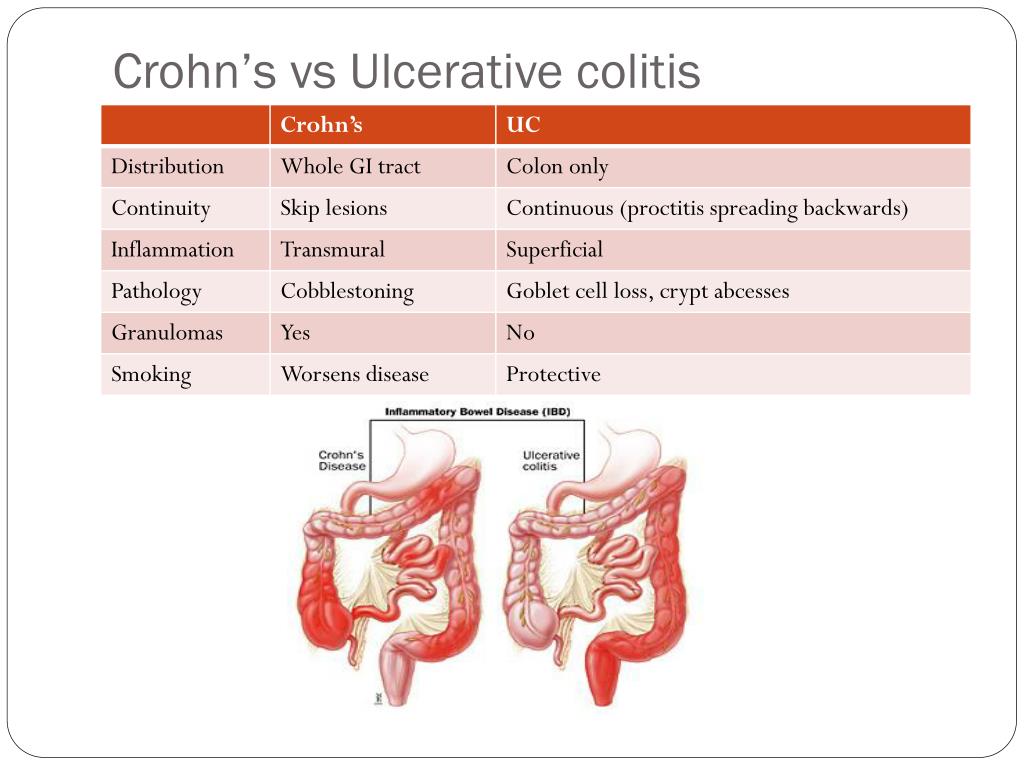
Correct Answer : C
Granulomas are a hallmark of Crohn's disease and are not seen in ulcerative colitis.
Q.94. A female was diagnosed with hemochromatosis with liver cirrhosis and reduced weight; her weight in last visit was 90kg, now it's 84kg. What is the best initial investigation?
Correct Answer : C
In a patient with hemochromatosis, cirrhosis, and weight loss, the best initial investigation to assess the liver and screen for complications is an abdominal ultrasound. The other options are used in follow-up.
Q.95. What is the probable etiological cause of inflammatory bowel disease?
Correct Answer : A
IBD, including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, is driven by an overactive immune system that mistakenly attacks intestinal tissue, causing inflammation.
Q.96. Which of the following is true regarding varicella vaccine during breast feeding ?
Correct Answer : A
There are no data on the excretion of varicella virus vaccine in human milk and is therefore safe.
Q.97. A patient was screened for HBV and his HBsAg and HBeAg were positive. What is the next step?
Correct Answer : A
HBV DNA load measures viral activity, helping assess disease severity and guide treatment decisions.
Q.98. A graph showing two curves one is labeled as A and the other is B. What will be the parameters?
