
Hello,
Dr. Batman
Hello Doctor, Welcome!
Profile

Name: Batman
Email: batman@gotham.com
NEPHROLOGY REVIEW
(Total Questions - 105)Q.1. A 62-year-old male with DVT and IVC obstruction due to thrombosis presents at your clinic. What's the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Nephrotic syndrome causes excessive protein loss in urine, which increases the risk of blood clots like DVT and IVC obstruction.
Incorrect options-
- SLE can cause clots but usually doesn't cause DVT/IVC obstruction as a main symptom.
- Christmas disease is a bleeding disorder.
- Nephritic syndrome is related to inflammation not blood clots or IVC obstruction.
Q.2. A patient with abdominal pain, hematuria, HTN and abnormality in chromosome 16 presents to you. What's the diagnosis?
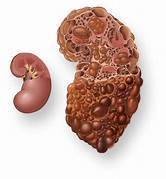
Correct Answer : A
PKD is a genetic disorder that causes cysts in the kidneys, leading to abdominal pain, hematuria, high BP, and abnormalities in chromosome 16.
Incorrect options-
- Horseshoe kidney is a congenital issue where kidneys are fused, it doesn't cause hematuria or high BP.
- Glomerulonephritis is the inflammation of kidney that causes hematuria and high BP, but not linked to chromosome 16.
- Goodpasture's syndrome is an autoimmune disease affecting the kidneys and lungs, not associated with chromosome 16.
Q.3. A patient with polydipsia and polyuria visits you. His serum osmolarity is high. Desmopressin induction shows no change in urine osmolarity and plasma osmolarity. What's the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
NDI occurs when kidneys don't respond to ADH, causing polyuria and polydipsia.
- Desmopressin acetate is a synthetic analog of ADH and can be used to distinguish central from nephrogenic DI. Desmopressin won't change urine osmolarity because the kidneys are resistant to it.
Incorrect options-
- Central DI is a condition in which the body doesn't produce enough ADH, but desmopressin would help increase urine concentration.
- Renal faliure causes reduced urine output and elevated BUN and creatinine, not high osmolarity.
- AKI is similar to renal faliure, typically leads to decreased urine output and abnormal blood tests.
Q.4. A female presented with features of thirst and polyuria, all her medical history is negative and she is not known to have any medical issues. She gave history of being diagnosed as bipolar and is on lithium. Her creatinine and BUN is normal. What is the cause of her presentation?
Correct Answer : A
Lithium used for bipolar disorder, can cause nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, leading to excessive urination and thirst.
Q.5. Adenosine dose should be reduced in which of the following cases ?
Correct Answer : B
Adenosine may not be effective at all in patients taking theophylline.
Q.6. What is the mode of inheritance in adult polycystic kidney disease?
Correct Answer : A
Adult polycystic kidney disease is inherited in autosomal dominant pattern, meaning one altered gene from either parent is enough to cause the condition.
Q.7. IVP study was done for a male & it showed a filling defect in the renal pelvis which was non-radio opaque. His U/S shows echogenic structure & hyper acoustic shadow. What's the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Uric acid stones are radiolucent meaning they dont show on X-rays, matching the IVP finiding of a non-radiopaque filling defect. On USG, they appear echogenic with a hyperacoustic shadow.
Q.8. A patient came with HTN, his KUB shows small left kidney, arteriography shows renal artery stenosis, what is the next investigation?
Correct Answer : B
Renal CT scan provides detailed images of the kidneys surrounding structures, helping assess kidney size and function confirming renal artery stenosis.
Q.9. What's the best way to diagnose post streptococcus Glomerulonephritis?
Correct Answer : A
Low C3 in post-strptococcal glomerulonephritis, the immune system is overactive, lowering C3 levels in the blood, which is a key indicator of the condition.
Q.10. A female patient did urine analysis which shows epithelial cells in urine, which part does it come from?
Correct Answer : C
Epithelial cells in urine usually come from urethra, as its lined with these cells, and shedding them is normal.
Q.11. A female presents with history of left flank pain radiating to groin with symptoms of UTI, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Renal colic is intense, cramping pain from kidney stone moving through the urinary tract. The pain starts in the flank and radiates to the groin, and the UTI symptoms fit this diagnosis.
Incorrect options -
- Appendicitis pain is usually in the right lower abdomen, not left flank.
- Diverticulitis causes pain in left lower abdomen not flank.
- Urolithiasis refers to kidney stones, but renal colic describes the pain caused by moving stone.
