
Hello,
Dr. Batman
Hello Doctor, Welcome!
Profile

Name: Batman
Email: batman@gotham.com
OPHTHALMOLOGY REVIEW
(Total Questions - 103)Q.1. A male patient developed corneal ulcer in his right eye after trauma, what is the appropriate management?
Correct Answer : A
Q.2. A elderly diabetic patient with mild early cataract and retinal pigmentation with Drusen formation, you have prescribed anti-oxidants, what to do next?
Correct Answer : B
Q.3. A picture of Snellen chart, how far should the patient stand?

Correct Answer : B
Q.4. Which of the following is not a sign or symptom of central retinal artery occlusion?
Correct Answer : A
Q.5. A female patient came in your clinic with a right eye pain and redness with watery discharge, no history of trauma, itching. On examination, there is a diffuse congestion in the conjunctiva and watery discharge. How will you manage?
Correct Answer : D
Q.6. A middle aged patient is complaining of pain while moving the eye, fundoscopy is normal. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.7. A child presents with a large periorbital hemangioma that causes obstruction to vision. What is the likely timeframe for permanent visual acuity loss due to the obstruction?
Correct Answer : C
Q.8. A Infant born with hemangioma on the right eyelid. What is appropriate time to operate in order to prevent amylopia?
Correct Answer : C
Q.9. A 50 year old man presented to ER with sudden headache, blurred of vision and eye pain. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.10. In Open globe injury, what is the appropriate treatment?
Correct Answer : D
Q.11. A 2 years old boy presented with coryza, cough and red eyes with watery discharge. What is the most likely diagnosis of the red eyes?
Correct Answer : A
Q.12. In a sickle cell anemia patient, if the macula is cherry red, and absence of afferent papillary light reflex, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.13. A patient has decrease bilateral visual acuity, but more at right eye. Visual field is not affected, but at fundus, there is irregular pigmentations and early cataract formation. What you will do?
Correct Answer : B
Q.14. A patient have tender, redness nodule on lacrimal duct site. Before referring him to an ophthalmologist what you will do?
Correct Answer : D
The most appropriate initial management for a tender, red nodule at the lacrimal duct site is to apply warm compresses.
Q.15. A male came to you complaining of a sudden progressive decreasing in vision of a left eye over last two-three days, also pain in the same eye. On fundoscopy, optic disk swelling was seen. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.16. A gardener has recurrent conjunctivitis. He can’t avoid exposure to environment. In order to decrease the symptoms in the evening, what should GP advise him?
Correct Answer : D
Q.17. A 45-year-old male patient presents at a medical camp with complaints of watery eye discharge and vision problems. On examination, the anterior chamber reveals red conjunctiva. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.18. A 60-year-old patient presents with complaints of hazy vision. Upon examination, subcortical keratinizing deposits are observed on the cornea. The patient denies any history of trauma but reports that the symptoms have been gradually worsening. What is the most appropriate management for this patient?
Correct Answer : A
The presence of subcortical keratinizing deposits suggests a condition like band keratopathy or a similar corneal degeneration. In this case, the most appropriate management would be artificial tears and lubricants to help alleviate symptoms and maintain eye moisture.
Q.19. A 30 years old patient presented with sticky eyes in morning. what is the probable cause?
Correct Answer : B
Q.20. What is the initial treatment of acute angle glaucoma?
Correct Answer : D
Q.21. A 35-year-old patient presents with photophobia, blurred vision, and reports eye pain. Upon examination, there is keratic precipitate behind the cornea, and the anterior chamber shows cells and flare. The patient also has a history of recurrent eye problems. What is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?
Correct Answer : C
The presence of keratic precipitates behind the cornea and cells in the anterior chamber suggests anterior uveitis (iritis), which is an inflammatory condition affecting the anterior part of the eye. The appropriate treatment for anterior uveitis is topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms.
Q.22. A Patient presented with trachoma in eyes. For prevention, What you should suggest?
Correct Answer : A
Q.23. Patient came with a history of flue like symptoms for many days & complain of periorbital edema now, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.24. A 45-year-old male presents with a yellowish, triangular growth on the nasal side of his eye. The growth is extending into the cornea, and he reports occasional irritation and redness in the eye. He works outdoors and is frequently exposed to dust and sunlight. What is the most appropriate treatment for him?
Correct Answer : A
Pterygium is a benign growth of fibrovascular tissue that usually originates from the conjunctiva and extends onto the cornea. It is often associated with chronic UV exposure and irritants like dust and wind, especially in outdoor workers.
