
Hello,
Dr. Batman
Hello Doctor, Welcome!
Profile

Name: Batman
Email: batman@gotham.com
INFECTIOUS DISEASE REVIEW
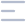
(Total Questions - 61)Q.1. Which of the following is treatment for Giardiasis?
Correct Answer : C
Metronidazole is the drug of choice for Giardia. It damages the parasite's DNA, stopping it from functioning and helping your body clear the infection.
Incorrect options-
- Praziquantel works on flat worms not Giardia.
- Mebendazole and Albendazole work on roundworms and whipworms, so they won't help against Giardia.
[Giardiasis “Beaver fever” is a diarrheal infection of the small intestine by a parasite: Giardia lamblia - Fecal-oral transmission]
Q.2. A patient with central line developed sepsis, which of the following is the causative organism?
Correct Answer : A
Staph. aureus is a common pathogen that can sneak into the blood stream through a cental venous line, causing infection.
Incorrect option-
- Neisseria usually causes reproductive system infections.
- Pseudomonas are less commonly associated with central venous line infection.
- E.coli is mostly involved in gut or urinary infections.
[All catheters can introduce bacteria into the bloodstream, but CVCs are known for occasionally causing Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis sepsis. Also can be caused by gram-negative rods, Candida spp., and Enterococcus spp.].
Q.3. Which of the following is the best way to prevent infection by Entamoeba histolytica?
Correct Answer : A
Boiling water is like a heat shield that destroys Entamoeba histolytica, making water and food safe to consume.
Incorrect options-
- Other options doesn't guarantee killing the bug.
[Fecal-Oral transmitted parasite; the most important complication is Liver abscess; Treatment - Metronidazole].
Q.4. In prevention of Lyme disease in kids, what is the best advice to parents?
Correct Answer : C
Ticks can attach to clothes while kids play outside. Washing in hot water and drying with heat acts like a tick destroying furnace, ensuring their destruction.
Incorrect options-
- Tick removal is an important step if a tick is found.
- Boiling not practical for cleaning clothes.
- Antiseptics are good for wounds but do not kill ticks.
Q.5. A 24-year-old patient came for checkup after having a promiscuous relation 1 month ago, he was clinically unremarkable, VDRL: 1/128, he is allergic to penicillin. What's the line of management?
Correct Answer : D
Doxycycline and tetracycline are alternatives if the patient has allergy to penicillin.
Incorrect options-
- Ampicillin and Amoxicillin are penicillin based and unsafe for this patient.
- Trimethoprim is not effective for treatment of syphilis.
[The first choice for uncomplicated syphilis is a single dose of intramuscular penicillin G or a single dose of oral azithromycin].
Q.6. Which of the following drugs is used for Leishmania?
Correct Answer : D
Sodium stibogluconate is a specialized medicine designed against Leishmania parasite.
Incorrect options-
- Azithromycin and Clarithromycin are used in bacterial infection not parasitic.
- Streptomycin is used for bacterial infection not parasitic.
Q.7. How do you prevent Lyme disease?
Correct Answer : D
- Light-colored clothing makes the tick more easily visible before it attaches itself.
- People should use special care in handling and allowing outdoor pets inside homes because they can bring ticks into the house.
- A more effective, communitywide method of preventing Lyme disease is to reduce the number of primary hosts on which the deer tick depends, such as rodents, other small mammals, and deer.
- Reduction of the deer population may over time help break the reproductive cycle of the deer ticks and their ability to flourish in suburban and rural areas. The areas around ornamental plantings and gardens are more hospitable for mice and ticks. The highest concentration of ticks is found in wooded areas.
- Individuals should try to prevent ticks from getting onto the skin and crawling to preferred areas.
- Long hair should be worn under a hat. Wearing long-sleeved shirts and tucking long pants into socks is recommended.
Q.8. What advice will you give to the parents for prevention of Lyme disease?
Correct Answer : A
The best prevention is targeting and eliminating the carrier of lyme disease which are ticks, before they cause harm.
Q.9. What is the drug of choice for schistosomiasis?
Correct Answer : A
Praziquantel is the go-to medicine for schistosomiasis. It targets and kills the parasites causing the infection.