Q.12. What does pre-renal failure indicate?
Correct Answer : C
In pre-renal faliure, the kidneys try to conserve sodium to help raise blood volume, leading to low sodium levels in the urine [less than 20mmol/l].
Q.13. A patient with history of severe hypertension, normal creatinine, and 4g protein in 24 hours [urine]. Right kidney is 16cm & left kidney 7cm with features suggesting of left renal artery stenosis. What's the next investigation of choice?
Correct Answer : A
Renal angiography is the gold standard but done after CT/MRI as it is invasive.
Q.14. All of them are renal complications of NSAIDs, except?
Correct Answer : D
All are complications of NSAIDs but upper GI bleeding is not a renal complication.
Q.15. A patient has bilateral abdominal masses with hematuria, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
PKD is a genitic condition where cysts form in the kidneys, causing them to enlarge and press on the surrounding organse leading to abnormal masses and hematuria.
Q.16. Regarding acute glomerulonephritis all are acceptable investigations, except?
Correct Answer : D
Acute glomerulonephritis is the inflammation of the kidney filters, and investigations typically include urinanalysis, ANA, and blood cultures to find infections. Cystoscopy is not used because it examines the bladder and urethra, not the glomeruli in the kidneys.
Q.17. A 20-year-old female presents with fever, loin pain & dysuria, management includes all of the following, except?
Correct Answer : C
We suspect pyelonephritis. So, treatment includes admission, tests like urinanalysis,urine culture, blood culture. Antibiotic & re-hydration
Q.18. Urine analysis will show all, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : C
Urine analysis checks for components like phosphate, specific gravity, and proteins which give clue about kidney function. However concentrating capacity, which measures how well the kidneys adjust urine concentration is not directly assessed in a routine urine test.
Q.19. In acute renal failure all are true, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : C
In ARF kidneys can't filter waste leading to issues like high phosphate, uremia and high potassium. However,acid phosphatase, an enzyme linked to tissue like prostate, isn't typically affected.
Q.20. An old patient who is bedridden presents with bacteremia, the organism detected is enterococcus faecalis, what the source of infection?
Correct Answer : A
Enterococcus faecalis is commonly found in urinary tract, and bed ridden patients often have a higher risk of UTIs due to difficulty urinating, catheter use, and a weakened immune system.
Q.21. A 56-year-old's CBC showed Hb=11, MCV= 93, Reticulocyte= 0.25%. What's the cause?
Correct Answer : A
The kidney plays a key role in producing erythropoietin, a hormone that signals the bone marrow to make RBCs. In CRF, reduced erythropoietin leads to decreased RBC with normal MCV, and a low reticulocyte count shows poor RBC production.
Incorrect oprions-
- Liver disease usually cause macrocytic anemia.
- Sickle cell anemia involves abnormal shaped cells and often shows a high reticulocyte count.
- G6PD deficiency leads to hemolysis with high reticulocyte.
Q.22. A 30-year-old with repeated UTIs, which of the following is a way to prevent her condition?
Correct Answer : A
Staying hydrated helps the bacteria to pass out of the urinary tract, reducing the risk of infections.
Q.23. A 65-year-old presented with acute hematuria, passage of clots, left loin and scrotal pain. What's the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Blood in urine with loin and scrotal pain suggests a problem in the kidney, like tumor, whick can bleed and press on nearby areas.
Incorrect options-
- Prostatitis causes urinary symptoms but rarely hematuria or loin pain.
- Cystitis is the infection of bladder, it may cause blood in urine but not loin or scrotal pain.
- Testicular cancer affects the testicles, not kidneys, and wouldn't cause hematuria.
Q.24. A patient has saddle nose deformity, he is complaining of SOB, hemoptysis and hematuria. What's the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
All these clinical feature are typically indicative of Wegener's granulomatosis. This condition is related to inflammation of blood vessels, often affecting the nose [saddle nose], lungs [SOB, hemoptysis], and kidneys [hematuria].
- Other options are related only to kidneys and don't present with saddle nose deformity.
Q.25. An old patient complains of urinary incontinence. It occurs at morning and at night without feeling of urgency or desire of micturition, without exposure to any stress, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
When the bladder overfills and can't empty properly, it leaks without warning.
Incorrect options-
- Urge incontinence will exhibit a sudden uncontrollable need to urinate.
- Stress incontinence will have a history of leakage triggered by activities like coughing or sneezing.
- BPH is not related to the patients presentation.
Q.26. A heavy smoker came to you asking about cancer, smoking increase risk of which cancer after lung cancer?
