
Hello,
Dr. Batman
Hello Doctor, Welcome!
Profile

Name: Batman
Email: batman@gotham.com
NEUROLOGY REVIEW
(Total Questions - 133)Q.1. What is the most reversible risk factor for stroke out of the following options?
Correct Answer : B
The most reversible factor is HTN. It can be effectively managed with lifestyle changes like a healthy diet, exercise, stress reduction, and medications. Even small reductions in blood pressure significantly lower stroke risk.
Incorrect options-
These options are comparatively less reversible.
- Diabetes has lasting vascular effects.
- Obesity reduces risk but is often difficult to maintain.
- Dyslipidemia can be managed but genetic factors remain.
Q.2. An 18-year-old male who was involved in an RTA had fracture of the base of the skull. O/E he had loss of sensation of the anterior 2/3 of the tongue & deviation of the angle of the mouth. Which of the following nerves is affected?
Correct Answer : C
Nerve supply of tongue-
Anterior 2/3-
- General sensation- Trigeminal nerve V3 via the lingual nerve.
- Taste - Facial nerve VII via the chorda tympani.
Posterior 1/3-
- General sensation and taste- Glossopharyngeal nerve IX.
Base of tongue-
- General sensation and taste- Vagus nerve X.
Motor supply-
- Hypoglossal nerve XII for all intrinsic and extrinsic muscles except platoglossus which is supplied by vagus nerve.
Q.3. A 30-year-old patient is on phenytoin since, she was 29 when she had partial epilepsy, she didn’t have any attack since. She wants to stop taking the drug due to facial hair growth. What is the next step?
Correct Answer : A
The patient has been seizure free for a year, indicating good control. Side effects like facial hair growth are distressing, making it reasonable to stop.
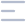
Q.4. A patient is 22-years-old and presents with unilateral headache attacks, the diagnosis is?
Correct Answer : B
Migraines commonly cause unilateral headaches, unlike tension headaches, which are usually bilateral.
Q.5. Which one of the following is true about migraine?
Correct Answer : C
Migraines typically present at throbbing pain on one side of the head.
Incorrect option-
- Aura occurs before, not after the headache.
- Migraines can last longer than 4 hours.
- 30 minutes is too short for migraine.
Q.6. A middle-age man presented with severe headache after lifting a heavy object. His BP was high. He was fully conscious, examination was otherwise normal. The most likely diagnosis is?
Correct Answer : A
A sudden, severe headache after lifting a heavy object suggests subarachnoid hemorrhage, often linked to HTN and ruptured blood vessels.
Q.7. A patient has neck stiffness, headache and petechial rash. Lumbar puncture showed high pressure, what would be the cause?
Correct Answer : B
- Meningitis symptoms- Neck stifness, headache, and petechial rash point to bacterial meningitis.
- CSF findings- Elevated pressure supports diagnosis.
Neisseria meningitides is the most common cause in young adults.
Q.8. The most common cause of non-traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage is?
Correct Answer : C
A ruptured aneurysm is the most common cause of non- traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage, leading to bleeding into the subarachnoid space.
Q.9. Which of the following is not true in emergency management of stroke?
Correct Answer : C
Seizures can occur after a stroke, and anticonvulsants are used to prevent or control them.
Incorrect options-
- Avoiding D5 50% prevents hyperglycemia which worsens brain injury.
- Diazepam is standard for stopping seizures.
- Correcting electrolytes is vital for recovery and preventing complications.
Q.10. A 26-year-old female is complaining of headache, it is more severe in the early morning and is mainly bitemporal, her past medical history is unremarkable. She gave history of OCP use since1 year. Ophthalmoscope examination showed papilledema but there are no other neurological findings. The most probable diagnosis is?
Correct Answer : B
BIH headaches are typically present on waking up or may awaken the patient. It could be accompanied by other signs of increased ICP like vomiting, papilledema, epilepsy or mental change.
Q.11. A 27-year-old male with tonic-clonic seizures presented in the ER, 20 mg Diazepam was given and the convulsion did not stop. What will be given next?
Correct Answer : A
Diazepam is the first choice for treating status epilepticus. If one doesn't stop the seizure, you can repeat it upto 40 mg in total.
Incorrect options-
- Phenytoin is used after benzodiazepines like diazepam fail.
- Phenobarbitone is another second-line option for seizures.
- Clonidine is for high pressure, not seizure.
Q.12. Definition of status epilepticus is?
Correct Answer : B
Status epilepticus is when seizures continue for more than 30min or recur without the person waking up or regaining consiousness in between.
Q.13. A 25-year-old student presented to your office complaining of sudden & severe headache for 4 hours. History revealed mild headache attacks during the last 5 hours. On examination: the patient was agitated & restless. The diagnosis is?
Correct Answer : A
Migraine often starts with a sudden, severe headache that intensifies quickly. A history of mild headaches fits with typical migraine pattern, where the intensity increases over time.
Q.14. All of the following precipitate seizure, except?
Correct Answer : A
Hyponatremia can cause neurological symptoms, but it's not the most common trigger for seizure compared to other electrolyte imbalance.
Q.15. Treatment of opioid toxicity is-
Correct Answer : A
Naloxone is used to reverse opioid overdoses, like those from heroin or fentanyl, by blocking the effects of opioids on the brain and restoring normal breathing.
Q.16. A 25-year-old patient presented with headache, avoidance of light & resist flexion of neck, next step of management is?
Correct Answer : D
We suspect meningitis, the treatment is antibiotic & lumbar puncture. The above mentioned options are not helpful in diagnosing and managing meningitis.
Q.17. Which of the following side effect is not associated with phenytoin?
