
Hello,
Dr. Batman
Hello Doctor, Welcome!
Profile

Name: Batman
Email: batman@gotham.com
PAEDIATRICS REVIEW
(Total Questions - 412)Q.1. A baby presented in ER with tonic-clonic convulsions. What drug will you give the mother to take home if there is another seizure?
Correct Answer : A
Q.2. A 4-weeks old male child with acute onset forceful non-bilious vomiting after feeding. He is the first child in the family. He is gaining normal weight and looks hungry. What’s your diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.3. A 3-months old baby presented in ER with stiff neck, high-grade fever and headache. What would be your initial treatment?
Correct Answer : C
Diagnosis - Meningitis
Q.4. What will you advice regarding a full-term baby who is on breastfeed?
Correct Answer : D
Q.5. A 9-days old neonate is brought by his mother for a check-up. He was delivered by spontaneous normal vaginal delivery without any complications. Birth weight was 3.4 and his birth weight now is 3.9. He is suckling well and looks normal except for jaundice. What’s your diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
This neonate's jaundice is likely physiological jaundice, which is common in newborns and usually appears around the 2nd to 3rd day of life and peaks at about 5-7 days before gradually resolving.
Q.6. A full term baby boy brought by his mother, weight 3.8 kg. He has developed jaundice at 2nd day of life. Coomb’s test –ve, Hb= 18g/dl, bilirubin: 18.9 & indirect: 18.4, O/E: baby was healthy and feeding well. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Breast milk jaundice is a different which tends to develop after the first 4-7 days of life, and continues up to the sixth week of life. It occurs early caused by insufficient breast milk intake. (Low calories).
Physiologic jaundice: manifests after the first 24 hours of life.
Q.7. The cardiac arrest in children is uncommon but if occurs what could be the cause?
Correct Answer : A
Respiratory failure can lead to hypoxia, which, if left untreated, can progress to cardiac arrest
Q.8. A 7-year-old child has been successfully resuscitated after experiencing a cardiac arrest. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) was performed, and the child is now stable but requires further intervention. After performing CPR on a child, which of the following drugs is most commonly administered to support the child’s circulation and increase the chances of survival?
Correct Answer : B
After CPR for cardiac arrest in children, epinephrine is the most commonly administered drug. According to Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) guidelines, epinephrine is recommended to improve the chances of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC).
Q.9. A baby was brought in ER with a history of harsh barky cough, stridor, air trapping, tachypnoea & chest retractions. What is the best management?
Correct Answer : D
Since croup is usually a viral disease, antibiotics are not used unless a secondary bacterial infection is suspected.
In cases of possible secondary bacterial infection, the antibiotics vancomycin and cefotaxime are recommended.
In severe cases associated with influenza A or B, antiviral neuraminidase inhibitors may be administered.
Management of croup - Humidified epinephrine, humidified O2, IV hydration, steroids.
Q.10. 5 year old boy is brought to the ER by his mother complaining of drooling saliva, inability to drink & eat. On examination there was congested larynx. What is the most appropriate diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
It occurs at any age, has rapid onset, causes drooling of saliva & inability to drink or eat, no cough & you could see the congested larynx.
Croup has a slow onset and occurs at ages <4 years with a barking cough & the ability to swallow fluids.
Management - Intubation
Q.11. 15 year old boy had history of URTI 2 weeks ago. Now he is complaining of fever, bilateral knee pain with swelling & tenderness. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Q.12. 10-year old boy presented with a 5 days history of skin lesion which was itchy, scaly & red-yellowish. What is the diagnosis?
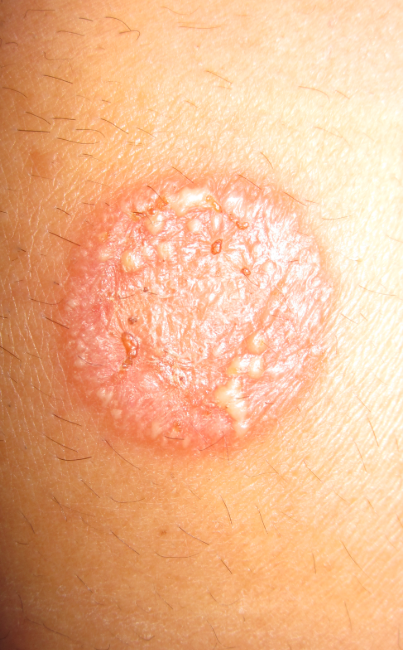
Correct Answer : A
Q.13. What is TRUE regarding Apgar score?