Incorrect options-
- Oxamniquine works but isn't as effective or commonly used.
- Artemether is used in treating malaria.
Q.10. A man had received blood transfusion back in 1975, now he developed jaundice. What is he likely to develop?
Correct Answer : B
As the scenario mentions that the blood transfusion was done in 1975, the blood wasn't screened most probably. So the man likely got infected through this transfusion. Hepatitis C leads to liver issues like jaundice which can appear years later.
Incorrect options-
- Hepatitis A/E spreads through feco-oral route.
- Hepatitis D needs Hepatitis B for co-infection.
Q.11. Best method to prevent plague is?
Correct Answer : B
Plague is a deadly infectious disease caused by the enterobacteria Yersinia pestis, carried by rodents mostly rats. Eliminating them stops the disease at its source, preventing it from spreading to humans.
Q.12. A patient presented to the ER with gunshot injury, a part of his bowel came out, you decide to give him antibiotic for Bacteroid fragilis, which of the following drugs will you give?
Correct Answer : B
The best antibiotic in this case is Clindamycin because it works well against Bacteroides fragilis and other gut bacteria, and it penetrates tissue effectively.
Incorrect options-
- Amoxicillin is not suitable due to resistance.
- Doxycycline is used for Chalmydia.
- Gentamycin targets gram negative bacteria but not Bacteroides fragilis.
Q.13. What is the treatment of peritonitis, if the organism is Bacteroid fragilis?
Correct Answer : B
[B. fragilis is involved in 90% of anaerobic peritoneal infections].
B. fragilis is susceptible to-
- metronidazole, carbapenems, tigecycline, beta-lactam/beta-lactamase inhibitor combinations (e.g., Unasyn, Zosyn), and certain antimicrobials of the cephamycin class, including cefoxitin.
Incorrect options-
- Clindamycin is no longer recommended as the first-line agent for B. fragilis due to emerging high-level resistance.
- Carbapenem is effective but reserved for more severe cases due to concerns about resistance.
- Amoxicillin doesn't work against it as Bacteroides are resistant to it.
Q.14. A 17-year-old boy admits to be involved in recurrent illegal drug injection, what is the screening test that you will order?
Correct Answer : C
In the given scenario its essential to screen for HIV, Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis C. However, Hepatitis C is the most common and concerning due to its high prevelance among IV drug abusers and has the potential to cause choronic liver damage.
Q.15. In a patient with gonorrhea infection, what else do you want to check for?
Correct Answer : A
When a patient is diagnosed with gonnorhea it's important to check for Chlamydia trachomatis because these to infections often occur together. Both are common STIs with similar risk factors and symptoms.
Q.16. A patient came to the ER after RTA, splenic rupture was clear, what is the next step in his management?
Correct Answer : B
If a patient has splenic rupture the next step is to give antibiotics for prophylaxis, even if they have been vaccinated against pneumococcus. This is because after splenectomy, the patient is on a higher risk for infections, especially from Streptococcus pneumoniae, and the spleen's role in fighting bacteria is lost.
Incorrect options-
- Pneumococcal vaccine is important but not the immediate next step.
- MMR vaccine is not relevant.
- None is not an option as immediate action is needed.
Q.17. Which of the following is an indication for pneumococcal vaccine?
Correct Answer : D
- The pneumococcal conjugate vaccine is currently recommended for all children under 5 years of age.
Polysaccharide pneumococcal vaccine that is currently recommended for use-
- 1) All adults who are older than 65 years of age
- 2) Persons who are 2 years and older and at high risk for disease (e.g., sickle cell disease, HIV infection, or other immunocompromising conditions).
- 3) Adults through 64 years of age who smoke cigarettes or who have asthma
Q.18. What are the characteristics of Yersinia bacteria ?
Correct Answer : B
Yersinia bacteria is a Gram-negative organism.
- It causes self-limited enterocolitis, fever & bloody watery mucoid diarrhea, which can be confused with appendicitis, so it is called Pseudoappendicitis.