Correct Answer : D
Side effects of phenytoin:
- 1) CNS: cerebral edema, dysarthria & extrapyramidal syndrome
- 2) ENT: diplopia, nystagmus & tinnitus.
- 3) CVS: hypotension
- 4) GI: gingival hyperplasia & altered taste
- 5) GU: pink or red urine.
- 6) Dermatology: hypertrichosis & exfoliative dermatitis
- 7) Hematology: Agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia & macrocytic anemia
- 8) Other: Asteomalasia, Hypocalcaemia
Q.18. Peripheral neuropathy can occur in all EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
All can cause peripheral neuropathy
Q.19. A patient presents with complaint of pain near eye, characterized by tingling and paresthesia. It occurs many times in a week at the same time, also there is nasal congestion and eye lid edema, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Cluster headaches are intense, short-lived pains around the eye, often with symptoms like tearing, nasal congestion, eyelid swelling, and restlessness.
Q.20. A girl presents with band like headache which increases with stress and is also periorbital. It occurs twice a week, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Tension headaches often feel like a tight band around the head, and stress can make them worse. They can also cause pain around the eye.
Q.21. The most common cause of intracerebral hemorrhage is?
Correct Answer : B
High BP weakens the brain's blood vessels, making them more prone to rupture causing bleeding, which is the leading cause of intracerebral hemorrhage.
Q.22. A patient presented with nausea, vomiting, nystagmus, tinnitus and inability to walk unless he concentrates well on the target object. His cerebellar function is intact, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Vestibular neuritis is an inner ear infection that infalmes the balance nerve [vestibular], causing dizziness, nausea, and trouble with coordination.
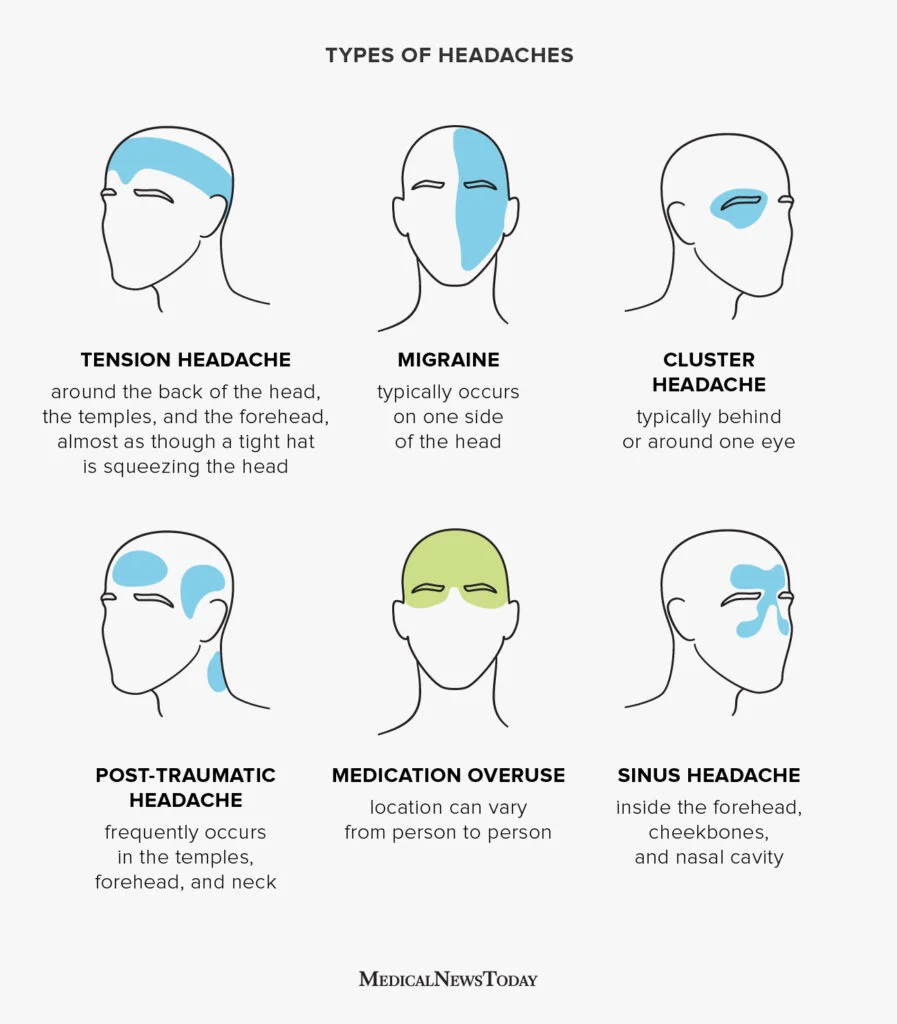
Q.23. A 80-year-old male patient, came with some behavioral abnormalities, he is annoyed, most postulated lobe to be involved is?
Correct Answer : A
As the frontal lobe controls behaviour, personality, and decision-making. Damage here can cause mood and behavioural changes.
Q.24. The commonest initial manifestation of increased ICP in patient after head trauma is ?
Correct Answer : A
Change in level of consiousness, as increased ICP affects brain function, leading to confusion, drowsiness, or unresponsiveness.
Incorrect options-
- Ipsilateral pupillary dilatation can be a sign of increased ICP but it's not the first symptom.
- Contralateral pupillary dilatation is similar to ipsilateral dilatation, it's not usually the initial sign.
- Hemiparesis is weakness of one side of the body and is not initial feature.
Q.25. Which of the following is true regarding systolic hypertension?
Correct Answer : A
As we age, stiffer arteries lead to higher systolic BP, making isolated systolic HTN a bigger risk for heart attacks and strokes in older adults.
Q.26. A patient presents with typical picture of oculomotor nerve palsy he has history of stroke with loss of smell, which lobe is affected?