Correct Answer : A
* This scoring system provided a standardized assessment for infants after delivery. The Apgar score
comprises 5 components: heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, reflex irritability, and color, each
of which is given a score of 0, 1, or 2. The score is now reported at 1 and 5 minutes after birth.
Q.14. A child has history of loose stools at home. He had several episodes throughout the day and developed dehydration. Weight of the child is 25 kgs. Replacement fluid was given in ER, now how much maintenance fluid would you give to this child?
Correct Answer : D
Q.15. 11 month old baby, his weight is 10 kgs. How much maintenance fluid would you advise?
Correct Answer : A
4-2-1 rule : For hourly requirements, administer 4ml/kg/hr for the first 10 kg, 2ml/kg/hr for the next 10 kg, and 1ml/kg/hr for weight above 20 kg.
Q.16. A mother brings her 3-month-old baby to the clinic for a follow-up. The baby was diagnosed with a cleft palate at birth. The mother asks about the likelihood of having another child with a cleft palate or cleft lip in future pregnancies. How will you respond to this question?
Correct Answer : D
The risk is about 2-4% for a second child, depending on whether the first child had a cleft lip, cleft palate, or both.
Q.17. A 10-year-old child was diagnosed with rheumatic fever with carditis as a clinical feature but was treated early, and there were no residual cardiac complications. The child is now in remission and presents to the clinic for follow-up care. For how many years should rheumatic fever prophylaxis (e.g., antibiotics to prevent recurrence) be continued in this child?
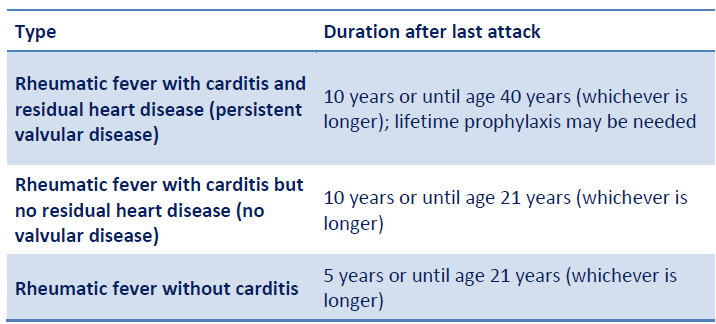
Correct Answer : D
Duration of Secondary Prophylaxis for Rheumatic Fever is in the table
Q.18. A 7-year-old child presents with acute onset of bruising and petechiae over the last few days. Laboratory tests show thrombocytopenia, and the child is treated with heparin and fresh frozen plasma (FFP). There is no history of trauma or bleeding disorders in the family. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
The combination of thrombocytopenia, acute onset of bruising and petechiae, and treatment with heparin and fresh frozen plasma (FFP) points to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
Q.19. A Child is complaining of severe headache which is unilateral, throbbing and aggravated by light. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.20. Infant with features of Down syndrome. What does this infant most likely have?
Correct Answer : A
Q.21. A 8 month old infant with on & off recurrent crying episodes & history of current-jelly like stools. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.22. A 8 month old infant with on & off recurrent crying episodes & history of current-jelly like stools. What is the management?
Correct Answer : A
Q.23. A 2-month-old baby was brought in your clinic. He was born to a mother with untreated HIV infection. The baby is being monitored for any signs of illness and is preparing for routine vaccinations. Which vaccination should not be given to this baby due to the risk of complications?
Correct Answer : A
Live attenuated vaccines (oral polio, MMR, rotavirus, varicella, BCG) are contraindicated in patients with immunodeficiency.
Q.24. What is the most common chromosomal abnormality?
Correct Answer : A
Q.25. Who should not get the oral polio vaccine?
Correct Answer : D
OPV should not be given when there is a higher risk of bad effects caused by the vaccine, including the
following:
1. Being moderately or severely (badly) ill with or without fever.
2. Having someone in the house with a weak immune system
3. History of a severe allergic reaction to a dose of OPV
4. Long-term treatment with steroid medicine.
5. Weak immune system. The immune system is the part of the body that normally fights off sickness and
disease. A weak immune system may be caused by cancer, HIV or AIDS, inborn immune deficiency, or
taking medicines, such as chemotherapy.
