
Hello,
Dr. Batman
Hello Doctor, Welcome!
Profile

Name: Batman
Email: batman@gotham.com
HAEMATOLOGY & ONCOLOGY REVIEW
(Total Questions - 71)Q.1. Which is not an indication for warfarin use?
Correct Answer : A
Q.2. Patient with Polycythemia vera took a bath then experienced a generalized itch all over the body. Which of the following statement best explains this phenomenon?
Correct Answer : A
Q.3. Man with polycythemia vera came with bruising, what causes decreased blood flow in Polycythemia vera?
Correct Answer : A
Polycythemia vera: Clonal proliferation of erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets. Elevated erythrocyte mass is the most prominent feature Increased blood viscosity leads to symptoms such as headache, dizziness, pruritus, vertigo, or occlusive vascular lesions (eg, stroke and intermittent claudication)
Platelet and erythrocyte abnormalities may cause symptoms such as gum bleeding, epistaxis, gastrointestinal bleeding, and thromboembolism.
Treatment is mainly by regular phlebotomy to reduce packed cell volume. Early diagnosis and treatment strongly influence prognosis.
Q.4. What is the major difference that tells you that patient has Polycythemia vera and not a secondary polycythemia?
Correct Answer : B
Q.5. A young patient with polycythemia Vera has frequent bleeding episodes. What is the cause of bleeding in polycythemia vera?
Correct Answer : A
Thrombosis and bleeding are frequent in persons with polycythemia vera (PV) and MPD, and the result from the disruption of hemostatic mechanisms because of (1) an increased level of red blood cells and (2) an elevation of the platelet count. There are findings that indicate the additional roles of tissue factor and polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMLs) in clotting, the platelet surface as a contributor to phospholipid-dependent coagulation reactions, and the entity of microparticles. Tissue factor is also synthesized by blood leukocytes, the level of which is increased in persons with MPD, which can contribute to thrombosis. Rusak et al evaluated the hemostatic balance in patients using thromboelastography and also studied the effect of isovolemic erythrocyte apheresis on patients with polycythemia vera. They concluded that thromboelastography may help to assess the thrombotic risk in patients with polycythemia vera Hyperhomocysteinemia is a risk factor for thrombosis and is also widely prevalent in patients with MPD (35% in controls, 56% in persons with PV). Acquired von Willebrand syndrome is an established cause of bleeding in persons with MPD, accounting for approximately 12-15% of all patients with this syndrome. von Willebrand syndrome is largely related to the absorption of von Willebrand factor onto the platelets; reducing the platelet count should alleviate the bleeding and the syndrome.
Q.6. Which of the following findings correlate with iron deficiency anemia?
Correct Answer : A
Q.7. A 25-year-old male presents with easy bruising and a history of prolonged bleeding after minor cuts. Laboratory tests show prolonged bleeding time and a Factor VIII deficiency. He has no family history of similar symptoms. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Prolonged bleeding time, often associated with Factor VIII deficiency because von Willebrand factor stabilizes Factor VIII in circulation.
Hemophilia A is clotting factor VIII deficiency & Involves Factor VIII deficiency but does not cause prolonged bleeding time.
Q.8. A 75-year-old male presents to the clinic with fatigue, pallor, and dyspnea on exertion. Blood tests reveal hemoglobin: 9 g/dL. There is no history of overt bleeding. Physical examination is unremarkable, and there is no organomegaly. What is the most appropriate investigation to determine the cause of his anemia?
Correct Answer : C
Anemia is a common sign of colon cancer in elderly
Q.9. Which one of the following factors is a high-risk factor for chronic lymphocytic leukemia?
Correct Answer : A
Risk factors: 1) Age. Most people diagnosed with chronic lymphocytic leukemia are over 60 2) Sex. Men are more likely than women to develop chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 3) Race. Whites are more likely to develop chronic lymphocytic leukemia than people of other races. 4) Family history of blood and bone marrow cancers. A family history of chronic lymphocytic leukemia or other blood and bone marrow cancers may increase your risk. 5) Exposure to chemicals. Certain herbicides and insecticides.
Q.10. 60 years old male patient presented in ER due to respiratory distress. He was referred to you after stabilization in ER. His lab investigations showed Hgb 8.5 g/l, hematocrit 64%, RBC= 7.8 million/mm3, WBC= 18300 /mm3 & Platelet= 570,000. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.11. All the following are indications of IV deferoxamine EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
Q.12. Blood film picture shows ring-like structure in the RBC. What is the diagnosis?