Correct Answer : D
Temporal, as the tempotal lobe processes sensory information, including smell, and damage here can cause anosmia.
Q.27. A man is brought to the ER after having seizure for more than 30 min, the most initial drug you will start with is?
Correct Answer : A
IV lorazepam, as it's the first-line tratment for stopping a prolonged seizure. Lorazepam works quickly by enhancing GABA, which calms the brain.
Q.28. Which is the 1st line drug in trigeminal neuralgia management?
Correct Answer : A
Carbamazepine, as it's the first-line treatment for trigeminal neuralgia. It helps by stabilizing nerve activity, providing effective pain relief.
Q.29. A middle-aged patient with ataxia, multiple skin pigmentation and decrease hearing comes at the clinic, one of his family members has the same condition. What is the most probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Neurofibromatosis, a genetic disorder that can cause ataxia, skin pigmentation, and hearing loss. The family history supports the diagnosis.
Q.30. A 19-year-old after bike accident, can't bring the spoon in front of himself to eat, lesion is in which of the following?
Correct Answer : B
Cerebellum, as its responsible for coordinating movement. Damage here can cause dysmetria, making it hard to bring spoon to the mouth.
Q.31. A young girl experienced crampy abdominal pain & proximal muscular weakness but has normal reflexes after receiving septra (trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole), what is the diagnosis ?
Correct Answer : D
Septra can trigger an attack of AIP.
Q.32. A patient is complaining of memory loss. Alzheimer disease is diagnosed what is the cause of this?
Correct Answer : C
Loss of cells, as Alzheimer's causes the gradual death of brain cells, particularly those involved in memory, leading to cognitive decline.
Q.33. A female patient presented with migraine headache which is pulsatile, unilateral, and increases with activity. She doesn't want to take medication. Which of the following is appropriate?
Correct Answer : A
Bio feedback has been shown to help some people with migraines. Biofeedback is a technique that can give people better control over body function indicators such as blood pressure, heart rate, temperature, muscle tension, and brain waves. The two most common types of biofeedback for migraines are thermal biofeedback and electromyographic biofeedback.
Q.34. A diabetic patient presented with spastic tongue, dysarthria and spontaneous crying what is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Pseudobulbar palsy, which causes symptoms like spastic tongue, dysarthria, and uncontrollable emotional outbursts like crying. It happens due to damage to the upper motor neurons that control the muscles of the face and tongue.
Q.35. What is the prophylactic treatment for meningitis contact?
Correct Answer : B
Rifampicin, an antibiotic used to prevent meningitis in people who have had close contact with someone infected.
Q.36. A patient with ischemic stroke presents after 6 hours, the best treatment is?
Correct Answer : A
TPA: is administered within 3 hours of symptoms onset (if no contraindication).
Incorrect options-
- ASA: is used within 48 hours of ischemic stroke to reduce the risk of death.
- Clopidogrel: can be used in acute ischemic& an alternative to ASA.
- Heparin & other anticoagulants: in patient has a high risk of DVT or AF.
Q.37. An old male presents with neck stiffness, numbness and paresthesia in the little finger, ring finger, and positive raised hand test, diagnosis is?
Correct Answer : A
TOS, which involves compression of the nerves and blood vessels between the collarbone and the first rib. Symptoms often include neck stifness, numbness, and tingling in the fingers, with a positive raised hand test.
Q.38. An old male with symptoms suggesting of parkinsonism such as difficulty walking, resting tremors and rigidity in addition to hypotension; what is the most common presenting symptom of this disease ?
Correct Answer : B
Tremors are usually the first symptom of Parkinson's disease, often starting as slight shaking in one hand and spreading to other parts of the body.
Incorrect options-
- Rigidity is a common symptom but typically comes after tremors.
- Unsteady gait appears later in disease.
- Hypotension can be a side effect of Parkinson's medication.
Q.39. Which of the following is a side effect of bupropion, a drug used to help smoking cessation?
Correct Answer : D
Bupropion can increase the risk of seizures, especially in individuals with history of seizures or certain health conditions.
Q.40. What's the most effective treatment of cluster headache?
Correct Answer : B
Sumatriptan works quickly by narrowing blood vessels in the brain, providing rapid relief during an attack.
Q.41. What is the treatment for an old patient with HTN and migraine?
Correct Answer : A
Beta-blockers are commonly used to treat both high BP and migraines. They help lower BP and can reduce the frequency and severity of migraines.
Q.42. A patient presented with progressive weakness on swallowing with diplopia and fatigability. The most likely underlying cause of her disease is?
Correct Answer : A
Antibody against acetylcholine receptors, which points to Myasthenia Gravis. This autoimmune disease attacks acetylcholine receptors, leading to muscle weakness, especially in muscles used for swallowing, eye movement causing diplopia andgeneral fatigue.
Q.43. A young adult is a k/c/o sickle cell disease. These patients are commonly affected with which of the following?
Correct Answer : B
In sickle cell disease, the altered RBCs can block flow in small vessels, leading to multiple cerebral infarcts in the brain.
Q.44. A 70-year-old with progressive dementia, no personality changes and neurological examination was normal but there is visual deficit, on brain CT shows cortex atrophy and ventricular dilatations, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia, typically leading to gradual memory and cognitive decline, visual problems, and in some cases, personality changes. The brain CT showing cortical atrophy and ventricular dilatation fits the pattern of Alzheimer's.