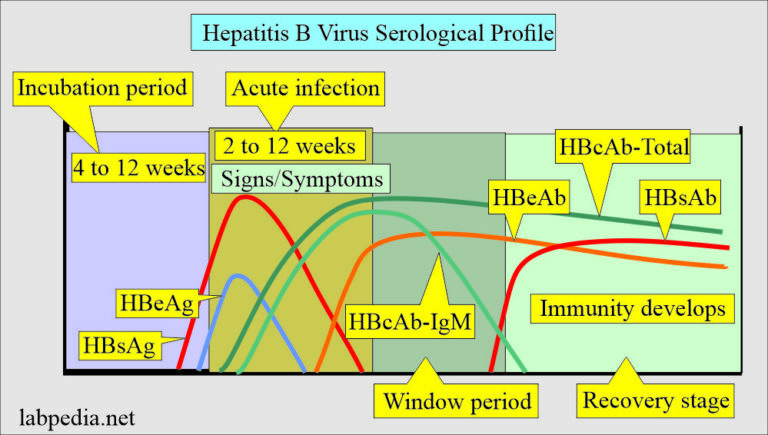
Correct Answer : B
- HBsAg indicates active infection of hepatitis B.
- IgG antibody appears later indicating immunity or chronic infection resolution.
Q.99. A lady presented with fatigue, RUQ pain, jaundice and bruises and had compression vertebral fracture. Investigation showed high cholesterol and positive anti mitochondrial antibodies. What is the likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
PBC is the correct answer as features of fatigue, RUQ pain, jaundice, bruises, compression fracture from osteoporosis, high cholesterol, and positive anti-mitochondrial-antibodies are specific for PBC.
Q.100. What's the best investigation for acute diverticulitis?
Correct Answer : C
CT scanning with intravenous, oral, or rectal contrast: [sensitivity and specificity] for CT are significantly better than for contrast enemas. When an abscess is suspected, CT scanning is the best modality for making the diagnosis and following its course because of the risk of perforation, endoscopy is generally avoided in the initial assessment of the patient with acute diverticulitis. Its use should be restricted to situations when the diagnosis is unclear, to exclude other possible diagnoses.
Diverticulitis: Chest X-ray with the patient upright can aid in detection of pneumoperitoneum. Abdominal X-rays may demonstrate small or large bowel dilation or ileus, pneumoperitoneum, bowel obstruction, or soft tissue densities suggesting abscesses. Contrast enemas: limited value; findings suggestive of diverticulitis include extravasated contrast material outlining an abscess cavity, intramural sinus tract, or fistula.
Q.101. What diet is good for patient with liver fibrosis?
Correct Answer : A
This is because the liver may struggle to process protein effectively, leading to issues like increased ammonia levels in the blood, which can cause confusion or even coma. A low protein diet helps reduce liver's workload and manage these complications.
Q.102. Which medication should not be given in patients with liver dysfunction?
Correct Answer : D
Warfarin relies on the liver to metabolize and produce clotting factors. In liver dysfunction this process is impaired, leading to-
- Increased bleeding risk due to higher warfarin levels in blood.
- Unpredictable effects making difficult to decide dose.
Q.103. Which of the following is true about reflux esophagitis?
Correct Answer : A
Reflux esophagitis can cause chest pain, nausea, and shortness of breath- symptoms that often resemble heart disease, making it hard to differentiate.
Incorrect options-
- GERD comes under reflux esophagitis.
- Achalasia is a swallowing disorder.
- Gastric carcinoma has different symptoms.
Q.104. A patient is diagnosed with Barrett's esophagus, what's the next step?
Correct Answer : A
Barrett's esohagus increases the risk of esophageal cancer, so regular endoscopy is crucial to monitor for dysplasia or other changes.
Q.105. A patient is diagnosed with Barrett's esophagus. What is the malignancy associated with it?
Correct Answer : A
Barrett's esophagus increases the risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma as the metaplastic columnar cells can transform into cancerous cells overtime.
Q.106. A patient presented with abdominal pain, distension with vomiting and constipation. He has mild symptoms of dehydration. There is evidence of air in the rectum. What is the treatment?
Correct Answer : B
This presentation suggests a bowel obstruction. A NGT helps relieve pressure by removing the trapped gas and fluid, while IV fluids address dehydration and correct electrolyte imbalance.
Q.107. A patient has dysphagia to solids, what is the next step?
Correct Answer : A
For dysphagia to solids, endoscopy is the next best step to directly visualize the esophagus and take biopsies of any suspicious areas helping diagnose causes like strictures, tumors, or esophagitis.