Correct Answer : B
Smoking introduces harmful chemicals into the bloodstream, which are filtered by the kidneys and stored in the bladder. Over time, these toxins damage bladder cells, raising risk of cancer.
Q.27. The most common cause of secondary hypertension is?
Correct Answer : A
Narrowed kidney arteries reduce blood flow, causing the kidneys to raise BP in an attempt to improve circulation.
Incorrect options-
- Adrenal hyperplasia, pheochromocytoma, cushing's disease are less common than renal artery stenosis.
Q.28. The most common cause of chronic renal failure is?
Correct Answer : B
The most common cause of chronic renal faliure is DM. High blood sugar damages the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys over time, leading to scarring and decreased kidney function.
Q.29. A male patient presents with features of prostatitis, culture showed gram negative rods. The drug of choice is?
Correct Answer : A
Ciprofloxacin is highly effective against gram-negative bacteria and penetrates well into the prostate tissue making it the first-line treatment.
Q.30. A patient is complaining of left flank pain radiating to the groin, dysuria and no fever. What's the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Renal calculi cause sharp flank pain that can radiate to the groin as they move through the urinary tract. Dysuria occurs as the stone irritates the tract, but no fever suggests there's no infection.
Q.31. A 3-week-old baby boy presented with a scrotal mass that was transparent & non-reducible. What's the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
The baby likely has a hydrocele, where fluid surrounds the testicle, making the scrotum swollen and soft. It's harmless and usually resolves on its own.
Q.32. What's the treatment of uncomplicated UTI?
Correct Answer : A
It's effective and clears most uncomplicated UTIs within a short course.
Incorrect options-
- Ciprofloxacin for 5 days is usually given for uncomplicated UTIs or resistant cases.
- Clarithromycin for 5 days is used for respiratory infections, not UTI.
- Penicillin G for 6 days is not a standard choice in UTI.
Q.33. A 29-years-old man is complaining of dysuria. He was diagnosed as a case of acute prostatitis. Microscopic examination showed gram negative rods which grows on agar yeast. What's the organism?
Correct Answer : D
Klebsiella is a gram-negative rod that commonly causes urinary tract and prostate infections. It can grow on agar yeast media, supporing its diagnosis in acute prostatitis.
Incorrect options-
- Chlamydia is associated with chronic prostatitis or STIs.
- Legionella causes repiratory infections.
- Mycoplasma is rarely linked to acute prostatitis compared to klebsiella.
Q.34. A patient with renal transplant, he developed rejection one week post transplantation, what could be the initial presentation of rejection?
Correct Answer : C
Immune system detects transplant as foreign→ Activates immune response →Inflammation and tissue damage →Symptoms like fever.
Q.35. A patient presents with hematuria and was diagnosed with bladder cancer. What’s the likely causative agent?
Correct Answer : A
Schistosoma haematobium is a parasitic worm that can infect urinary tract and cause long term bladder inflammation, increasing the risk of bladder cancer.
Incorrect options-
- Chlamydia and N.gonorrhoeae are STIs and not related to bladder cancer.
- Sterp. aureus is a bacteria and causes various infections but is not associated with bladder cancer.
Q.36. What's the most common manifestation of renal cell carcinoma?
Correct Answer : A
Blood in urine is the most common sign of RCC because the growing tumor can cause bleeding in the kidney.
Q.37. A patient with presented with complains of excessive thirst and frequent urination, his FBS is 6.8. What's the diagnosis?
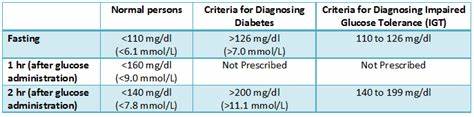
Correct Answer : B
An FBS of 6.8 is considered impaired fasting glucose, meaning the blood sugar is higher than normal but not high enough for a diabetes diagnosis. This explains the excessive thirst and frequent urination.
Q.38. A patient presents with DKA , his laboratory values are pH=7.2, HCO3=5, K+=3.4. What's the treatment?
Correct Answer : C
DKA causes metabolic acidosis, and the main treatment is correcting the acidosis, replacing fluids, and addressing electrolyte imbalances.
- Insulin infusion lowers blood sugar and reduces ketone production.
- NS replaces fluid lost due to dehydration and balances electrolytes.
Q.39. A 6-year-old presented with cola colored urine with nephritic symptoms. What's the first test you would like to do?