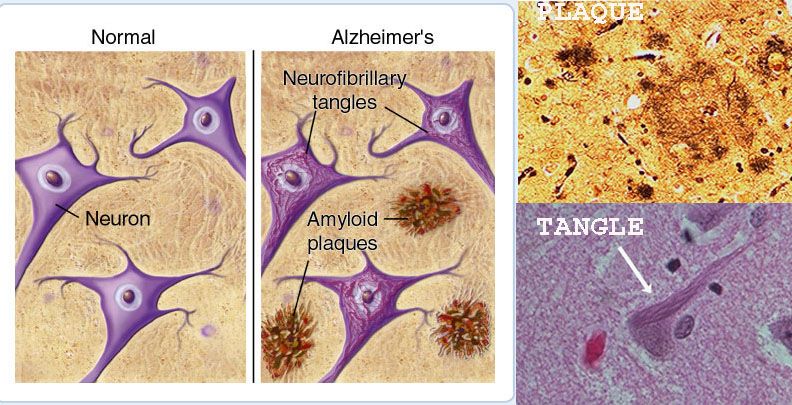
Q.45. A 70-year-old with progressive dementia, on brain microscopy amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles are clearly visible also plaques are seen, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles and are key features of Alzheimer's disease, disrupting communication between brain cells and leading to cognitive decline.
Q.46. A 87-year-old who was brought by his daughter, she said he is forgettable, creating mess in room, not able to maintain attention , neurological examination and the investigation are normal, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Alzheimer's is the most common form of dementia in older adults and often starts with gradual memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and disorganization, as described.
Incorrect options-
- Multi-infarct dementia is caused by multiple strokes, has a sudden onset and stepwise decline in cognitive abilities.
- Lewy body dementia includes features of hallucinations, Parkinson symptoms, and fluctuating cognition.
- Schizophrenia is a mental health disorder with hallucinations and delusions, but it typically occurs earlier in life.
Q.47. A 73-year-old patient complaint of progressive loss of memory with decrease in cognition function. C.T reveals enlarge ventricle and cortical atrophy, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Alzheimer's is the most common dementia, presenting with progressive memory loss and cognitive decline. CT findings of enlarged ventricles and cortical atrophy are classic indicators.
Q.48. A female patient complaining of severe migraine that is affecting her work, to prevent that what medication should be used?
Correct Answer : B
Beta blocker are used in prevention of migraine attack. It works by blocking the effect of certain chemicals in the body that trigger migraine.
Q.49. A 6-month-old boy with fever presents at your clinic, you should give antipyretic to decrease risk of which of the following?
Correct Answer : A
A 6-month-old with fever should be given antipyretics to reduce the risk of febrile convulsions.
Q.50. After infarction, the patient becomes disinhibited, angrier & restless. The area responsible for these features is?
Correct Answer : C
These features are indicating damage in the prefrontal area. The prefrontal cortex is key for impulse control, emotional regulation, and social judgement.
Q.51. A 65-year-male presented with 10 days history of hemiplegia, CT shows: infarction, he has HTN. He is on lisinopril & thiazide, 2 years back he had gastric ulcer. What treatment would you add?
Correct Answer : D
Dipyrimadole is safer for stroke prevention inpatients with history of gastric ulcers. It is an antiplatelet agent and reduces the risk of further strokes without significantly increasing the risk if GI bleeding compared to aspirin.
Q.52. Regarding indication for CT brain for dementia all are true, except?
Correct Answer : A
Alzheimer’s disease is primarily a clinical diagnosis. Based on the presence of characteristic neurological and neuropsychological features and the absence of an alternative diagnosis. It is commonly found in people over 65 presenting with progressive dementia for several years.
Q.53. Investigation of multiple sclerosis include all, except ?
Correct Answer : D
Tests used to investigate multiple sclerosis-
- Visual evoked potential assesses brain response to stimuli.
- Lumbar puncture analyzes CSF for inflammation.
- MRI detects brain and spinal cord leisons.
Q.54. A young man comes with headache, he is describing that this headache is the worst headache in his life. Which of the following will be less helpful?
Correct Answer : C
Skull X-ray, as it's not sensitive for causes like subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Q.55. All of the fallowing are criteria of subarachnoid hemorrhage, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : A
Paraplegia is not a feature of SAH, as it involves loss of sensation/movement below waist, which is unrelated to SAH.
Q.56. The best treatment for SAH is?
Correct Answer : D
The listed options are not primary treatments of SAH.
SAH is usually treated with-
- Endovascular coiling or surgical clipping
- Supportive care to manage complications.
- Medications like nimodipine to prevent further brain damage.
Q.57. A 26-year-old female presents with 6 month history of bilateral temporal headache, increased in morning & history of OCP for last 1 year, on examination her BP is 120/80mmHg & papilledema is present, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
The patient's history of bilateral morning headaches align with BIH, which is associated with increased intracranial pressure. OCP use is a known risk factor of BIH, as it can contribute to hormonal and pressure changes.
Q.58. A 72-year-old man with loss of vision in one eye, and jaw claudication, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
- The patient's vision loss and jaw claudication are calssic signs of temporal arteritis.
- Age is a significant risk factor, as this condition is more common in adults.
Q.59. A patient comes to you with long time memory loss and you diagnosed him as dementia (Alzheimer), what to do to confirm the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
A CT scan is often the first test used to rule out other causes of dementia-like symptoms, such as stroke or brain tumors.
Q.60. Side effects of levodopa is?
Correct Answer : A
Dyskinesia refers to involuntary movements such as tics, tremors, or muscle twisting, and is a common side effect of levodopa,especially with long-term use or high doses.
Q.61. A patient presents with generalized seizures, he has no previous history of any seizure. The most important thing to do now is?
Correct Answer : B
When a patient has a first-time seizure, it's crucial to identify potential causes quickly. Lab results in ER help rule out immediate triggers like infections, electrolyte imbalances, low blood sugar, or toxins. These tests are fast and essential to guide further steps.