Q.19. A man presents with painless ulcer on his penis with indurated base and everted edge, what's the likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
The features mentioned above regarding the ulcer are strongly indicating towards syphilis. This is because the first stage of syphilis presents with a chancre, a firm painless ulcer with a clean base.
Incorrect options-
- Gonorrhea causes discharge and pain, not painless ulcer.
- Chancroid causes painful, soft ulcers with ragged edges.
- HSV causes a painful, recurrent sore, often with tingling or burning sensations.
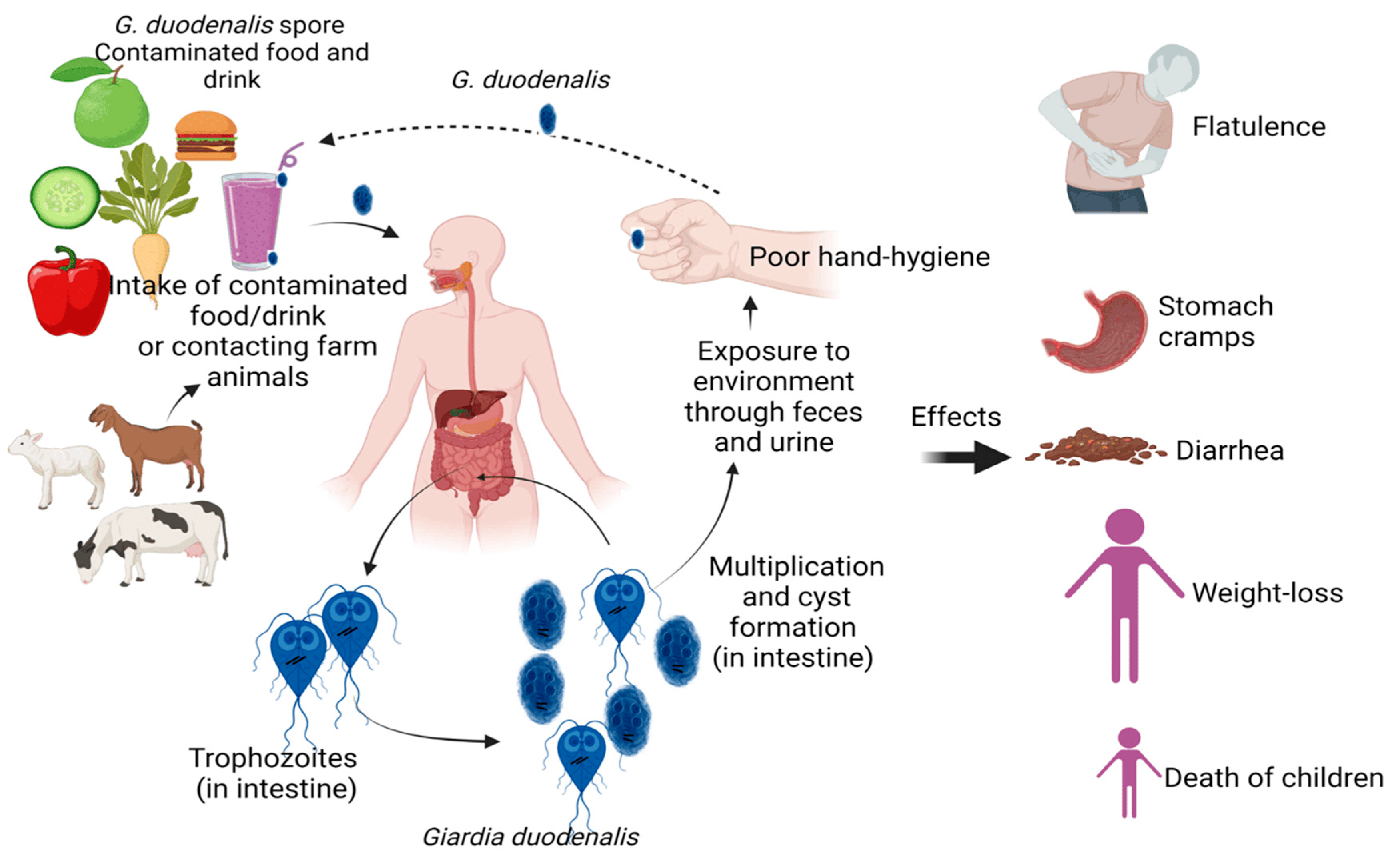
Q.20. Leishmania transmission occurs by which of the following?