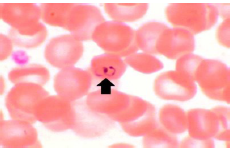
Correct Answer : A
Q.13. Patient with Hodgkin’s lymphoma has reed-Sternberg cells in pathology report and there are eosinophilic lymphocyte in blood sample. What is the pathological classification of the disease?
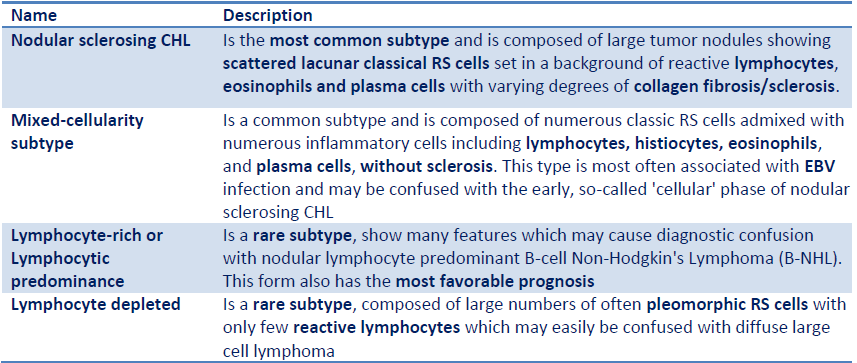
Correct Answer : A
Classical Hodgkin's lymphoma can be subclassified into 4 Pathologic subtypes based upon Reed-Sternberg cell morphology and the composition of the reactive cell infiltrate seen in the lymph node biopsy specimen “the cell composition around the Reed-Sternberg cells”.
Q.14. What is the drug of choice in reversing heparin-induced bleeding in case of life-threatening bleeding?
Correct Answer : B
Q.15. What is the appropriate treatment of choice for von Willebrand disease?
Correct Answer : B
Q.16. Patient with CML taking imatinib, mesylate and Ondansetron. He presented in an ER with tachycardia, fever, diaphoresis, flushing and hyperreflexia. What is the possible complication?
Correct Answer : D
Q.17. Patient presented in your clinic with fatiguability. His CBC was: Hb: 9.6 g/dl, WBC: 5800 (Neutrophils: 68%, Lymphocytes: 38%, Monocytes: 4%, Eosinophils: 2%, Basophils: 0.5%, Myeloblasts: 4%, Myelocytes: 1%, Metamyelocytes: 0.3%). What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Q.18. weeks. Physical examination reveals pallor, mild hepatosplenomegaly, and petechiae. Laboratory findings: WBC count: 75,000/µL, RBC count: 3.2 million/µL, Hemoglobin: 8.5 g/dL, Platelets: 45,000/µL, Peripheral smear: circulating leukemic blasts ,Bone marrow biopsy: Hypercellularity with >20% myeloblasts, Cytochemistry: Positive myeloperoxidase stain. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.19. A 10-year-old boy, known case of Sickle Cell Anemia (SCA), presents with a hemoglobin level of 7 g/dL and reticulocyte count of 12%. He reports recurrent painful swellings in his hands, feet, and elbow over the past few months. Physical examination reveals tender, swollen joints and no signs of infection. What is the prophylactic treatment for this patient?
Correct Answer : B
Hydroxyurea is the standard prophylactic treatment in SCA to reduce the frequency of painful vaso-occlusive crises and acute chest syndrome.
Q.20. A 25-year-old male presents with a painless swelling in the left testicle that he noticed 3 weeks ago. On examination, the swelling is firm, non-tender, and does not transilluminate. There is no history of trauma or infection. His scrotum appears normal without skin changes or erythema. Ultrasound of the testicle reveals a hypoechoic mass with increased vascularity. Tumor markers show: Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP): Normal, Beta-Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (Beta-hCG): Elevated, Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH): Elevated. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Seminoma is the most common radiosensitive testicular cancer and typically presents as a painless, firm, non-tender swelling in young males.
Q.21. Patient came to you for routine checkup in an OPD and you confirmed that the patient has sickle cell disease. He did not come with any specific illness. What will you do next?
Correct Answer : D
Q.22. What is TRUE regarding Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma?