Correct Answer : D
Cola colored urine and nephritic symptoms suggest kidney issue. This test looks for RBCs, WBCs, and castes in the urine, helping identify the cause.
Q.40. A young adult presented with painless penile ulcer which has rolled edges, what is the next step that you will proceed to?
Correct Answer : B
A painless penile ulcer with rolled edges suggests syphilis. Darkfield microsocpy is the fastest and most affordable way to detect Treponema pallidum, the bacteria causing syphilis.
Q.41. A diabetic female patient's 24h-urine protein is 130mg, what is the management?
Correct Answer : C
The normal 24-hour urine protein level is ususlly less than 150 mg. Since the patient's value falls within the normal range, no treatment or further action is reuiqred
Q.42. A patient presents with flank pain, fever, and vomiting, what is the treatment?
Correct Answer : A
This is most likely a case of pyelonephritis which need urgent hospitalization. Hospitalization ensures close monitoring, IV antibiotics directly combat the infection, and fluids help with hydration and flushing the infection.
Q.43. An elderly patient complains of urination during night and describes that when he feels the bladder is full he needs to wake up to urinate, he suddenly urinates on the bed. What is the condition called?
Correct Answer : B
Urge incontinence is marked by a sudden, intense urge to urinate, followed by involuntary leakage. This fits the patient's symptoms of losing control after waking up with a full bladder.
Incorrect option-
- Urgency incontinence is another term for urge incontinence.
- Stress incontinence is cause by pressure on the bladder.
- Overflow incontinence is characterized by constant leakage due to full bladder.
Q.44. The best test for detection of renal stones is?
Correct Answer : A
A CT scan without contrast is gold standard for detecting kidney stones. It provides detailed images without the risk of contrast dye obscuring the stones.
Q.45. A 70-year-old male patient with mild urinary dripping and hesitancy presents to your clinic, your diagnosis is mild BPH. What is your next step in management?
Correct Answer : B
For mild BPH, medications are the first-line treatment. They relax prostate and bladder muscles, improving urine flow and reducing symptoms without the need for invasive procedures.
Q.46. A patient presents with complaint of dysuria, frequency and urgency but no flank pain, what is the treatment?
Correct Answer : A
The symptoms indicate an uncomplicated UTI. Ciprofloxacin, a fluroquinolone is effective against common UTI pathogens and is taken for a short duration, ensuring fast recovery.
Q.47. A female patient complains of UTI >14 days, most probably which one causes pyelonephritis?
Correct Answer : D
With a UTI more than 14 days, the risk of pyelonephritis is significantly high, around 50%. The prolonged duration allows the infection to ascend to the kidneys.
Q.48. A man has a long history of urethral stricture present with tender right testis & WBC in urine, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Epididymo-orchitis is inflammation of epididymis and testicle, often caused by bacterial infections. A urethral stricture increases the risk by trapping bacteria, leading to infection and inflammation.
Q.49. None opaque renal pelvis filling defect is seen with IVP, US revels dense echoes & acoustic shadowing, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
- Radiopaque: calcium oxalate, cystine, calcium phosphate, magnesium-ammonium-phosphate.
- Radiolucent: uric acid, blood clots, sloughed papillae.
Q.50. An opaque renal pelvis with filling defect is seen with IVP, US revels dense echoes & acoustic shadowing. Patient has 20 years history of smoking. The most likely diagnosis is?
Correct Answer : B
An opaque filling defect on IVP suggests a solid mass like tumor. On ultrasound tumors often appear as dense structures with acoustic shadowing, consistent with a hard, solid mass.
Incorrect option-
- Blood clot can cause filling defect but lacks the dense shadowing typical of a tumor.
- Uric acid stones are radiolucent and wouldn't appear opaque on IVP.
- Sloughed renal papilla can cause a defect but doesn't produce findings consistent with a tumor.
Q.51. Which of the following is a complication of rapid correction of hypernatremia?
Correct Answer : A
Rapid correction of hyponatremia can lead to brain edema, where water rushes into brain cells, causing them to swell due to sudden shift of sodium levels.
Q.52. Regarding epididymitis which one of the following statement is true?
Correct Answer : D
- Disease of adults, most commonly affecting males aged 19-40 year.
- Erythematous edematous scrotum.
- Cremasteric reflex will be present, like it is present normally, as genitofemoral nerve is intact.
Q.53. The most important diagnostic test for epididymitis is?
Correct Answer : A
In epididymitis inflammation can irritate urinary tract, causing microscopic RBCs to appear in the urine. This is a key diagnostic clue, especially alongside symptoms like scrotal pain and swelling.