Correct Answer : A
Leishmaniasis is transmitted by sand fly, which bite infected rodents and then pass the parasite to humans when they bite.
Q.21. Which of the following is NOT transmitted by mosquitoes?
Correct Answer : C
Relapsing fever, is an infection caused by certain bacteria in the genus Borrelia. It is a vector-borne disease transmitted through the bites of lice or soft-bodied ticks.
Incorrect options-
- Rift Valley fever, is most commonlycaused by the Aedes mosquito.
- Yellow fever, viral hemorrhagic fever are transmitted by infected mosquitoes.
- Filariasis, Lymphatic filariasis is transmitted by different types of mosquitoes for example by the Culex mosquito.
Q.22. A patient presents with previous history of EBV and +ve culture for EBV what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
The diagnosis is infectious mononucleosis. It's caused by EBV, and the positive culture and patient's history confirms the infection.
Q.23. Trichotillomania is treated by which of the following medication?
Correct Answer : A
Fluoxetine is the correct treatment ofr Trichotillomania because it's an antidepressant that helps regulate serotonin levels, reducing the urge to pull hair.
Incorrect options-
- Amoxicillin,Azithromycin are antibiotics used to treat bacterial infection.
- Clomipramine is another antidepressant that can also help, but it may cause more side effects compared to fluoxetine.
Q.24. A pregnant lady presents with cystitis, which one of the following drugs is contraindicated in her case?
Correct Answer : C
In a pregnant woman with cystitis, Fluoroquinolones are contraindicated because they can harm fetal bone and cartilage development, particularly in the second and third trimester.
Q.25. A pregnant woman with UTI has penicillin allergy, which drug will you prescribe?
Correct Answer : A
Nitrofurantoin is the best choice becuase it's safe and effective during pregnancy.
Q.26. A male patient gave history of left knee swelling & pain since 5 days, two days back he had right wrist swelling & redness. He had recently traveled to India. On examination there was tenderness & limitation of movement. 50 cc of fluid was aspirated from the knee. Gram stain showed gram negative diplococci. What is the most likely organism?
Correct Answer : B
As gram-negative diplococci were present on staining, it is suggestive of Neisseria gonorrhoeae the bacterium responsible for gonnorhea. The patient is most probably suffering from gonococcal arthritis, which explains the joint symptoms.
Q.27. A patient has infection with EBV, during abdominal examination he became pale with tender LUQ, what should be done next?
Correct Answer : B
Given the patients history our main concern is a splenic rupture, which is a complication of infectious mononucleosis. The urgent CT scan is best next step to confirm this.
Other options-
- IVF is necessary if the patient has hypotension, but diagnosis the rupture is our first priority.
- Rushing to OR- Surgery might be the definitive treatment but diagnosis comes first.
- Adrenaline IV is not relevent as there is no allergic reaction.
Q.28. A person living in an area with malaria outbreak comes to you for advice, what is the common way to prevent getting infected in this scenario?

Correct Answer : A
To prevent malaria in areas with outbreaks, the most effective approach is vector eradication and avoiding mosquito bites.
Q.29. Which of the following is treatment of EBV if the patient presents with tonsillar exudates, lymphadenopathy, and splenomegaly?
Correct Answer : D
Treatment of patients with infectious mononucleosis generally includes-
Supportive care-
- Rest to allow body to recover
- Use pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen for fever and discomfort.
Q.30. The following can be used as prophylaxis for malaria in chloroquine resistant area, except?
Correct Answer : D
In chloroquine-resistant areas, Dapsone is not used for malaria prophylaxis.
- The other options, doxycycline, chloroquine with proguanil, and pyrimethamine, are effective for preventing malaria in these reigons.
Q.31. What is the best method that can be adopted to prevent malaria?

Correct Answer : A
The best way to prevent malaria is by killing the vector that spreads it.