Q.108. A 70-year-old male is chronic Hepatitis B virus antigen carrier. What is the screening test to be done?
Correct Answer : A
Chronic Hepatitis B carriers are at a higher risk of hepatocellular carcinoma [HCC]. AFP detects tumor markers, and liver ultrasound identifies structural changes, making this combination ideal for screening.
Q.109. A 60-year-old male presented with progressive jaundice without abdominal pain. What is the diagnosis ?
Correct Answer : A
Progressive jaundice without abdominal pain strongly suggests bile duct obstruction often caused by a pancreatic head tumor compressing the duct.
Q.110. An old patient with sense of abdominal fullness without pain, and no GI symptoms presents to you. He has no other complaints, he is a k/c/o HTN,DM. O/E pulsatile mass in the mid abdomen was found. What is the diagnosis ?
Correct Answer : C
The key signs here are abdominal fullness and a pulsatile abdominal mass in the mid-abdomen, which are a classic sign of abdominal aortic aneurysm. The patient's history of HTN and DM also increases the likelihood.
Q.111. A young boy presented with jaundice, high liver enzymes and Kayser-Fleischer rings. What is the most appropriate treatment?
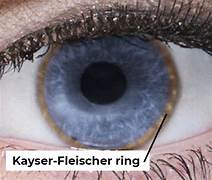
Correct Answer : B
The combination of high liver enzyme, and Kayser-Fleischer rings points to Wilson's disease, which causes copper buildup. Penicillamine helps remove excess copper by building to it and promoting its excretion.
Q.112. An elderly patient presents with glossitis, diarrhea, weight loss, anorexia and macrocytic anemia. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
The above mentioned combination of clinical features are pointing towards vitamin B12 deficiency, which is characterstick of pernicious anemia. This condition occurs when the body can't absorb B12 due to lack of intrinsic factor.
Q.113. A patient is on TB prophylaxis INH (Isoniazid). What monitoring is needed?
Correct Answer : A
Isoniazid [INH] is commonly used for TB prophylaxis, but it can cause liver toxicity. Regular liver function tests, including ALT, AST, and bilirubin levels, help detect any liver damage early.
Q.114. A patient with trauma has abdominal pain diagnosed as intramural hematoma, otherwise the patient is stable. What is the management?
Correct Answer : A
Intramural hematoma, a collection of blood within the intestinal wall, often resolves on its own in stable patients. Resting the bowel and observing the patient is usually sufficient to allow healing and prevent complications like bowel obstruction.
Q.115. A patient presents with loin pain radiating to the groin. Renal stones are suspected. What is the test that has the most specificity & sensitivity in diagnosing this condition?
Correct Answer : A
A non-contrast CT scan is the gold standard for diagnosing kidney stones because of its high senstivity and specificity. It also provides quick results for treatment plan.
Q.116. An old man presented with gastric ulcer, he is negative for H.pylori. What is the treatment?
Correct Answer : A
As the patient is negative for H.pylori we will prescribe PPI as it-
- Causes acid supression helping the ulcer to heal.
- It also provides symptom relief and alleviates the discomfort.
Q.117. A patient is diagnosed with celiac disease. Which food is safe for him?
Correct Answer : B
Rice is naturally gluten-free making it an excellent option for people with celiac disease.
Q.118. A patient with muscle weakness & decreased reflexes gives history of diarrhea. What is the probable electrolyte abnormality?
Correct Answer : D
Diarrhea can cause significant loss of potassium, which is critical for muscle and nerve function. Hypokalemia often leads to symptoms like muscle weakness and decreased reflexes.
Q.119. A patient with chronic heartburn, treated with antacids, has no improvement. What is the next action?
Correct Answer : C
Chronic heartburn, often a symptom of GERD, occurs when stomach acid repeatedly flows back into the esophagus. If antacids are not working, it's time to escalate treatment to PPI, which are stronger at reducing acid production and offer more effective relief for most patients.
Q.120. A patient presents with diffuse abdominal pain, diminished bowel sounds, and his x-ray shows dilated loop specially in the transverse colon. What’s the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Acute pancreatitis is suggested by -
- Diffuse abdominal pain and diminished bowel sounds, common in acyte pancreatitis.