Q.54. A 17-year-old male presented to you with history of abdominal pain and cramps in his leg. He has vomited twice since morning, and his past medical history was unremarkable. On examination he looks dehydrated with dry mucous membranes. His investigation: Na: 155 mmol/l, K: 5.6 mmol/l , Glucose; 23.4 mmol/l, HCO3: 13, best tool to diagnose this condition is?
Correct Answer : D
The patients symptoms and lab results are suggestive of DKA. A urine dipstick is the best diagnostic tool here, as it detects ketones in urine, which are produced when the body breaks down fat due to lack of insulin.
Q.55. A patient came with the complaint of abdominal pain with hypernatremia, hyperkalemia, vomiting and diarrhea, what is the next investigation?
Correct Answer : B
The clinical features are suggestive of adrenal insufficiency. The next investigation should focus on assessing the adrenal glands ability to produce cortisol. This can be done by checking the ACTH levels which will be high if adrenal glands are not responding to ACTH, suggesting primary adrenal insufficiency, or low if the problem is at pituitary level, indicating secondary adrenal insufficiency.
Q.56. A patient present with URTI, after 1 week the patient presents with hematuria and edema, what is most probably diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
PSGN is a renal condition that usually develops 1-3 weeks after a streptococcal infection. In this case the patient initially has a URTI, which could have been caused by a streptococcal infection.
Q.57. Most common cause of ESRD is?
Correct Answer : B
Causes of End-stage renal disease include:
1) Kidney disease – obviously ESRD starts as an early kidney disease. 2) Diabetic nephropathy - 43.2% of kidney failure is due to diabetes 3) Chronic kidney failure -ESRD is by definition the last state of chronic kidney failure 4) Hypertension - 23% of cases 5) Glomerulonephritis - 12.3% of cases 6) Polycystic kidney disease - 2.9% of cases.
Q.58. Regarding BPH all of the following are true, except ?
Correct Answer : A
BPH Symptoms :
- Waking at night to urinate
- Sudden and strong urge to urinate.
- A frequent need to go, sometimes every 2 hours or less pushing or straining to begin aweak stream.
- Dribbling after finishing.
- Feeling the bladder has not completely emptied after finishing.
- Pain or burning while urinating.
Q.59. The most accurate test to diagnose acute glomerulonephritis is?
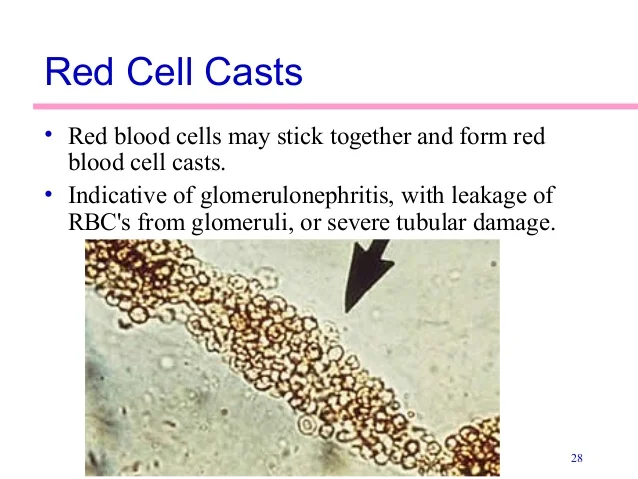
Correct Answer : A
When the glomeruli are damaged, RBCs leak into the urine. These cells clump together inside the kidney tubules, forming casts shaped like the tubules. The precense of these casts is a strong sign of glomerular damage, making it a key diagnostic feature.
Q.60. A 75-year-old man came to ER complaining of acute urinary retention. What will be your initial management?
Correct Answer : B
When a patient presents with acute urinary retention, the first priority is to relieve pressure in the bladder. This is done by inserting foley's catheter which drains the urine.
Q.61. Regarding group A strep. pharyngitis which of the following statement is true?
Correct Answer : A
Treating the infection early significantly reduces the risk of PSGN.
Q.62. The investigation of high sensitivity and specificity for urolithiasis is?
Correct Answer : B
- CT scan is highly sensitive for detecting kidney stones, even small ones, providing detailed 3D images of the urinary tract.
- X-ray after CT is useful for some stones like uric acid stones, which might not show on CT but are detectable on X-ray.
Q.63. A patient with PID has lower abdominal tenderness, on pelvic exam there is small mass in broad Ligament, what is the treatment?