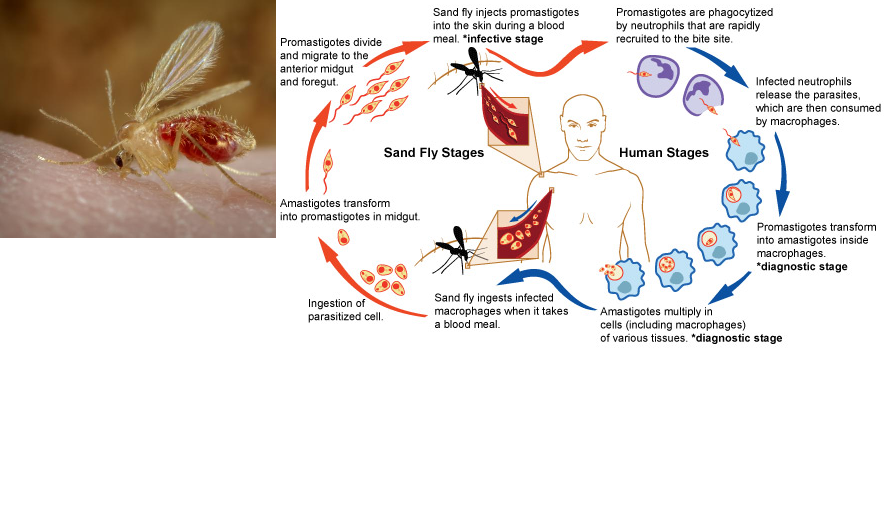
Q.32. Giemsa stained blood film is the diagnosis of which of the following infections?
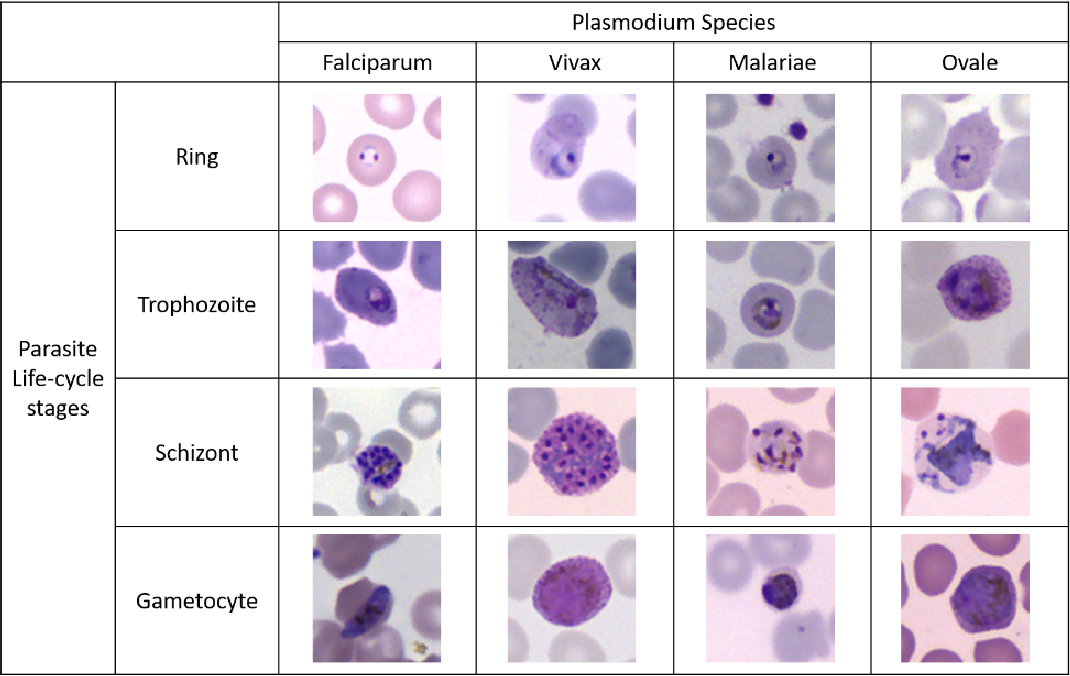
Correct Answer : A
Blood films are usually examined to investigate hematological problems (disorders of the blood) and, occasionally to look for parasites within the blood such as malaria and filaria.