Q.25. A patient presented in OPD with with ptosis, which nerve is affected?
Correct Answer : A
Oculomotor nerve
Q.26. A patient came with sudden painless loss of vision. Before losing the vision, he use to see flashes and high lights. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.27. A patient with URTI. When he coughs or sneezes, he see flashes of light. What is the probable cause of the light flashes?
Correct Answer : C
Q.28. A patient presented with lateral and vertical diplopia, he can’t abduct both eyes, which nerve is affected here?
Correct Answer : C
Q.29. A patient with pain in ophthalmic division of trigeminal nerve & vesicle, which of the following is used to decrease post herpetic neuralgia?
Correct Answer : B
Q.30. A male patient developed corneal ulcer in his right eye after trauma. What is the appropriate management?
Correct Answer : C
Q.31. A 25-year-old male presents with swelling and redness of the eyelid after an accident in which he was struck by a ball during a game. He complains of double vision and difficulty looking up. Upon examination, there is swelling, bruising, and redness around the periorbital area. Further evaluation shows restricted eye movement and mild tenderness in the area. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
A blow-out fracture refers to a fracture of the orbital floor, typically caused by a blunt trauma, such as being struck in the face. It can result in eyelid swelling, redness, double vision, and restricted eye movement. The fracture often causes entrapment of the eye muscles, leading to difficulty moving the eye in certain directions, particularly upward (in cases of inferior rectus muscle entrapment).
Q.32. A patient came with a trauma to his left eye by tennis ball. Examination shows anterior chamber hemorrhage. Which of the following should be excluded?
Correct Answer : C
Q.33. Regarding acute angle glaucoma, you can use all of the following drug except?
Correct Answer : D
Q.34. a patient with foreign body sensation in the eye. After the removal of the foreign body, it was an insect, what is the appropriate treatment?
Correct Answer : A
Q.35. What is the diagnosis for Mucopurulent discharge?
Correct Answer : A
The mainstay of medical treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis is topical antibiotic therapy
Q.36. A patient with hypertensive retinopathy grade 2 with AV nicking. He has normal BP, no decrease in vision, cupping of optic disc. How will you manage?
Correct Answer : B
Q.37. A 30 years old male present to E.R. complaining of visual deterioration in right eye since last 3 days followed by loss of light perception, what is the least possible cause?
Correct Answer : A
Q.38. Anterior uveitis is a character of all of the following except?
Correct Answer : A
Causes of Iritis (anterior uveitis): “idiopathic, seronegative spondyloarthropathies (e.g. Riter's syndrome, Ankylosing spondylitis), IBD, diabetes mellitus, granulomatous disease(e.g. Sarcoidosis), infection(e.g.gonococal, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, brucellosis, T.B.), Behcet disease. Eye involvement of R.A. episcleritis, scleritis, keratoconjunctivitis”
Q.39. A patient (known case of COPD and DM) came with open angle glaucoma. What is the treatment?
Correct Answer : C
Q.40. A 30-year-old male presents to the clinic with complaints of watery eye discharge, redness in both eyes, and blurry vision. He mentions that his symptoms started in the right eye three days ago and have now spread to both eyes. On examination, there is conjunctival redness, watery discharge, and corneal ulceration. There is no history of trauma or foreign body sensation. What is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Correct Answer : A
This patient's symptoms of bilateral watery eye discharge, redness, and corneal ulceration suggest viral conjunctivitis, with Adenovirus being the most common cause.
Q.41. A 70 years old female says that she play puzzle but for a short period she can't play because as she develop headache when playing. What you will examine for?
Correct Answer : A
Q.42. A patient is wearing contact lenses for vision correction since ten years. Now. she is complaining of excessive tearing when exposed to bright light. what will be your advice to her?
Correct Answer : D
Q.43. A patient complains of dry eyes, a moisturizing eye drops were prescribed to him 4 times daily. What is the most appropriate method of application of these eye drops?
Correct Answer : A
Q.44. A Diabetic patient have neovascularization and vitreous hemorrhage, what is the next step?
Correct Answer : A
Q.45. A 17 years old school boy was playing foot ball and he was kicked in his Right eye. Few hours later he started to complain of double vision & ecchymoses around the eye, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.46. A 35 years old female patient complaining of acute inflammation and pain in her Left eye since 2 days. She gave history of visual blurring and use of contact lens as well, On examination: fluorescence stain shows dendritic ulcer at the center of the cornea, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.47. A patient presented in OPD with corneal abrasion, what is the treatment?