Q.26. A Mother brought her 18-month-old infant to ER with a history of URTI for the last 2 days with mild respiratory distress. The infant started to have barky cough with respiratory distress. O/E: RR 40/min, associated with nasal flaring, suprasternal & intercostal recessions. No stridor. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Q.27. A 6-year-old child is brought to the pediatric clinic for a developmental assessment. The parents are concerned about the child’s ability to learn and understand new concepts compared to other children of the same age. Which of the following is most commonly used to measure the intellectual ability of a child?
Correct Answer : A
Q.28. A 3-year-old child is brought to the emergency department after swallowing a relative’s medication approximately 15 minutes ago. The parents are concerned and want to know the best approach for gastric decontamination. What is the best approach for gastric decontamination in this child?
Correct Answer : D
In cases of poisoning or accidental ingestion, the first step is to determine the type of substance ingested and the timing. For a child who swallowed a medication 15 minutes ago, activated charcoal is often the best choice for gastric decontamination, as it can absorb many toxic substances and prevent their absorption into the bloodstream.
Q.29. Infant swallowed a cohesive material, presented within half an hour to ER with saliva drooling & crying. What is the initial thing to do?
Correct Answer : C
Q.30. A 4-year-old child is brought to the emergency department after accidentally ingesting an overdose of iron supplements. The child is showing signs of vomiting, abdominal pain, and lethargy. The parents are concerned and are asking about the best way to manage the overdose. How will you manage?
Correct Answer : A
Iron overdose is a medical emergency, and the best immediate management involves deferoxamine, a specific iron-chelating agent
Q.31. A 6-year-old child presents with pallor and a history of eating little meat. On investigation, the child is found to have microcytic hypochromic anemia. The parents are concerned, and you need to guide them regarding the next step in management. What would it be?
Correct Answer : A
Iron deficiency anemia
Q.32. A 7-year-old child presents with complaints of fatigue, stunted growth, and pallor. On further workup, the child’s blood tests reveal microcytic hypochromic anemia. The child has no history of excessive blood loss or chronic infections. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Q.33. A 12-year-old girl is brought to the clinic for a routine growth assessment. Her height is at the 10th percentile, and her parents are concerned about her growth and development. The child has already had her menarche (onset of menstruation) 6 months ago. When is the spinal length expected to complete its growth after menarche?
Correct Answer : C
After menarche, a girl’s growth spurt starts to slow down. However, spinal growth (a key contributor to height) continues for approximately 3-4 years after menarche. This is because the vertebral column is one of the last skeletal components to complete growth during puberty.
Q.34. 6 year old child's mother has Hepatitis B. The child did not receive any vaccination except BCG. Which vaccines should he receive now?
Correct Answer : C
Q.35. A 6-month-old infant is brought to the emergency department with a history of bright blood in the stool, black tarry stool, and foul-smelling stools over the past 24 hours. The infant is otherwise well, with no significant history of illness or recent trauma. Which diagnostic test is most accurate to determine the underlying cause of the infant’s symptoms?
Correct Answer : B
The combination of bright blood in the stool, black tarry stools, and foul-smelling stools raises suspicion for Meckel’s diverticulum, the most common congenital abnormality of the GI tract.
Q.36. A 3-day old baby's mother has HBV positive, and she is concerned about her child's health. What advise you would give?
Correct Answer : A
Infant of mother HBV-positive must receive immunoglobulin within first 12 hour and vaccination as 0,1 and 6 months For this child it is too late for immunoglobulin, While the optimal window is within 12 hours of birth, it can still offer protective benefits if given later.
Q.37. A 2-month-old infant is brought to the emergency department with a 12-hour history of recurrent vomiting. The vomiting started suddenly and is bilious (greenish). The parents report the baby has been irritable and inconsolable. On examination, the baby has mild abdominal distension, and there is no palpable mass. The baby passed meconium within the first 24 hours of birth, but has had reduced stool output since the onset of symptoms. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Midgut volvulus is a surgical emergency caused by twisting of the bowel around the superior mesenteric artery, leading to bowel obstruction and possible ischemia.
Q.38. A 6-year old child was sick since 5 days. Blood culture taken and was positive for meningococcal. Patient is now at home and asymptomatic. What's your action?
Correct Answer : B
Q.39. Which of the following injection is routinely given to new-born to prevent hemorrhage?