Q.33. A patient presents with history of fever, his peripheral blood film is positive for malaria due to which of the following?
Correct Answer : B
The majority of malaria infection is caused by P. falciparum.
Q.34. Malaria in a child is due to which the following?
Correct Answer : D
Plasmodium falciparum is the most common and dangerous malarial parasite, especially in children and causes the majority of malaria-related deaths.
Incorrect options-
- P.vivax is a different species and its gametocytes are found in blood, not stool.
- Primaquine is used in liver stage of P.vivax not acute malaria.
- Treatment duration varies.
Q.35. German Measles (Rubella) causes which of the following feature?
Correct Answer : B
It can cause arthritis, especially in adult women. This is often called Rubella arthritis, affecting multiple joints.
Q.36. Regarding protective measures of malaria, all are true, except?
Correct Answer : A
The statement ''infection occurs more in day than night'' is incorrect because female Anopheles mosquitoes are most active during dusk and dawn.
Q.37. A 40-year-old white male is transferred to your institution, he suffers from septic shock less than 24 hours after onset of symptoms of a non-specific illness. He underwent a splenectomy for trauma 5 years ago. Antibiotic coverage must be directed against which of the following?
Correct Answer : D
After a splenectomy, the risk of infection by a capsulated bacteria, especially Streptococcus pneumoniae, increases because the spleen is vital for filtering such bacteria. Therefore, this organism is most likely cause of sepsis in this patient.
Q.38. What is seen in a gram negative bacterial septicemia ?
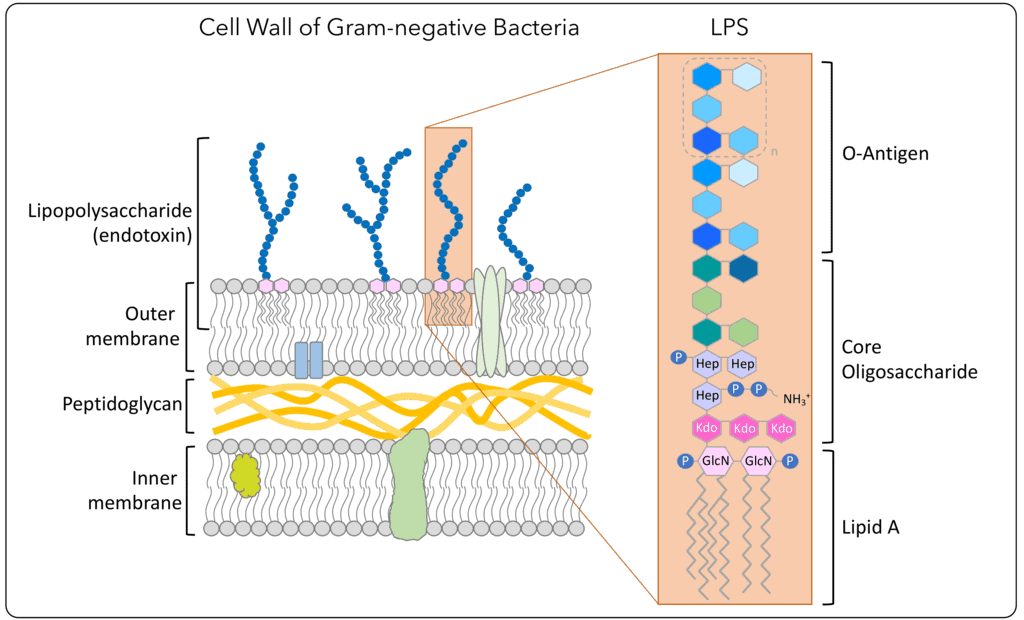
Correct Answer : B
Endotoxins are bacterial wall lipopolysaccharides that are responsible for many of the cellular and hemodynamic effects of septic shock. When the bacteria die endotoxins are released, triggering an intense inflammatory response that leads to fever, hypotension, and organ dysfunction.
Q.39. Characteristics of septic shock is?
Correct Answer : C
- The mortality rate in septic shock may reach up to 50%.
- Though gram-negative bacteria are the most common pathogens, other gram-positive and some fungi may cause it.