Correct Answer : A
Q.23. In polycythemia, what is the cause of anemia?
Correct Answer : B
Q.24. A 25-year-old female presents with a 6-month history of night sweats, unintentional weight loss, and fatigue. On examination, she has splenomegaly and palpable lymphadenopathy in the cervical region. Blood work shows anemia and elevated ESR. A lymph node biopsy reveals the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells.What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.25. Which of the following gives the most accurate prognosis for Chronic lymphocytic leukemia?
Correct Answer : A
Q.26. What is the therapeutic range of INR during treatment with Anticoagulant?
Correct Answer : B
Normal range in absence of anti coagulant - 0.8-1.2
Q.27. What's the most common symptom of soft tissue sarcoma?
Correct Answer : B
Q.28. A 12-year-old patient with a known history of sickle cell anemia (SCA) comes for a routine follow-up. The doctor is planning to administer the pneumococcal vaccine as part of the preventive care to reduce the risk of infections. Which of the following is TRUE regarding pneumococcal vaccination in this patient?
Correct Answer : A
Q.29. A 10-year-old patient, known case of sickle cell anemia (SCA), was admitted to the hospital due to an acute painful vaso-occlusive crisis. The patient was treated with IV fluids, analgesics, and oxygen therapy as needed. The acute attack has resolved, and the patient is stable. You are preparing to discharge the patient. Which of the following drugs should the patient be discharged on to reduce the frequency of future crises?
Correct Answer : A
Penicillin prophylaxis is essential in younger patients (<5 years) to prevent pneumococcal infections but may not be continued in older patients depending on their vaccination status.
Q.30. In which of the following diseases the splenectomy is NOT a management option?
Correct Answer : D
Q.31. A 23-year old white female is diagnosed to have chronic ITP. Which of the following will best predict a favorable remission after splenectomy?
Correct Answer : D
Q.32. All of the following drugs are contraindicated in G6PD deficiency, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : A
Drugs & medications that can induce hemolysis in G6PD deficiency patients include: acetanilide, doxorubicin, Methylene blue, naphthalene, nitrofurantoin, primaquine, pamaquine & sulfa drugs.
Q.33. How to differentiate low iron levels from Iron deficiency anemia and Anemia of chronic disease?
Correct Answer : A
Low in IDA
Q.34. A 26-years old man presented in a clinic with a complaint of headache and fatigue. Investigations revealed: Hb= 8 g/dl, MCV= 85 fL, reticulocyte =10%. All the following investigations are relevant to the case EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
This is a case of hemolytic anemia.
Iron deficiency anemia causes decrease in bone marrow production of RBC so reticulocyte count wouldn’t be high
Q.35. Hb electrophoresis done for a patient shows HbA1=58%, HbS = 35%, HbA2 = 2%, HbF = 5 %. What is the most likely diagnosis?
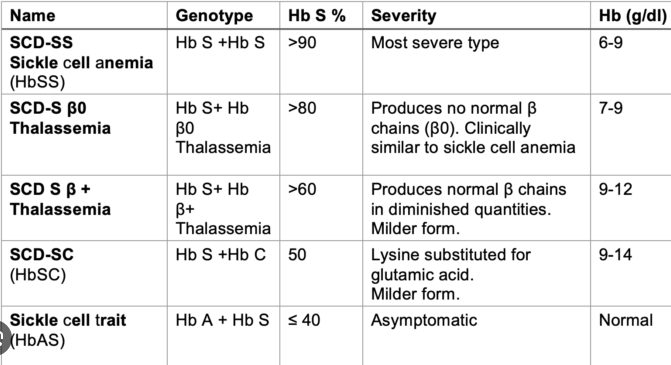
Correct Answer : C
Sickle cell anemia: In sickle cell trait, usually see HbS concentrations of 35 to 45% of total Hemoglobin because the HbS has a slower rate of synthesis than HbA. If HbS is less than 33%, start thinking about S-alpha-thalassemia. If HbS is greater than 50%, worry about S-Beta-thalassemia or Sickle cell disease with transfusion.
Q.36. A 55-year-old male patient presents for a routine checkup. On physical examination, the patient appears well with no abnormal findings. However, lab investigations reveal microcytic hypochromic anemia with a hemoglobin level of 9 g/dL. Which of the following is a possible cause for this patient's anemia?