Q.62. A lactating mother is newly diagnosed with epilepsy, for which she is now taking phenobarbital, what is your advice for her?
Correct Answer : C
Breastfeeding is safe even while taking phenobarbital. The benifits of breastfeeding outweight the minimal risks, but it's important to monitor the baby for drowsiness or other side effects.
Q.63. Sciatica is associated with which of the following?
Correct Answer : D
Sciatica occurs due to irritation or compression of the sciatic nerve, leading to symptoms like pain, numbness, or weakness in the leg including possible calf muscle weakness.
Q.64. An old male with history of stroke came to your clinic, after 9 days he lost vision in his left eye, what is the affected structure?
Correct Answer : C
The occipital lobe processes visual information. A stroke affecting this area can cause vision loss including issues with visual fields like hemianopia.
Q.65. A male old patient has signs & symptoms of facial palsy (LMNL), which of the following is correct about it?
Correct Answer : A
Bell's palsy a temporary facial muscle weakness or paralysis, often begins to improve within two weeks. Most cases recover fully within few months.
Q.66. A patient is a known case of epilepsy he is currently on phenytoin, he presented with history of abdominal pain, and bilateral axillary lymph node enlargement, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Phenytoin can cause side effects, including hypersenstivity reactions, which may present as abdominal pain and lymph node enlargement.
Q.67. An old age patient presented with neck stiffness, cervical arthritis, paresthesia on palm and medial 2/3 fingers, the proper management is?
Correct Answer : D
These symptoms suggest carpal tunnel syndrome, caused by compression of the median nerve. Decompression surgery relieves pressure on the nerve and resolves the symptoms.
Q.68. Diaphoresis and hyperreflexia features are present in a patient, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
NMS is a serious reaction to antipsychotics, with symptoms like diaphoresis, hyperreflexia, muscle rigidity, fever and altered mental status.
Q.69. A young man suddenly develops ear pain and facial dropping, what should be done?
Correct Answer : A
This presentation is likely Bell's Palsy, which usually resolves on its own within weeks to months.
Q.70. A man with high fever and petechial rash presented at your clinic, laboratory investigation shows decrease glucose in CSF, he has which of the following?
Correct Answer : A
These symptoms strongly indicate meningococcal meningitis. The petechial rash and low CSF glucose are hallmark signs of this bacterial infection.
Q.71. Romberg sign is seen in which lesion?
Correct Answer : A
The Romberg sign tests balance by having a person stand with their eyes closed. If they sway or fall, it suggests a problem with proprioception. The dorsal column of the spinal cord carries proprioception signals to the brain. If it's damaged, it causes positive Romberg sign.
Q.72. A patient has positive Romberg test, what is the affected part ?
Correct Answer : A
The sensory cortex processes proprioception signals. Damage here leads to a positive Romberg sign.
Q.73. Common cause of intracranial hemorrhage is?
Correct Answer : A
HTN is a common cause of intracranial hemorrhage. It puts extra pressure on the brain's blood vessels, making them more prone to rupture and causing bleeding inside the skull.
Q.74. In aseptic meningitis, in the initial 24 hours what will happen?
Correct Answer : C
Lymphocytes increase as the body is fighting against viral infections.
Q.75. A 50-year-old female has DM which is well controlled on metformin, now she c/o diplopia in right side eye, along with lid ptosis and loss of adduction of the eyes and up word and out word gaze. Reacting pupil with no loss of visual field, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
These symptoms point towards a problem in occulomotor nerve, which controls eye movement.
Q.76. Increase of IgG in CSF indicates what?
Correct Answer : A
MS is an autoimmune disease where the body attacks the myelin sheath in the brain and spinal cord. This leads to inflammation and immune activity in CNS. The immune system produces IgG antibodies against myelin, which can be detected in CSF, this is hallmark of MS.
Incorrect options-
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a genetic disorder, not linked ti immune mediated IgG increase in CSF.
- Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder at the neuromuscular junction, but immunoglobulin is not elevated in CSF.
- Bell's palsy is a temporary facial nerve inflammation, not related to autoimmune IgG in CNS.
Q.77. A patient with Alzheimer disease is not recognizing his wife and fighting with her, which part is affected?
Correct Answer : A
The temporal lobe is key for memory and recognizing familiar faces. In Alzheimer's, damage here leads to problem like not recognizing loved ones and emotional outbursts.
Incorrect options-
- Cerebellum is responsible for balance and coordination, not memory.
- Parietal lobe deals with sensory processing and spatial awareness.
- Occipital lobe focuses on vision, not recognition or emotions.
Q.78. An old male had history of MI. He presented with hemiplegia of the right side for 6 hours and is diagnosed with stroke. His medication is atorvastatin and antihypertensive, he had history of gastric ulcer 3 years ago, you will add which medication to it?
Correct Answer : A
Aspirin is started immediately because it thins blood, prevents clot formation reducing the risk of another attack. Stroke is time-sensitive and should be managed as early as possible.
Q.79. First sign of increased intracranial pressure is?
Correct Answer : C
Increased pressure in the skull causes stretching and irritation of pain sensitive areas leading to a headache often the first noticeable sign.
Q.80. A person presented with band like throbbing headache associated with stress. What’s the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Stress and muscle tension creates a band-like, dull pain around the head which is a classic sign of tension headache.
Q.81. A man with severe headache and high ESR presents to the clinic, what is the treatment?
Correct Answer : C
Severe headache and high ESR suggest giant cell arteritis, an inflammation of blood vessels. Corticosteroids quickly reduce this inflammation and prevent complications like vision loss.