Correct Answer : C
Laproscopy is the best option because it's minimally invasive. It involves small incisions and allows the surgeon to precisely remove the mass while minimizing tissue disruption.
Q.64. A 60-year-old male known to have (BPH) came to your clinic. His digital rectal examination shows soft prostate with multiple nodularity & no hard masses, the patient request for (PSA) for screening of prostatic cancer. What will you do?
Correct Answer : A
The PSA test is not 100% accurate. High PSA levels can be caused by things like BPH or inflammation, not just cancer. Overdiagnosis and overtreatment of slow growing cancers are also risks. Therfore it's important to talk through these risks and benifits so the patient can take a well informed decision.
Q.65. The most likely cause of gross hematuria in a 35-year-old man is ?
Correct Answer : B
When a kidney stone moves through the urinary tract, it can irritate and damage the lining causing visible blood in urine.
Incorrect options-
- Cystitis is more common in women.
- Renal carcinoma is less common in young people.
- Prostatic carcinoma is common in older man and hematuria is not a typical presentation.
Q.66. Concerning urinary calculi, which one of the following is true?
Correct Answer : B
Urinary calculi are often idiopathic, 90% are radiopaque and 75% are calcium oxalate stones
Q.67. A young male patient with dysuria, fever, and leukocytosis comes to your clinic, DRE indicates soft boggy tender prostate, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
The patients features and DRE findings are clearly indicating towards acute prostatitis.
Q.68. Which of the following investigations is done for BPH?
Correct Answer : C
This blood test measures PSA levels, a protein produced by prostate. Elevated PSA levels can be a sign of BPH, although its not specific to BPH. An elevated PSA can also indicate prostate cancer, but its commonly used to monitor prostate health.
Q.69. An 80-year-old male presented with dull aching loin pain & interrupted voiding of urine. BUN and creatinine were increased. US revealed a bilateral hydronephrosis. What is the most probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
The patient likely has BPH due to-
- Dull loin pain from urine backup.
- Interurpted urination from prostate obstruction.
- Increased BUN/ creatinine indicating kidney impairment from urinary retention.
- Bilateral hydronephrosis caused by urinary obstruction.
Q.70. The best investigation for kidney function is?
Correct Answer : B
It is the best investigation as it measures how well kidney filters waste.
Q.71. A patient has DM and renal impairment, how long does it take to impair the renal function further?
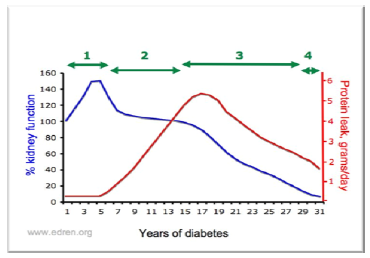
Correct Answer : B
Microalbuminuria generally precedes overt proteinuria by 5-10 years. Once proteinuria is detected, renal function gradually deteriorates over 10-15 years.
Q.72. Regarding benign prostatic hyperplasia all are true, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : A
Parotitis is the inflammation of parotid gland caused by viral infection like mumps.
BPH causes urinary symptoms such as nocturia,diminished stream and sometimes hematuria but doesn't cause parototis.
Q.73. In testicular torsion, all of the following are true, except ?
Correct Answer : C
Testicular torsion usually presents with severe pain, swelling, and is more common in young males, and requires surgical treatment to restore flow.
Q.74. A 50-year-old patient is complaining of episodes of erectile dysfunction, he has history of stress attacks and he is now in stress what will you do?
Correct Answer : A
Stress can lead to ED. Relaxing techniques like deep breathing and meditation can lower stress, improving ED.
Q.75. For premature-ejaculation, all are true except?
Correct Answer : B
Premature ejaculation (PE) is the most common sexual dysfunction in men younger than 40 years.
Q.76. Best laboratory finding in urinalysis for active glomerulonephritis is?
Correct Answer : B
RBC castes are formed when red blood cells get trapped in kidney tubules indicating direct damage and inflammation in the glomeruli. This makes them highly specific for active glomerulonephritis.
Incorrect options-
- HIgh creatinine indicates kidney dysfuction but is not specific to glomerulonephritis.
- WBC casts suggest infection but are more common in pyelonephritis.
- Proteinuria is not specific.
Q.77. For a patient with pyelonephritis which of the following treatment will you prescribe?
Correct Answer : B
Pyelonephritis is a severe kidney infection that needs close monitioring. IV antibiotics act faster and more effectively than oral ones, while IV fluids ensure proper hydration and support recovery.