Correct Answer : B
Iron deficiency anemia- Microcytic hypochromic anemia is most commonly associated with iron deficiency anemia, where there is a lack of adequate iron for hemoglobin production. This leads to smaller (microcytic) and paler (hypochromic) red blood cells.
Q.37. A 45-year-old male patient presents to your clinic with concerns about his overall health. He is a regular smoker, smoking approximately 10 cigarettes a day for the past 20 years. He has no history of significant medical conditions but expresses concern about the risks associated with smoking. After a thorough examination, you need to provide advice regarding health risks. Which of the following conditions carries the lowest risk for this patient due to his smoking history?
Correct Answer : B
Q.38. A 45-year-old female presents with a history of malaise, fatigue, and decreased meat intake in her diet. On examination, she appears pale. Laboratory results reveal a hemoglobin level of 9 g/dL, and a peripheral blood smear shows hypochromic, microcytic anemia. What is the most appropriate management?
Correct Answer : C
She has Iron deficiency anemia
Q.40. What is the investigation of choice to diagnose Thalassemia minor?
Correct Answer : A
Autosomal Recessive disorder; Inheriting defect genes from both parents; Thalassemia major, but from one parent; Thalassemia Minor.
By Serum electrophoresis
Q.41. What is the main prognostic factor for Leukemia?
Correct Answer : A
Q.42. What is the critical count of platelets that leads to spontaneous bleeding?
Correct Answer : A
Q.43. Serum ferritin levels reflect which one of the following?
Correct Answer : A
Serum iron is reflected by TIBC which is an indirect measure of transferrin.
Q.44. 32-year old Saudi man from Eastern province came to you for routine pre-employment physical exam. He has always been healthy and his examination is normal. Lab: HCT: 35% MCV: 63fL WBC: 6800/ul, retics: 4000/ul (0.7%) Platelet: 27000/ul, stool: -ve for occult blood. What do you do next for diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
This is a case of Thalassemia.
Q.45. A 68 year old businessman is newly diagnosed to have hepatocellular carcinoma. Which of the following is true regarding disclosure (informing patient)?
Correct Answer : D
Patient with malignancy: telling the patient is by the most senior doctor, whether or not to tell the patient is individualized according to the patient's wish and sometimes the family depending upon his mental capacity.
Q.46. Which of the symptom of Hodgkin lymphoma is not seen in non-Hodgkin lymphoma?
Correct Answer : D
Q.47. Patient presented in ER with weakness of left half of the body and he had a history of swollen painful hands and feet. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.48. A 40-year-old female presents with fatigue, pallor, and shortness of breath on exertion. Laboratory investigations show a macrocytic anemia with a high mean corpuscular volume (MCV), but the peripheral blood smear does not show megaloblasts. What is the most likely cause of the macrocytic anemia in this patient?
Correct Answer : C
Q.49. A 7-year-old boy presents with a painless neck mass that has been gradually increasing in size over the past 5 weeks. He has also been experiencing fatigue, generalized pruritus (itching), and a mild cough during this period. There is no history of trauma or fever. On examination, there is a non-tender, firm cervical lymphadenopathy, and no signs of acute infection. What is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
Correct Answer : A
Clincher - Painless neck mass
Q.50. Increased bleeding time is seen in which of the following?
Correct Answer : C
Q.51. A 25-year-old male patient presents to the emergency department with pain and swelling in his left knee after a minor trauma. On examination, the knee is swollen, and there is tenderness on palpation. The joint is warm, and there is difficulty in moving the knee. A joint aspiration reveals blood in the joint (hemarthrosis). The patient denies any history of significant trauma or bleeding tendencies but reports occasional easy bruising. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Factor V and VIII deficiency of the two factors was accompanied by a life-long bleeding tendency in males
Q.52. A 30-year-old male presents to the emergency department after a traumatic injury to his right knee. He was involved in a motor vehicle accident and reports immediate pain and swelling in the knee. On examination, the knee is significantly swollen, warm, and tender to palpation. The patient is unable to fully extend the knee due to pain. What is the most likely underlying pathophysiology?
Correct Answer : B
After trauma to the knee, the most common underlying cause of significant swelling is hemarthrosis, which refers to the presence of blood within the joint space.