Q.82. A patient with sudden severe occipital headache came to emergency. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
The classic symptom of subarachnoid hemorrhage is thunderclap headache (a headache described as "like being kicked in the head", or the "worst ever", developing over seconds to minutes). This headache often pulsates towards the occiput (the back of the head).
Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Patients with intraparenchymal bleeds have symptoms that correspond to the functions controlled by the area of the brain that is damaged by the bleed.
- Other symptoms include those that indicate a rise in intracranial pressure due to a large mass putting pressure on the brain. Intracerebral hemorrhages are often misdiagnosed as subarachnoid hemorrhages due to the similarity in symptoms and signs. A severe headache followed by vomiting is one of the more common symptoms of intracerebral hemorrhage. Some patients may also go into a coma before the bleeding is noticed.
Q.83. Which drug is contraindicated in cluster headache?
Correct Answer : A
Bupropion can trigger cluster headcahes in some individuals, so it should be avoided in these patients.
Q.84. A patient on aspirin, and taking phenytoin for seizures came to clinic for routine follow up, on examination she has bilateral painless lymph nodes, no other symptoms or signs, lymph node biopsy showed hyperplasia. Diagnosis is?
Correct Answer : D
Phenytoin can cause painless lymph node swelling as a rare side effect without other symptoms.
Q.85. Sciatica shows increased incidence in which of the following?
Correct Answer : A
Excessive inward curvature of the lower back can put pressure on the sciatic nerve, increasing the risk of sciatica.
Q.86. A patient presents with echolalia, echopraxia, poor hygiene, insomnia, and weird postures. The treatment is?
Correct Answer : B
Benzodiazepines are calming medications that help slow down overactive brain activity. This makes them really useful for treating catatonia, which can cause behaviors like repeating other's words and mimicking their movements. They also help with related issues like anxiety and insomnia.
Q.87. An old male patient with headache and lower back pain came to the clinic. His X-ray of spine shows multiple lytic lesion and head X-ray shows moth eaten appearance. What is the appropriate next step?
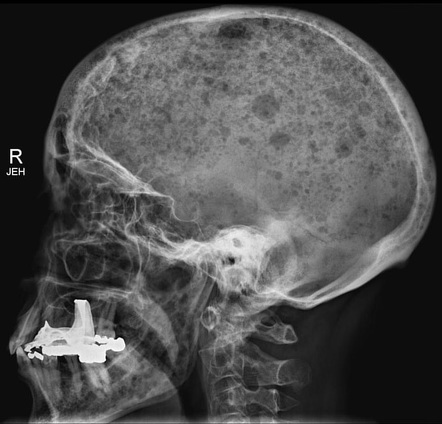
Correct Answer : A
The spine and head X-rays show signs of possible multiple myeloma, a bone cancer that can spread to the chest. A chest X-ray helps check if the disease has affected the ribs or sternum.
Q.88. A patient presents with, cognitive impairment, shuffling gate and pin rolling tremor, what is the diagnosis ?
Correct Answer : A
Parkinson's cause tremors, shuffling gait, and cognitive impairment, which match the patient's symptoms of shaking hands and difficulty walking.
Q.89. An exaggerated reflex in jaw, no fasciculation, and difficulty in swallowing, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Pseudobulbar palsy results from an upper motor neuron lesion to the corticobulbar pathways in the pyramidal tract.
Patients have difficulty chewing, and swallowing and demonstrate slurred speech (often initial presentation). Individuals with pseudobulbar palsy also demonstrate inappropriate emotional outbursts.
S/S: 1) Speech is slow 2) thick and indistinct 3) Gag reflex is normal 4) exaggerated or absent 5) Tongue is small stiff and spastic 6) Jaw jerk is brisk 7) upper motor neuron lesion of the limbs 8) Dysphagia (difficulty in swallowing) 9) Labile affect 10) Dysarthria 11) Uncontrollable laughing or crying.
Bulbar palsy refers to bilateral impairment of the function of the lower cranial nerves IX, X, XI, and XII, which occurs due to lower motor neuron lesions either at a nuclear or fascicular level in the medulla oblongata or from bilateral lesions of the lower cranial nerves outside the brainstem.
S/S : 1) dysphagia (difficulty in swallowing) 2) difficulty in chewing 3) nasal regurgitation 4) slurring of speech 5) choking on liquids 6) Nasal speech lacking in modulation and difficulty with all consonants 7) Tongue is atrophic and shows fasciculations 8) Dribbling of saliva 9) Weakness of the soft palate, examined by asking the patient to say aah – 10) The jaw jerk is normal or absent 11) The gag reflex is absent 12) lower motor neuron lesions of the limbs.
Q.90. What is true about Alzheimer’s disease?
Correct Answer : A
Alzheimer's, the brain shrinks in multiple areas, not just one leading to memory loss, confusion, and other symptoms.
Q.91. Migraine headache is treated by which of the following?
Correct Answer : A
It works by narrowing blood vessels in the brain, which helps relieve migrane pain and symptoms. Other medications can help with general headache but are not as effective.
Q.92. A patient with tingling of the little finger, atrophy of the hypothenar, and limitation of the neck movement. X-ray shows degenerative cervicitis, EMG study shows ulnar nerve compression, what will you do?
Correct Answer : A
The correct treatment for ulnar nerve compression in this case is surgical cubital decompression. Surgery can relieve pressure and prevent further damage.
Q.93. Drug used in smoking cessation is contraindicated in patient : M-N is?
Correct Answer : A
Varenicline drug used for smoking cessation is contraindicated in patients with a history of seizure.
Q.94. A patient presents with bradycardia, hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, and muscle weakness what is the cause of his weakness?
Correct Answer : A
High potassium levels disrupt electrical signals needed for muscle contraction, leading to weakness and, in severe cases, paralysis.