Q.78. A 10-year-old boy woke up at night with lower abdominal pain, which of the following area is the most important to examine?
Correct Answer : D
Conditions like testicular torsion can cause severe abdominal pain. Early detection is vital to prevent damage to the testicle.
Incorrect options-
- Kidney related issue is less likely to cause sudden severe pain.
- Lumbar back pain is unrelated in this case.
- Rectal issues present with localized pain.
Q.79. A patient present with testicular pain, O/E there is bag of worms sensation on palpation, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
The cahracterstic feature ''bag of worm'' sensation is indicative of varicocele. It occurs due to dilated veins in the scrotum causing this unique texture.
Q.80. An old man presented with tender, enlarged prostate and full bladder. Investigations show hydronephrosis. What is the likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
In older man large prostate can block flow of urine, causing a full bladder and hydronephrosis.
Q.81. A patient with gross hematuria after blunt abdominal trauma has a normal-appearing cystogram after the intravesical instillation of 400 ml of contrast. You should next order which of the following investigation?
Correct Answer : B
A normal cystogram rules out bladder injury, but gross hematuria after trauma suggests possible damage to the kidneys or ureters. An IVP helps visualize the entire urinary tract to locate the bleeding source.
Q.82. A patient who suffered from left hypochondrial pain did a cystoscopy, what is the next step in the management?
Correct Answer : B
Left hypochondrial pain could involve kidney or urinary tract. Since the patient already underwent a cystoscopy, a urologist is best suited to evaluate and manage any urinary issues.
Q.83. An old patient complaining of hematuria presented at your clinic, on investigation patient has bladder calculi, most common causative organism is which one?
Correct Answer : A
This parasitic infection can damage urinary tract, leading to stone formation and hematuria.
Q.84. An old man with presents with urinary incontinence, palpable bladder after voiding, & sense of incomplete voiding, what is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
A full bladder that can't empty completely causes dribbling, urgency, a palpable bladder, and a sense of incomplete voiding.
Q.85. A young male with history of dysuria since 3 days, and anal pain presents at the clinic. O/E per rectum boggy mass is diagnosed. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Dysuria, anal pain, and a boggy mass on rectal exam are hallmark of prostate inflammation, often due to bacterial infection.
Q.86. Which of the following options is a radiosensitive testicular cancer?
Correct Answer : B
Seminoma are highly radiosensitive tumors, meaning they respond very well to radiation therapy, making it an effective treatment option.
Q.87. A patient who is a k/c/o DM, HTN with MI is receiving metformin, diltiazem and other medications. His creatine clearance is high, what is the treatment offered?
Correct Answer : B
Metformin can accumulate in blood if kidney function is impaired, leading to lactic acidosis, a potentially life threatening condition. Even with high creatinine clearance, the patient's kidney function may not be adequate for metformin, so it should be stopped.
Q.88. An old patient with presented with diarrhea, dehydration was corrected with 3 liters of DS, later he became confused with headache. Which of the following is most probable cause?
Correct Answer : A
Rapid fluid replacement with hypotonic solution like DS can dilute sodium levels in blood, leading to hyponatremia. This condition can cause confusion and headaches due to low sodium level.
Q.89. What is the best test for renal stones?
Correct Answer : A
Ct scans are highly accurate for detecting renal stones. Without contrast, it provides clear images of stones, size, location, and number, without the risk of contrast material interfering with results.
Q.90. An healthy old lady, with signs of UTI presented at your clinic, she has taken a lot of medication but had no improvement. On examination mild bladder tenderness was present everything else is normal, what is the most probable cause?
Correct Answer : B
This condition involves inflammation of spaces between the kidney tubules. It can be caused by infections, medications, or autoimmune disease. The patient's persistent UTI symptoms despite treatment, along with mild bladder tenderness suggest kidney involvement beyond just bladder infection.
Q.91. An old lady with signs of UTI presents at your clinic. Medication didn`t work for her, after examination there is a mass palpable, what is the treatment?
Correct Answer : A
Colpotomy is a surgical procedure to investigate and treat a palpable mass causing persistent UTI symptoms, especially when medication fails
Q.92. A patient looking pale, diaphoretic has left flank pain and vomiting, his abnormal labs are low K+-2.3, high CL -114, low HCO3-15, urea-n, Na+-n, urine pH -6.5 , what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) is composed of a group of disorders characterized by an inability of the kidney to resorb bicarbonate/ secrete hydrogen ions, resulting in hyperchloremic, normal anion gap metabolic acidosis. Renal function (glomerular filtration rate [GFR]) must be normal or near normal.