Q.53. A 32-year-old female patient presents with a 2-week history of periorbital swelling, generalized itching, and fatigue. She also reports recent weight loss and a feeling of fullness in her abdomen. On examination, the patient has noticeable periorbital swelling, generalized pruritus (itching), lymphadenopathy, and both hepatomegaly and splenomegaly. Laboratory tests show an elevated white blood cell count, with a predominance of eosinophils. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
The combination of periorbital swelling, generalized pruritus, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and an eosinophilic predominance in the blood is highly suggestive of Tropical eosinophilia.
Q.54. Name the food that causes bleeding in a patient who is on anticoagulants?
Correct Answer : D
Q.55. Which one of the following is a prognostic factor for CML?
Correct Answer : B
In CML there is chromosomal translocation (Philadelphia) .CML was the first malignancy to be linked with a clear genetic abnormality.
Q.56. Iron deficiency anemia will have which of the following?
Correct Answer : B
In anemia of chronic disease without iron deficiency, ferritin levels should be normal or high, reflecting the fact that iron is stored within cells, and ferritin is being produced as an acute phase reactant but the cells are not releasing their iron.
In iron deficiency anemia ferritin should be low.
TIBC should be high in genuine iron deficiency, reflecting efforts by the body to produce more transferrin and bind up as much iron as possible;
TIBC should be low or normal in anemia of chronic.
Q.57. Fresh frozen plasma is given in which of the following condition ?
Correct Answer : D
Q.58. Target cells on peripheral smear are seen in which of the following condition?
Correct Answer : A
Q.59. A 25-year-old male presents to the clinic complaining of generalized fatigue and weakness over the past few months. He also reports feeling more easily winded during physical activities, which is unusual for him. On physical examination, the physician notices that his nails are spoon-shaped (concave), and the patient mentions that he has also been experiencing occasional headaches and dizziness. His medical history is otherwise unremarkable, and he does not have any history of trauma or infections. Laboratory results reveal: Hemoglobin: 10 g/dL (low), Ferritin: Low, Total iron-binding capacity (TIBC): High. what is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.60. Leukemia with blast cells are seen in?
Correct Answer : B
Q.61. A 30-year-old female patient presents with fatigue and weakness. Laboratory results show: Low serum iron levels, High aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels, High mean corpuscular volume (MCV), A peripheral blood smear shows no evidence of megaloblasts. What is the most likely cause?
Correct Answer : A
Q.62. A 22-years old with low Hb, low PLT ,and high WBC, peripheral smear shows blast cell with large nucleus, scanty cytoplasm and positive myeloperoxidase test and negative esterase. What's the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.63. A 40-year-old male patient is brought to the emergency room after a traumatic injury. His blood type is identified as A, and during the initial treatment, he is accidentally transfused with blood of group B. The medical team realizes the mistake shortly after the transfusion and begins to assess the patient for any potential complications. What is the likely complication?
Correct Answer : C
Q.64. Which of the following is a feature of iron deficiency anemia?
Correct Answer : A
Q.65. A 46-year old patient, on chemotherapy. presented in an emergency room with fever, all should be done EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : C
Explanation: Because of its SE it should be discussed thoroughly.
Q.66. A 70 years old patient, presented in a clinic with investigations that showed osteolytic lesion in skull, monoclonal spike, rouleux formation. What is the most probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.67. A young male who is a known case of sickle cell anemia presented with severe abdominal pain & joint pain. He is usually managed during hospitalization. how should he be managed now?
Correct Answer : A
Q.68. 22-year old, a known case of sickle cell anemia, Last year, he was hospitalized twice in hospital because of abdominal pain. Now he presented with abdominal pain, back pain and chest pain, how will you manage??
Correct Answer : A
Q.69. A 38-year old female patient came in the clinic with complaint of fatigue, muscle weakness, paranesthesia in the lower limbs and unsteady gait. What is the next step in the management?
Correct Answer : B
Q.70. What is the best treatment for DVT patients initially that is cost effective also?
Correct Answer : A
Enoxaparin
Q.71. What is the role of Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) in the treatment of DVT, and how does it compare to warfarin?
Correct Answer : C
Low-molecular-weight heparin is a relatively recent addition to the list of therapies for prophylaxis and treatment of deep venous thrombosis (DVT). As a prophylactic, low-molecular-weight heparin is as effective as standard heparin or warfarin and does not require monitoring of the activated partial thromboplastin time or the International Normalized Ratio.