Q.95. Which of the following is found to reduce the risk of post therapeutic neuralgia after shingles?
Correct Answer : C
The best option for reducing the risk of post therapeutic neuralgia is valacyclovir. When started within 72 hours of the rash onset, Valacyclovir helps reduce the likelihood of persistent pain after the rash resolves.
Q.96. A young girl experienced crampy abdominal pain & proximal muscular weakness but has normal reflexes after receiving septra (trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole), what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Septra can trigger the attack of acute intermittent porphyria, a condition that affects the production of heme. This leads to symptoms like abdominal pain and muscle weakness.
Q.97. What is true about headache?
Correct Answer : D
Cluster headaches are indeed more common in men than women, making this a well established fact.
Q.98. All of the following may mimic Guillian-barre syndrome, except?
Correct Answer : C
While tetanus causes muscle spasms and stiffness, its presentation is distinct from Guillian-Barre syndrome, which causes progressive weakness and numbness. Tetanus typically involves rigidity and difficulty swallowing, not the same pattern of muscle weakness is seen in Guillian-Barre.
Q.99. A patient presents with dysphagia, proximal muscle weakness, and spasticity. His eyes are not affected, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
MND also known as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis causes progressive muscle weakness, spasticity, and dysphagia while typically sparing eye muscles in the early stage.
Q.100. Greatest single risk factor for stroke is?
Correct Answer : B
The greatest single risk factor for stroke is HTN. HTN strains blood vessels, increasing the risk of both hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes by causing vessel rupture or promoting blood clots
Q.101. An old patient with progressive weakness of hand grip and dysphagia presents at your clinic, the diagnosis is?
Correct Answer : A
The mot likely diagnosis is Myasthenia Gravis. This condition causes progressive muscle weakness, often affecting voluntary muscles, including those involved in swallong leading to dysphagia and decreased hand grip strength
Q.102. A young female , is complaining of severe headache over a long period, now she has started to avoid alcohol, smoking. She notes that she has improved over her last pregnancy, what do you think about her condition?
Correct Answer : A
This technique helps manage headaches, especially those linked to stress. By using sensors to monitor bodily functions like heart rate or muscle tension, patients can learn to control these functions and reduce headache triggers.
Q.103. A man with unilateral headache, eye pain and tenderness in the temporal region presents at your clinic. His investigations show mild anemia and ESR 111,the treatment of choice is?
Correct Answer : A
The most likely diagnosis is giant cell arteritis [GCA] and the treatment of choice is corticosteroids.
Q.104. A patient complains of diplopia, weakness, and frequent aspiration pneumonia in last 2 months. On examination there is spasticity and fasciculation. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
The most likely diagnosis here is MND also known as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis [ALS]. This condition involves progressive muscle weakness, spasticity, fasciculations, and dysphagia, all of which match the patient's symptoms. Diplopia can occur due to weak eye muscles in MND.
Q.105. Cause of Tension headache is which of the following?
Correct Answer : D
Tension-type headache: constant pressure, frequent bilateral; a/w myofacial sensitivity in neck or head.
- Triggers: stress, sleep, deprivation, dehydration, hunger.
- TTT: OTC analgesics (NSAID, acetaminophen; risk of med overuse HA) for episodic; TCAs for chronic.
Q.106. A lady presents with retro-orbital pain, tearfulness, and other feature of cluster headache. She was given treatment, which was not effective. All of the following are possible treatments for her, except?
Correct Answer : D
Methysergide was once used for preventing cluster headaches, but it ahs been largely discontinued due to serious side effects including heart valve damage and fibrosis.
Q.107. An old patient of 83 years presents at your clinic. He has resting tremor, abnormal gait, fatigue and on examination shows bradykinesia, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Parkinson's is characterized by symptoms like a resting tremor , bradykinesia, abnormal gait, and fatigue, which match the symptoms described in this case.
Q.108. Pathology of Alzheimer disease is?
Correct Answer : B
Alzheimer's disease is primarily characterized by the progressive death of brain cells, which leads to formation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles.These disrupt communication between brain cells and result in the cognitive decline associated with Alzheimer's.
Q.109. Guillain-Barre syndrome is closely associated with which one of the following ?
Correct Answer : C
In GBS weakness usually begins in the lower limbs and ascends upwards towards the trunk and arms, which is a key feature of this condition.
Q.110. An old patient around 70 years is complaining of loss of memory, forgetting names, and language problems. Examination- memory and visuospatial abnormalities , the CT show enlarged ventricle with brain atrophy. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Alzheimer's is characterized by gradual memory loss and cognitive decline due to brain cell death, leading to the formation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles.
Incorrect options-
- Multi infarct dementia is caused by multiple small strokes, leading to stepwise cognitive decline.
- Parkinsonism primarily affects motor functions, causing tremors, bradykinesia, and rigidity, not memory.
Q.111. A patient complains of migraine symptoms that are not relieved completely by acetaminophen, she is not a smoke or alcoholic and avoiding stress. What is the best way to prevent the migraine attacks ?
Correct Answer : A
Beta-blockers reduce the heart rate, making them useful for preventing migraine by reducing overall stress on your body.
Q.112. A patient came complaining of severe headache and pain in the periorbital area that is preceded by numbness. On examination there was periorbital eye lid swelling and nasal congestion, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
A cluster headache is an intense one sided pain around the eye, often waking you up at night. It may also cause eye watering and drooping.
Q.113. A patient is suspected of having brain abscess, what is the most important question in his history?
Correct Answer : A
When frontal sinus gets infected, the infection can spread to brain causing abscess. That is why frontal sinusitis is important to consider when someone has a brain abscess.