- It is more common in children, elderly, and immunocompromised patients.
- The most common primary sources of infection resulting in sepsis are the lungs, the abdomen, and the urinary tract, but in one-third of cases, no source is found.
Q.40. HSV type 1 infection of the oral cavity, all are true, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : C
Primary infection may be associated with fever & headache, all other choices are true
Q.41. Which medication should be given for Positive meningococcal TB?
Correct Answer : A
Rifampicin is given for 7 days as a preventive measure against meningococcal disease, especially for close contacts of someone who has the infection.
- Other options like ceftriaxone, aminophylline, or ranitidine are not suitable for prevention in this case.
Q.42. When assessing a hand injury caused by human bite which hand position carries the greatest risk of infection?
Correct Answer : B
When a human bite occurs during a fist fight, the clenched fist often impacts the teeth, leading to deep puncture wounds that can inoculate bacteria into joints and tendons, significantly increasing the infection risk.
Q.43. All true about cephalosporin use, except?
Correct Answer : A
Allergic reactions to cephalosporin are infrequent but may cause life-threatening reactions such as severe difficulty breathing and shock. It is common in penicillin-allergic patients.
Common side effects of Cephalosporin are mainly associated with digestive system:
- mild stomach cramps or upset, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. [These are usually mild and go away over time].
- Sometimes cause an overgrowth of fungi normally present in the body, causing mild side effects such as a sore tongue, mouth, or vaginal yeast infections.
Q.44. Cat bite predisposes to skin infection by which of the following organism?
Correct Answer : C
This bacterium is commonly found in the mouths of cats and is the primary cause of infections after cat bites.
Incorrect options-
- Staph. aureus can cause infection but is less common in cate bite.
- Streptococcus species can cause skin infection but are not frequent compared to pasteurella in cat bites.
- Legionella causes pneumonia and is not related to cat bites.
Q.45. What measures should we take for a human bite?
Correct Answer : B
Tetanus prevention is crucial for human bite wounds, as they carry a high risk of infection. A vaccine or booster shot helps prevent this serious complication.
Q.46. A boy who was bitten by his brother and received tetanus shot 6 months ago presented to you at clinic. His laceration was 1 cm and you cleaned his wound, what is the step next you will do?
Correct Answer : A
Human bites carry a high risk of infection due to oral bacteria. Even though the boy recently received a tetanus shot, an antibiotic like Augmentin is necessary to prevent infection.
Incorrect options-
- Suturing of wound is not recommended as it can trap bacteria and increase infection risk.
- A tetanus shot is unnecessary since the boy received one 6 months ago.
- Send home with close observation is insuuficient.
Q.47. Most common causes of hand infection is ?
Correct Answer : A
Most hand infections are bacterial and are the result of minor trauma that have been neglected. Human bite wounds are the second most common cause of hand infections.
Q.48. Rubella infection, which one of the following statement is true?
Correct Answer : C
Rubella:
- Spread - person to person
- Shedding of virus begins 7 days before the rash to 14 days after.
- The incubation period varies from 12 to 23 days (average, 14 days).
Signs and symptoms:
- Fever, rash, adenopathy, and arthralgia, arthritis is one of the rubella complications.
Q.49. A 15-year-old Saudi boy presented to the ER with fever, skin rash, and shock. He was resuscitated and admitted to the isolation ward with a strong suspicion of meningococcal meningitis. LP confirmed the diagnosis. Which one of the following statements are TRUE?
Correct Answer : B
Patient with meningococcal meningitis isolation for 24 hours after starting the antibiotics is of prime importance, since it spreads by droplet infection.
Chemoprophylaxis is given to contacts (including staff) who didn’t receive the vaccine in the past 2 years.
The chemoprophylaxis is ciprofloxacin 500 mg po OD (this is preventive, not therapeutic).
Q.50. Most common source of bacterial infection in I.V canula is ?
Correct Answer : C
The most common source of infection is through the skin by the flora present there which is staph. Epidermidis.
Q.51. In brucellosis, all of the following are true, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : A
This is incorrect because there is no strong evidence supporting that Brucella abortus causes a more severe disaease in children compared to B. melitensis, which is typically more virulant.