Q.93. All the following are cause of hyponatremia, except?
Correct Answer : B
Diabetes insipidus leads to excessive urine production, causing dehydration and hypernatremia, not hyponatremia.
Q.94. A patient with HTN presented with edema, azotemia, and the GFR was 44, what is the cause of her kidney disease?
Correct Answer : A
Bilateral renal artery stenosis reduces blood flow to the kidneys, leading to kidney dysfunction with symptoms like edema, azotemia, and a decreased GFR.
Q.95. The uric acid in body is removed by which of the following methods?
Correct Answer : B
The kidneys filter uric acid from the blood vessels and excrete it in the urine, making this the main way the body removes it.
Q.96. All of the following are side effect of thiazide diuretics, except?
Correct Answer : D
A flat curve response is not a recognized side effect of thiazide diuretics. It's more of a term related to certain drug condition responses, but not specific to thiazides.
Q.97. When lactic acid accumulates in body how will it respond?
Correct Answer : B
If lactic acid accumulates →metabolic acidosis, the body compensates to some extent by hyperventilation, via medullary chemoreceptor, leading to removal of CO2 in the lung.
Q.98. An old age man, feels that the voiding is not complete and by examination there is moderate BPH and PSA = 1ng/ ml, what you will do?
Correct Answer : A
The patient with moderate BPH is expreriencing incomplete voiding, a common symptom of BPH. If medications don't work, surgery is often recommended to relieve urinary obstruction and improve bladder emptying.
Incorrect options-
- Catheter might temporarily help but isn't a long-term fix.
- Increasing water intake might help in some cases but won't resolve with moderate BPH.
- Increased carbohydrate intake is irrelevant to BPH treatment.
Q.99. An old patient has loin pain with high serum urea and creatinine, U/S showed bilateral hydronephrosis, what is the most common cause?
Correct Answer : D
Ureteral stricture, a narrowing of the ureters, block urine flow, leading to hydronephrosis. This condition can cause loin pain and elevate serum urea and creatinine levels, however, having bilateral ureteral stricture is extremely rare condition. Best option would be D- prostate cancer.
Q.100. A patient with hypertension comes to the clinic, renography shows size of right kidney as 14 cm and left kidney as 7 cm. Arteriogram shows renal artery stenosis in left kidney. What to do next?
Correct Answer : D
While arteriogram confirms renal artery stenosis in the left kidney, a biopsy is necessary to rule out other causes like chronic kidney infections or tumors. This will provide a definitive diagnosis and guide further treatment.
Q.101. What is the best investigation regarding renal function?
Correct Answer : A
Serum creatinine is a byproduct of muscle metabolism, and kidneys filter it out. Elevated levels of serum creatinine are a reliable indicator of kidney dysfunction because the kidneys ability to clear creatinine decreases as their function declines.
Q.102. A patient has frequent, strong urgency to urinate at night time and when she woke up to go to washroom she found herself wet. What does she have?
Correct Answer : A
Urge incontinence happens when bladder contracts involuntarily, leading to dribbling or involuntary leakage. This patient's frequent nighttime urgency and wetness upon waking suggest her bladder is contracting, producing a strong urge to urinate.
Q.103. A female with dysuria, urgency and small amount of urine passed. She received several courses of antibiotic over the last months but no improvement, all investigations done urine analysis and culture with CBC are normal,what you should consider the next?
Correct Answer : A
This is a chronic condition causing bladder pain, urgency and frequent urination. The patient's symptoms have persisted despite use of various antibiotics, making a bacterial infection unlikely. The lack of improvement is therefore suggestive of interstitial cystitis.
Q.104. US showed enlarged kidneys with multiple sized spaces & patient has trisomy of chromosome 16, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
PKD is a genetic disorder that causes multiple fluid-filled cysts to form in the kidneys, leading to kidney enlargement. The ultrasound showing enlarged kidneys with multiple cycts, along with patients trisomy of chromosome 16 strongly points in favor of this diagnosis.
Q.105. An old patient presents with dehydration which was corrected with 3 liters of D5, later he became confused with headache. What can be the most probable cause?
Correct Answer : A
After correcting dehydration with 3 liters of DS the patient likely developed hyponatremia, a condition where sodium levels in blood drop too low. DS is a hypotoic sloution which can dilute sodium, especially in elder patients. This can lead to confusion and headache.