Q.114. All of the following are extrapyramidal symptoms, except?
Correct Answer : D
EPS are movement disorders that occur due to dysfunction in the extrapyramidal system, which is involved in coordination of movement. Thses symptoms are commonly associated with antipsychotic medications and other drugs that block dopamine receptors.
Q.115. How to confirm the diagnosis of migraine?
Correct Answer : B
Careful history and examination are essential for diagnosing migraine.
Q.116. An adult presents with unilateral headache which is pulsatile and increase with activity & light. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Unilateral headache which is pulsatile and increases on exposure to light and sound is indicative of migraine.
Q.117. A patient presented with CVA , after 6 hours you will give him what medication?
Correct Answer : A
Aspirin is an antiplatelet that inhibits cyclooxgenase, reducing thromboxane A2 and platelet aggregation, which further helps prevent clot formation and reduces the risk of ischemic damage during an acute ischemic stroke.
Q.118. Most common cause of CVA [embolic] resource is?
Correct Answer : A
AF is a common cause of embolic stroke due to irregular rhythms that can lead to blood clot formation in the atria, which can travel to brain.
Q.119. A young man predicts that he is going to have a seizure , then he became rigid for 15 sec followed by generalized tonic colonic convulsion for 45 sec. Your initial action in future attacks will be ?
Correct Answer : A
During a seizure its crucial to keep the airway open. An airway device helps prevent choking and ensures breathing.
Q.120. A 27-year-old with tonic colonic seizure presents in ER, 20 mg diazepam was given but the convulsion did not stop, what is the next step?
Correct Answer : A
Diazepam is the drug of choice and can be given a maximum of 40mg
Q.121. An 85-year-old male patient wakes many times from his sleep because of leg pain, this pain is relieved when he moves his foot, but it recurs again, the best management is?
Correct Answer : D
RLS is a neurological disorder characterized by an irresistible urge to move one's body to stop uncomfortable or odd sensations. It most commonly affects the legs but can affect the arms & torso.
- Symptoms: urge to move - worsening of symptoms by relaxation - worse in the evening and early in the night.
- Treatment: Dopamine agonists “Ropinirole, Pramipexole or gabapentin enacarbil” as first-line drugs for daily restless legs syndrome; and opioids for treatment of resistant cases.
Q.122. What is the organism that causes meningitis in college dormitories?
Correct Answer : D
Neisseria meningitides is a bacterium that causes bacterial meningitis, especially in close contact environments like dormitories. It is spread through respiratory droplets and can lead to severe infection of the meninges.
Q.123. All of the following are criteria of chronic fatigue syndrome, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
All the options mentioned above are a part of CFS.
Q.124. Penis numbness after sitting for long time is due to ?
Correct Answer : A
Pudendal nerve entrapment occurs when the pudendal nerve, which supplies sensation to the genital area, becomes compressed or pinched, often due to prolonged sitting. This leads to symptoms like genital numbness and pain.
Q.125. Regarding chronic fatigue syndrome, which is true?
Correct Answer : B
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome:
characterized by profound mental and physical exhaustion, in association with multiple systems and neurotic symptoms that last at least 6 months.
- Must be new (not lifelong), must not be relieved by rest, and must result in greater than 50% reduction in previous activity.
- Presentation with 4 or more: poor memory/ concentration, myalgia, arthralgia, sore throat, tender lymph node, recent onset headache, unrefreshing sleep, excessive tiredness with exercise.
- Treatment by cognitive and exercise therapy. Also, diet, physiotherapy, dietary supplements & antidepressants.
Q.126. A female patient with migraine doesn't want any daily medications, what will you suggest her?
Correct Answer : A
Biofeedback is the best method if she doesn't want regular medication.
Q.127. A 65-year-old man with history of stroke 5 years ago complains of behavioral change, he becomes aggressive. Where is the site of lesion in the brain?
Correct Answer : B
Frontal lobe is responsible for personality, decisions, and soical behavior. When it's damages it can lead to agression.
Q.128. A patient after URTI later on develops proximal muscle weakness , what is the diagnosis most probably?
Correct Answer : B
D/D of proximal muscle weakness:
- Myasthenia Gravis and Lambert Eaton Syndrome- both have ocular symptoms with proximal muscle weakness.
- Endocrinopathies- hypo/hyperthyroidism, adrenal insufficiency.
- Drug-induced- steroid, statins, cyclosporine.
- Inflammatory myopathies- dermatomyositis, polymyositis
Q.129. What is true regarding syncope?
Correct Answer : C
None of the options are correct.
Q.130. A 33-year-old presents with c/o of pain in his lip and right cheek. Pain was stabbing and triggered with touch. O/E, cranial nerves were intact, The best treatment is?
Correct Answer : A
Trigeminal neuralgia causes sudden, stabbing pain in the face due to overactive nerves. Oxcarbazepine helps calm these nerves, relieving pain.
Q.131. In brainstem damage which of the following occurs?
Correct Answer : B
Brainstem damages can disrupt breathing control, leading to build-up of CO2 in blood.
Q.132. A patient complaint of tension headache, she was on acetaminophen but showed no improvement, she notices that the headache improved when she was pregnant; What she should do now?
Correct Answer : C
Drug induce amenorrhea refers to the cessation of menstruation caused by medications that alter hormone levels, such as those used in hormone therapy or birth control. This can mimic pregancy which in some cases , may alleviate headache symptoms, especially thise related to hormonal fluctuation, as seen in tension headache.
Q.133. Which of the following nerves are matched with appropriate injury?
Correct Answer : D
Tarsal tunnel syndrome occurs when the tibial nerve is compressed as it passes through a narrow space in ankle. This leads to symptoms like pain, numbness, and tingling in the foot.