Correct Answer : B
Q.48. A patient came in OPD due to subconjunctival hemorrhage. How will you treat him?
Correct Answer : A
Q.49. A patient with recent history of URTI ,develops severe conjunctivitis. Injection with redness of conjunctiva, tearing , and photophobia. What is the treatment?
Correct Answer : D
Q.50. A patient presented with constricted pupil, ciliary flushing and cloudy anterior Chamber. There is no abnormality in eye lid, vision and lacrimal duct, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.51. A newborn was brought in an OPD due to yellowish eye discharge. You suspect eye infection. How will you manage?
Correct Answer : C
Q.52. A man who bought a new cat and now he developed watery discharge. what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.53. How to differentiate between Uveitis and Keratitis in red eye?
Correct Answer : D
Dark, floating spots along the visual field in Uveitis.
Q.54. A 7-year-old child is brought to the clinic by his parents due to concerns about his eyes. The parents report that his right eye sometimes drifts outward, especially when he is tired or daydreaming. On examination, you perform a cover test, and when one eye is covered, the uncovered eye is observed to turn laterally. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Exotropia is a type of strabismus where one eye drifts outward (laterally) when not actively focused. The cover test helps detect this condition by revealing the compensatory movement of the uncovered eye. Esotropia involves inward turning of the eye, while amblyopia refers to reduced visual acuity without structural abnormalities. Cranial nerve III palsy typically involves ptosis and other deficits, which are not described in this case.
4o
Q.55. A 55-year-old male with a history of hypertension visits the ophthalmology clinic for a routine check-up. On examination, the optic disc shows increased cup-to-disc ratio. The patient denies any visual complaints such as pain, vision loss, or other symptoms. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.56. What is the side effect of long term topical corticosteroid use?
Correct Answer : B
Q.57. A female patient who wear optical glasses since 10 years is diagnosed recently with type 2 DM. How frequently she should get her eye-examination now?
Correct Answer : B
Q.58. A patient came to you, after trauma, complaining of loss of the abduction of his right eye. So which cranial nerve gets affected?
Correct Answer : D
Q.59. A child came to ophthalmology clinic and did cover test. During eye cover , his left eye move spontaneously to left, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.60. A patient came to you complaining of gradual loss of vision & now he can only identify light. Which of the following is the LEAST cause of his problem?
Correct Answer : B
Q.61. A 45 years old male presented to the ER with sudden headache, blurring of vision, excruciating eye pain and frequent vomiting, What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
These are typical features of closed-angle glaucoma which presents acutely with red painful eyes, nausea and vomiting, halos around light, hazy cornea, mid-dilated non-reactive pupil, and extremely high intraocular pressure.
Q.62. Which of the following suits the most with a glaucoma diagram attached below?
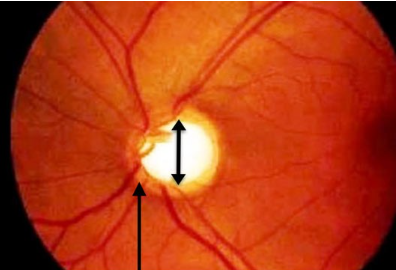
Correct Answer : A
Q.63. A 6 years old boy came in your OPD. He developed conjunctivitis after 3 days of flu symptoms. On examination, you found occipital lymphadenopathy. Which of the following organism is responsible for the condition?
Correct Answer : A
Q.64. A 2-month-old infant is brought to the clinic with a diagnosis of iris coloboma. The parents are concerned about the cosmetic appearance and ask about the timing of surgery. On examination, there is no retinal involvement or vision-threatening complications. When is the appropriate time to consider surgery for this condition?
Correct Answer : A
Q.65. What is the management of Uveitis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.66. Patient has painful red left eye associated with photophobia, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.67. All of the following may cause sudden unilateral blindness EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : A
Retinitis pigmentosa. It causes gradual night blindness.
Q.68. A 45-year-old male patient with a history of pulmonary tuberculosis presents with a painful red eye, photophobia, and decreased vision. Examination reveals ciliary injection, keratic precipitates on the corneal endothelium, and cells in the anterior chamber. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.69. About Retinal detachment, all are true EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : A
This is a condition in which there is separation of the two retinal layers, the retina proper and the pigmentary epithelium by the subretinal fluid.