Q.52. Which of the following is appropriate method to prevent brucellosis ?
Correct Answer : C
Brucellosis “Malta fever, Maltese fever, Mediterranean fever”
It is a zoonotic infection caused by ingestion of unsterilized milk or meat from infected animals or close contact with their secretions [“Gm-ve Coccobacillus”].
Symptoms: Septicemia leads to “fever + sweating + migratory arthralgia and myalgia”
Treatment: Daily IM injections of streptomycin 1 g for 14 days and oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 45 days (concurrently).
Q.53. In brucellosis all of the following statements are true, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
Brucellosis typically does not cause gastroenteritis. Its main symptoms include fever, fatigue, joint pain, and organomegaly.
Q.54. Fecal leukocytes come with all of the following, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : B
Clindamycin-induced-colitis causes diarrhea due to inflammation of gut, but it typically does not lead to significant presence of WBCs in the stool.
Incorrect options-
- Shigellosis, idiopathic ulcerative colitis, salmonellosis- these conditions cause inflammation of gut, leading to white blood cells being sent to the area, which can appear in the stool.
Q.55. A patient with meningococcal meningitis was discharged as he is now asymptomatic, what is next step?
Correct Answer : B
Ceftriaxone is the best choice to eliminate meningococcal bacteria in asymptomatic carriers, preventing them from spreading the infection to others.
Q.56. A patient with 2nd syphilis received 2nd dose of penicillin and became hypotensive, what we should do?
Correct Answer : A
Hypotension is a serious reaction to penicillin, possibly signaling an adverse event like anaphylaxis. Stopping penicillin immediately is an essential step in preventing further worsening of condition.
Q.57. A patient presents with papules in the genital area with central umbilication, he has history of unprotected sex, what is the treatment of choice in this patient?
Correct Answer : A
Acyclovir is the treatment of choice for genital herpes, characterized by papules with central umbilication. It helps combat the HSV.
Incorrect options-
- Gancyclovir is used for CMV.
- Cefotaxime is an antibiotic.
- Cephalosporin is an antibiotic.
Q.58. A man travelled to a country, where there is endemic of onchocerciasis, he stays there for 1 week. His liability to get this disease is?
Correct Answer : C
Onchocerciasis requires repeated exposure to infected black fly bites over time. A short stay of one week poses no risk.
Q.59. A patient came with fatigue, weight loss and diarrhea. He received a blood transfusion when he was in kenea. He has low grade fever. The vitals are stable, on skin examination there is contagious molloscum in groin area. There is generalized lymphadenopathy and palpable liver, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
The correct diagnosis is HIV as it commonly causes symptoms like fatigue, weight loss, diarrhea, and fever. A history of blood transfusion in an area with high HIV prevelance increases the risk.
Q.60. In window period of hepatitis B which of the following markers are present?
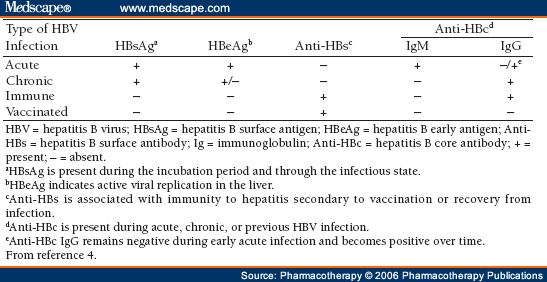
Correct Answer : A
HBc because during window period of hepatitis B, this core antigen is the firsst detectable marker before the body starts producing antibodies.
Q.61. A 12-year-old girl presents with malaise, fatigue, sore throat and fever. On examination there were petechial rash on palate, large tonsils with follicles, cervical lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly. All are complications except?
Correct Answer : D
Choronic active hepatitis because the combination of fatigue, malaise, fever, and hepatosplenomegaly points towards liver involvement.
Incorrect options-
- Encephalitis usually causes neurological symptoms like confusion or seizure's which aren't present.
- Transverse myelitis causes numbness and weakness, not described in this case.
- Splenic rupture would cause sudden abdominal pain, not seen here.