- Dialated bowel loops on X-ray especially in the transverse colon, indicates possible bowel obstruction due to inflammation.
Q.121. What is the diet instruction for a patient with liver cirrhosis and ascites?
Correct Answer : B
In general, recommendations for patients with severe liver disease may include:
- Large amounts of carbohydrate foods.
- Moderate intake of fat .
- About 1 gram of protein per kilogram of body weight.
- Vitamin supplements, especially B-complex vitamins.
- Reduce the salt intake.
Q.122. A young female complaining of severe diarrhea, weight loss, vomiting, and abdominal pain, has been diagnosed to have Crohn’s disease. Which of the following is true?
Correct Answer : B
In Crohn's disease granulomas are a key feature and found in intestinal wall.
Q.123. How do we confirm if the peptic ulcer is caused by H. Pylori or not?
Correct Answer : D
A combination of tests are used-
- Serology to detect antibodies against H. pylori.
- Rapid urease test is done during endoscopy, detecting urease production from H. pylori.
- Histopathology and culture.
Q.124. Which drug increases incidence of reflux esophagitis?
Correct Answer : A
Theophylline, used for asthma and COPD can relax LES increasing the risk of acid reflux and reflux esophagitis.
Some common medications also can cause a chemical burn in the esophagus.
- Pills that are most likely to cause esophagitis include: aspirin, doxycycline, iron supplements, NSAIDs such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn) osteoporosis medications such as alendronate (Fosamax) or risedronate (Actonel)
Q.125. A 50-year-old male, presented with yellowish discoloration of eyes and body, fatigue. O|E Jaundice, pallor, vitiligo. Investigations - WBC- 2500, Hb - 7.5, Plt - 51. LFT - Elevation of total bilirubin and direct bilirubin. Which one of the following is true?
Correct Answer : A
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia: antibodies directed against the persons own red blood cells the primary illness is idiopathic ,secondary can result from many other illness (autoimmune) evidence of hemolysis (incresse unconjugated bilurbin,decrease haptoglobin,increase lactic dehydrogenase).
- Specific investigation:positive direct coombs test.
Q.126. A hypertensive patient presents with liver cirrhosis, lower limb oedema and ascites. What's the management?
Correct Answer : A
In a patient with liver cirrhosis, ascites and lower limb edema, a potassium-sparing diuretic is the best choice. It helps reduce fluid buildup without causing potassium depletion, which is important in liver cirrhosis.
Q.127. A patient with SOB, cardiomegaly on CXR, pleural effusion presents to you. Pleural fluid : Lactate dehydrogenase < 200 mg/dl & protein < 27 g/L . Which condition is associated with the above finding?
Correct Answer : A
The patients features of SOB, cardiomegaly, pleurasl effusion, and low LDH and proteinon pleural fluid analysis suggest a transudative effusion which is typical in CHF.
Q.128. An active 64-year-old male complains of dysphagia. Endoscopic biopsy confirms oesophageal adenocarcinoma carcinoma. What is the predisposing factor?
Correct Answer : A
GERD leads to development of Barrets Esophagus, which will lead to Adenocarcinoma. Smoking, Alcohol increase the risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Q.129. A male patient presents with exercise intolerance, HG is 9, MCV is 78 and positive fecal occult blood test. Upper GI scope show chronic gastritis. How to treat him ?
Correct Answer : A
The patient has IDA, suggested by low Hb, microcytic anemia [MCV 78], and a positive fecal occult bllod test indicating possible GI bleeding. Oral iron supplementation is the first line treatment.
Q.130. An obese patient and newly diagnosed DM , all normal laboratory findings including liver function test. On examination: Patient had palpable & mildly enlarged liver. How will you manage this patient?
Correct Answer : A
Biguanides helps in weight loss, especially metformin is the first-line medication for management of type-2 DM..
Q.131. Which of the following is true about HCC?
Correct Answer : B
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC, also called malignant hepatoma) is the most common type of liver cancer. Most cases of HCC are secondary to either a viral hepatitis infection (hepatitis B or C) or cirrhosis (alcoholism being the most common cause of hepatic cirrhosis).