Correct Answer : A
Q.40. A 5-year-old child presents with a history of upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) one week ago. The parents now report that the child has frequent nosebleeds (epistaxis), bleeding from the gums, and easy bruising. There is no history of fever, significant trauma, or family history of bleeding disorders. On examination, the child is alert, with no hepatosplenomegaly or lymphadenopathy. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.41. A Child came in your OPD, with his father, has high BMI and looks older than other children of same age. On examination, child has >95th percentile of weight and height. What is the appropriate management?
Correct Answer : C
Q.42. A newborn is brought to the clinic with a red patch on the left shoulder noticed since birth. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.43. A 3 month old infant was brought in your clinic due to red colored swelling over neck that increases in size rapidly. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.44. A newborn presented with congenital hepatomegaly, jaundice and raised LFT. Which is the likely organism causing these symptoms?
Correct Answer : D
Q.45. Which of the following is NOT a feature of Henoch-Schonlein purpura (HSP)?
Correct Answer : B
Q.46. A child presented in your clinic with URTI. Which of the following symptom suggests viral infection?
Correct Answer : A
Q.47. A 2 year old child with Sickle cell anemia should be maintained on which of the following drugs?
Correct Answer : A
Q.48. After an insect bite, a 5-year old boy presented in ER with abdominal pain and vomiting. On examination, he was vitally stable but rash over buttock and lower limbs, edema of hands and soles were observed . Urine function was normal but microscopic hematuria was present. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.49. A child developed purpuric rashes over his extremities, this rash was preceded by upper respiratory tract infection 1 week ago. What is your probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
HSP skin rash distribution: lower extremities (dorsal surface of the legs), buttocks, ulnar side of arms & elbows.
Workup: CBC: can show leukocytosis with eosinophilia & a left shift, thrombocytosis in 67% of cases.
Decreased platelets suggest thrombocytopenic purpura rather than HSP.
Q.50. Which organism causes cellulitis in neonate?
Correct Answer : A
Q.51. Which vessels are affected by Henoch-Schoenlein purpura?
Correct Answer : C
Q.52. Which of the following is more common when a baby presents with conjugated hyperbilirubinemia?
Correct Answer : A
Q.53. Which HLA is responsible in diabetes mellites?
Correct Answer : D
Q.54. A 7 year old child had a history of chest infection which was treated with antibiotics. The patient presented 1 weeks after stopping antibiotics with a abdominal pain, fever and profuse watery diarrhea. Which of the following organism is responsible for the patient’s condition?
Correct Answer : B
It causes severe diarrhea when competing bacteria in the gut flora have been wiped out by antibiotics.
Q.55. Which of the following is an appropriate gross motor developmental milestone 6 months of age?
Correct Answer : A
Q.56. Which of the following drug overdose needs an urgent attention in a child?
Correct Answer : D
Q.57. Child woke up with a sudden onset of croupy cough. What could be the possible cause?
Correct Answer : C
Q.58. A child came with in your clinic with wheezing and cough. He was diagnosed to have asthma, and you have prescribed beclomethasone space inhalers twice daily. What is the most concerning side effect of using it?
Correct Answer : A
Q.59. A father of twin children came in your clinic for routine check up. He is concerned about the girl attaining puberty before the boy. What will you tell him?
Correct Answer : B
- Girls: Puberty usually begins between 8–13 years, with thelarche (breast budding) as the first sign.
- Boys: Puberty typically starts between 9–14 years, with testicular enlargement as the first sign.
Q.60. In a boy with nocturnal enuresis, psychotherapy failed to show results. What medication will you start for the boy?
Correct Answer : A
Q.61. What is the earliest sign of puberty in male?
Correct Answer : B
The first sign of puberty in boys in testicular enlargement more than 2.5 centimeters which is followed by a growth spurt 1-2 years later and beginning of spermatogenesis.
Q.62. A boy came in your clinic with a history of wheals on erythematous base 10 days before. Now, during examination, you found that he has preorbital swelling, supraclavicular Lymph node enlargement, hepatomegaly and splenomegaly. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Presence of LNpathy is always concerning.
Q.63. 6 months old male patient presented with acyanotic heart disease, all of the following are acyanotic heart lesions EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
Q.64. What is the most common cause of cellulitis in children?
Correct Answer : B
* Staphylococcus aureus is the most common bacteria that causes cellulitis.