Causes are: Vitreous hemorrhage, toxemia of pregnancy that results in accumulation of exudates in the subretinal space, weakness of the retina such as lattice degeneration that increases the probability of a tear forming, highly myopic people, those who had undergone cataract surgery, the detached retina in the fellow eye and recent severe eye trauma.
Q.70. Acute glaucoma, all are true EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : B
Acute closure angle glaucoma
Initial Rx is aimed primarily at lowering IOP through systemic medication. This is b/c when the IOP is more than 50, the iris sphincter is usually ischemic & paralyzed, so that, intensive miotic therapy is seldom effective in pulling the peripheral iris away from the angle. It can present with eye pain, headache, nausea & vomiting. In acute glaucoma, the pupil is mid-dilated.
Q.71. A 70 years old patient can only read up to the 3rd line of the Snellen's chart, what is his visual acuity?

Correct Answer : B
Note that the numbers on the side were erased from the chart.
Q.72. All are true about congenital squint EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : A
Strabismus is a condition in which one eye deviates away from the fixation point .under normal condition both the eyes are in proper alignment. The presence of epicanthus and high errors of refraction stimulate squint and this is called apparent squint but in fact, there is no squint.
In a non-paralytic squint, the movements of both eyes are full but only one eye is directed towards the fixated target, the angle of deviation is constant and unrelated to the direction of gaze.
In paralytic squint, there is underaction of one or more of the eye muscles due to nerve palsy, extraocular muscles that tether off the globe.
Q.73. Which of the following is true regarding red eye?
Correct Answer : A
Q.74. Regarding Stye infection of the lower eyelid, all true except?
Correct Answer : D
A hordeolum (ie, stye) is a localized infection or inflammation of the eyelid margin involving hair follicles of the eyelashes (ie, external hordeolum) or meibomian glands (ie, internal hordeolum).
A chalazion is a painless granuloma of the meibomian glands.
Management
1) Warm soaks (qid for 15 min)
2) Drainage of a hordeolum
3) Antibiotics are indicated only when inflammation has spread beyond the immediate area of the
hordeolum. Topical antibiotics may be used for recurrent lesions and those actively draining.
Topical antibiotics do not improve the healing of surgically drained lesions.
Systemic antibiotics are indicated if signs of bacteremia are present or if the patient has tender
preauricular lymph nodes
4) Surgical If the lesion points at a lash follicle, remove that one eyelash
Consultations: If the patient does not respond to conservative therapy (ie, warm compresses, antibiotics)
within 2-3 days, consult with an ophthalmologist
Consultation is recommended prior to drainage of large lesions.
Q.75. A 35-year-old patient presents with redness in the right eye, photophobia, and itching. Upon examination, the left eye shows signs of uveitis. What is the most appropriate initial treatment for this condition?
Correct Answer : B
The patient presents with symptoms suggestive of uveitis (inflammation of the uveal tract), and the most appropriate treatment for uveitis is typically topical corticosteroids, which help reduce inflammation. If the uveitis is severe or doesn't respond to topical treatment, oral corticosteroids may be needed. Antihistamines and topical antibiotics are not appropriate treatments for uveitis as they do not address the underlying inflammation.
Q.76. A 35 years old male patient came in your OPD due to flu like symptoms since two days and now he has red eye, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.77. What is the most dangerous red eye that need urgent referral to ophthalmologist?
Correct Answer : D
Q.78. A patient came with pterygium in one eye, and the other eye is normal. What is a correct statement for this patient?
Correct Answer : B
Q.79. A patient presented with eye pain and watery discharge. A fly hit his eye but it was removed. What you will give?
Correct Answer : A
Q.80. An old male presented with cough and SOB. He was treated for a long time for glaucoma. What is the most likely cause of his respiratory symptoms?
Correct Answer : A
Q.81. A 58-year-old patient presents with decreased vision and reports difficulty seeing from the periphery. Upon examination, you measure the intraocular pressure using a tonometer. The right eye measures 24 mmHg, and the left eye measures 22 mmHg. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism behind this patient's condition?
Correct Answer : B
Open-angle glaucoma is the most common form of glaucoma and occurs due to a gradual obstruction of aqueous humor outflow through the trabecular meshwork or Schlemm's canal, despite the normal production of aqueous humor. This leads to increased intraocular pressure and subsequent damage to the optic nerve, causing peripheral vision loss.