In countries where hepatitis is not endemic, most malignant cancers in the liver are not primary HCC but metastasis (spread) of cancer from elsewhere in the body, e.g., the colon.
- Treatment options for HCC and prognosis are dependent on many factors especially on tumor size and staging.
- Tumor grade is also important
Q.132. What is the risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma?
Correct Answer : D
Main risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma-
1) Alcoholism 2) Hepatitis B 3) Hepatitis C (25% of causes globally)[3] 4) Aflatoxin 5) Cirrhosis of the liver 6) Hemochromatosis 7) Wilsons disease 8) Type 2 Diabetes (probably aided by obesity) 9) OCP 10) Tobacco 11] Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) most commonly appears in a patient with chronic viral hepatitis (hepatitis B or hepatitis C, 20%) or/and with cirrhosis (about 80%).
Q.133. Risk of colorectal cancer recurrence is strongly related to which of the following?
Correct Answer : A
Older patients tend to have more aggressive tumors, and the risk of recurrence increases with age at diagnosis.
Q.134. What is the treatment for refractory hiccup?
Correct Answer : A
Chlorpromazine, Carbamazepine, Nifedipine, Nimodipine, Baclofen, Metoclopramide, Haloperidol, Ketamine, Phenytoin, and Lidocaine
Q.135. What is the most specific characteristic of hiatal hernia?
Correct Answer : C
Hiatal hernias can cause stomach acid to reflux into the esophagus, leading to heart burn, which is a hallmark symptom.
Q.136. A 20-year-old male found to have Hepatitis B surface antibodies. Which of the following is most likely cause?
Correct Answer : B
This is indicative of a previous vaccination.
Q.137. An alcoholic patient is known to have association with which of the following?
Correct Answer : B
Alcoholism causes macrocytic anemia, where RBCs are larger than there normal size. This is reflected by a high MCV due to alcohol interfering with vitamin B12 absorption, which is essential for RBC production.
Q.138. A patient presented with peptic ulcer, which of the following supports the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Pressing on the upper abdomen often elicits pain, a common physical exam finding in peptic ulcers.
Q.139. In a patient with primary biliary cirrhosis which drug will help in restoring the histology of the liver?
Correct Answer : D
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is a safe medical therapy for primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC)
Q.140. A female patient came with fatigue and jaundice. Her CBC shows WBC =9 , Hb= 9.5 ,PLT= 200 and his LFT show total bilirubin =5, direct = 0.9. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
- A rare inherited liver disorder characterized by mild jaundice with predominantly unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia.
- Normal liver enzymes and no other signs of liver damage support the diagnosis.
Q.141. A 70 year old presented with weight loss, fatigue, anemia, upper quadrant pain without any previous history, the stool showed high fat. He is a known smoker. What's the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
A combination of chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic carcinoma explains the symptoms.
Q.142. Which of the following causes reflux esophagitis?
Correct Answer : B
This asthma medication can relax the LES, allowing stomach acidto reflux into the esophagus and cause inflammation.
Q.143. A patient was diagnosed with acute pancreatitis and has low albumin. How do you provide nutrition to this patient?
Correct Answer : D
This method bypasses the stomach and pancreas, delivering nutrients directly to the jejunum. It reduces stress on the inflamed pancreas while ensuring proper nutrition and protein delivery to address low albumin levels.
Q.144. A patient has abdominal pain and was found to have gastric ulcer. All are predisposing factors, except?
Correct Answer : D
SUCRALFATE leads to the formation of a coat over the base of the ulcer and prevents the effects of HCL promotes the healing of ulcers.
Aggressive factors for peptic ulcer:
Acids, Pepsin, H.pylori infection, Alcohol & Smoking, Diet (spicy food), Drugs (NSAID, Corticosteroid), Stress.
Q.145. A patient had abdominal pain for 3 months. What supports the diagnosis of duodenal ulcer?
Correct Answer : C
Ulcer-related pain generally occurs 2-3 hours after meals and often awakens the patient at night and this pattern is believed to be the result of increased gastric acid secretion, which occurs after meals and during the late night and early morning hours when circadian stimulation of gastric acid secretion is the highest. Pain is often relieved by food, a finding often cited as being specific for duodenal ulcer.