* Group A Streptococcus is the next most common bacteria that cause cellulitis. A rather superficial cellulitis caused by strep bacteria is called erysipelas, characterized by spreading hot, bright red circumscribed area on the skin with a sharply raised border. The so-called “flesh-eating bacteria” are, in fact, also a strain of strep which can – in severe cases – destroy tissue almost as fast as surgeons can cut it out.
Q.65. In developing countries to prevent dental caries, what should be added to water?
Correct Answer : A
Q.66. A baby presented in an ER with complains of fever, chills, rigors and neck rigidity, on examination, signs of meningeal irritation are positive along with rashes on his lower limb. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.67. A 6-month old baby was brought in clinic with complaint of undescended testis. Which of the following is TRUE?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Most of spontaneous descent cases occur before the age of 6 months. If no descent occurs at 6 months, surgery is indicated before the age of 2 years.
Q.68. By forcing the child to go to the toilet before bedtime and early in the morning. Which of the following problem will you control?
Correct Answer : A
Q.69. A 7-month old child presented with cellulitis of the face associated with fever and bluish skin discoloration. What is the most likely cause?
Correct Answer : B
Whilestreptococcus can cause cellulitis, it is less likely to cause the distinctive bluish discoloration seen in Hib-associated cellulitis.
Q.70. A 2-year old boy presented with atopic dermatitis and cough with wheezing. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.71. A child who is known case of sickle cell disease is admitted with recurrent UTI which has now been treated. He is now stable and is ready for discharge. Which of the following medications will you start prophylactically for him now?
Correct Answer : A
Q.72. A 2 year old child, known case of sickle cell disease, presented in ER with hand and foot swelling, and excessive crying. Which medications will you prescribe him on discharge?
Correct Answer : A
Q.73. What is most common malignancy in children?
Correct Answer : A
Wilms tumor: The most common feature at presentation is an abdominal mass. Abdominal pain occurs in 30%-40% of cases. Other signs and symptoms of Wilms tumor include hypertension, fever caused by tumor necrosis, hematuria, and anemia.
A renal tumor of embryonal origin is most commonly seen in children 2–5 years of age.
Associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (hemihypertrophy, macroglossia, and visceromegaly), neurofibromatosis, and WAGR syndrome (Wilms’, Aniridia, Genitourinary abnormalities, mental Retardation).
Presents as an asymptomatic, non-tender, smooth abdominal mass, abdominal pain, fever, hypertension, and microscopic or gross hematuria.
Treatment: Local resection and nephrectomy.
Q.74. What is the management of mild dehydration during diarrhea?
Correct Answer : A
Q.75. Most common intra-abdominal tumor in children?
Correct Answer : A
Q.76. How will you diagnose thalassemia minor?
Correct Answer : A
Beta Thalassemia Minor:
The peripheral smear will show target cells and basophilic stippling. See increased HbA2 in the 5-9% range with normal HbF. Diagnosis may be obscured in concomitant iron deficiency present because Beta-thalassemia causes an increase in HbA2 while iron deficiency causes a decrease in HbA2. Both create a microcytosis.
Q.77. Which of the following does not cause Celiac disease?
Correct Answer : A
Q.78. Celiac disease involves which of the following?
Correct Answer : A
Q.79. 4 year old baby found comatose and cyanotic in the kitchen. There were peanuts in his hand. What is the likely cause?
Correct Answer : D
Q.80. A 15 year old boy came with complaint of unilateral gynecomastia. What would be your advice?
Correct Answer : A
Uni- or bilateral gynecomastia occurs normally in newborns & at puberty.
Q.81. A 6-year-old child presents with cyanosis, which was similar to an episode 6 months ago. The child has no significant past medical history, but parents report that the child occasionally has difficulty breathing during physical activity. The child appears comfortable at rest, but cyanosis is noted during the episode. What is the best investigation to confirm the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
- Echocardiogram is the gold standard investigation to evaluate structural heart anomalies and assess blood flow through the heart, making it the best test for diagnosing congenital heart defects that could cause cyanosis. It will help identify abnormalities such as septal defects, pulmonary stenosis, or shunts that cause cyanosis.
Q.82. A 6 month old presented with fever, cough and wheezy chest. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
A. After 1 years of age
B. Before 1 years of age
C. Associated with crepitations
D. Sudden onset wheezing
Q.83. Child presented with anemia. He has family history of thalassemia. What is the most diagnostic test?