Q.82. A patient complains of discomfort in the eye. There is no discharge. On examination with dye, a dendritic shaped ulcer is seen on the surface of the cornea. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Corneal ulcer, ulcerative keratitis, or eyesore is an inflammatory or more seriously, infective condition of the cornea involving disruption of its epithelial layer with involvement of the corneal stroma.
Q.83. A patient complains of 2 days history of sticky lashes on waking up. There is muco- purulent discharge. Anterior Chamber, uvea and iris are clear. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Bacterial conjunctivitis is usually a benign self-limiting illness, although it can sometimes be serious or signify a severe underlying systemic disease. Occasionally, significant ocular and systemic morbidity may result.
Q.84. What is true for Blow out fracture?
Correct Answer : A
Q.85. An old diabetic man presented in ER with sudden unilateral visual loss. There is multiple pigmentation in retina with macular edema. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.86. What is the difference between uveitis and keratitis?
Correct Answer : C
foreign body sensation more common in keratitis
Q.87. A 70-year-old male with a history of diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension (HTN), multiple cardiac events, and a cerebrovascular accident (CVA) presents for a routine check-up at a primary healthcare center. Upon examination, bilateral opacification of both lenses is noted, and there is a decrease in visual acuity. What will you do next in the management of this patient?
Correct Answer : C
Bilateral opacification of the lenses with decreasing visual acuity in an elderly patient with DM and HTN is highly suggestive of cataracts
Q.88. A patient presents with a history of sudden eye pain, burning vision, photophobia, and on examination, you find a small pupil, herpetic cells on the cornea, and cells in the anterior chamber (hypopyon). What is the most appropriate treatment for this condition?
Correct Answer : C
The most appropriate treatment for this patient with herpetic keratitis and anterior uveitis is a combination of topical antiviral therapy (such as acyclovir) and topical corticosteroids (used cautiously and under supervision to prevent viral spread).
Q.89. Patient came with eye pain, watery discharge and light sensitivity. eye examination showed corneal ulceration. Her symptoms are frequently repeated. Which of the following is triggering for recurrence of her symptoms?
Correct Answer : A
Q.90. What is the most dangerous red eye that need urgent referral to ophthalmologist?
Correct Answer : D
Q.91. A 7 day old neonate was brought in your OPD with mucopurulent eye discharge, lid swelling and culture positive for gram negative diplococci. what is the treatment?
Correct Answer : A
Q.92. A 30 year old male patient presented with red eyes for one day with watery discharge. No itching or pain or trauma was recalled by the patient. On examination, there is conjunctival injection, visual acuity 20/20, what is next management?
Correct Answer : D
If allergic rhinitis: topical steroid, second line: antihistamine.
Q.93. Which of the following is the common cause of keratitis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.94. A patient presents with a history of erythema and vesicles on the forehead, but no affect on vision. What is the best management for this patient?
Correct Answer : B
Q.95. Which one of the following is diagnosed through cover test?
Correct Answer : A
Q.96. A 6 year old child presented in OPD with proptosis, a red eye, and restricted eye movement. The general examination appears normal. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.97. 4 years old in his normal state of health presented with decrease visual acuity bilaterally without any defect in visual field his VA Rt eye= 20/100 VA Lt eye=20/160 fundoscopic exam showed early signs of cataract and drusen with irregular pigmentations. No macular edema or neovascularization. What is the appropriate action beside antioxidants and Zn?
Correct Answer : B
Q.98. Farmer with allergic conjunctivitis in spring and he can't avoid working. what would you advise him?
Correct Answer : B
Q.99. A 60 year old patient who is a known case of DM and HTN, is gradually losing vision. Eye exam shows maculopathy, what is the Treatment?
Correct Answer : D
Q.100. What could cause painful vision loss?
Correct Answer : A
Q.101. A 45-year-old male presents to the emergency department with complaints of sudden onset of drooping of the right eyelid, blurred vision, and difficulty moving his right eye. He mentions that his right eye seems to be
Correct Answer : A
The patient's symptoms — complete ptosis, fixed and dilated pupil, downward and outward deviation of the eye, and restricted ocular movements — are characteristic of third nerve pal
Q.102. A 13 years old otherwise healthy boy has bought a new cat, now the boy has developed congested eyes and nose with stingy discharge. what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
The patient's symptoms — complete ptosis, fixed and dilated pupil, downward and outward deviation of the eye, and restricted ocular movements — are characteristic of third nerve palsy.