Correct Answer : A
The most diagnostic test is hemoglobin electrophoresis.
Q.84. Child presented in ER with Shortness of breath. On x-ray there is an infiltration in mid & lower zone on right lung. After 24hr of antibiotics, the patient became cyanosed and the x-ray shows total lung collapse with mediastinal shift. What is the causative agent?
Correct Answer : D
This case describes a rapidly progressing pneumonia with lung collapse and a mediastinal shift, which strongly suggests empyema or parapneumonic effusion. The sequence of events, including initial pneumonia and subsequent worsening despite antibiotics, is highly suggestive of a complicated pneumonia. In this case, Staphylococcus aureus, particularly Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), is the most likely cause.
Q.85. An 8-month-old boy presents with fever, shortness of breath, poor feeding, and confusion. On examination, the right ear is red and tender, and the ESR is high. The infant appears distressed and lethargic. What is the next best step in diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
This case presents a child with fever, shortness of breath, poor feeding, and confusion, along with a red, tender ear and elevated ESR, which suggests a systemic infection. The most likely underlying condition here is an acute otitis media (AOM) with potential complications, such as mastoiditis or an associated intracranial infection. The presence of shortness of breath and confusion may suggest a severe bacterial infection with a possible complicated ear infection.
Q.86. Infant presented in ER with coryza, wheezing and URTI symptoms and now he has shortness of breath. What is the initial management?
Correct Answer : A
Q.87. 12 year old boy came to you complaining that he worries about himself because he sees that his friends have axillary hair and he is not like them. What is the first to develop in boys at puberty?
Correct Answer : A
Q.88. A child brought by mother due to bleeding per nose. On examination you found many bruises on his body, mostly over his back, abdomen and thigh. What is your probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.89. A 9-month old child who is a known case of congenital heart disease now presented in ER due to central and peripheral cyanosis. What is the most probable condition?
Correct Answer : A
Q.90. Child presented with a recurrent episodes of spontaneous epistaxis. What is the likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.91. 3 year old child presented in ER due to diarrhea with blood & mucus since 10 days. On investigation, no cyst in stool examination. What is the most common cause?
Correct Answer : D
The clinical presentation of diarrhea with blood and mucus for 10 days, without finding any cysts on stool examination, is highly suggestive of dysentery, which is often caused by a bacterial infection. The absence of cysts in the stool rules out amoebic dysentery (which would be caused by Entamoeba histolytica) and points towards a bacterial cause.
Q.92. A child presented with dry cough & wheeze. CXR showed hyper-inflated lung with some infiltrate. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.93. A 4-year old child presented in OPD with complaint of abdominal pain. he is anemic and also had blood in stools . What would be the initial investigation?
Correct Answer : A
Diagnosis of Malrotation with Volvulus :
AXR may reveal the absence of intestinal gas but may also be normal.
If the patient is stable, an upper GI is the study of choice and shows an abnormal location of the
ligament of Treitz. Ultrasound may be used, but the experience of the ultra-sonographer determines sensitivity.
Q.94. A patient who is a known case of endocarditis will be undergoing a dental procedure. What would be the prophylaxis regime?
Correct Answer : A
Q.95. How does cow milk differ from mature human milk?
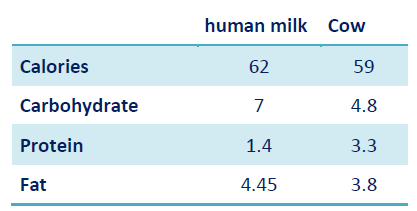
Correct Answer : A
All minerals are much more in cow milk than human milk except iron & copper.
Q.96. A child came in a clinic due to congested throat & tonsil. He had white plaque on erythematous base on tongue & lips, and there is gingivitis. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.97. What is the dietary feature that leads to Kwashiorkor?
Correct Answer : C
Q.98. What is the definition of nutritional marasmus?
Correct Answer : C
Kwashiorkor is caused by insufficient protein consumption but with sufficient calorie intake,distinguishing it from marasmus. Marasmus is a form of severe protein-energy malnutrition characterized by energy deficiency caused by inadequate intake of proteins and calories. A child with marasmus looks emaciated. Body weight
may be reduced to less than 80% of the average weight that corresponds to the height. Marasmus occurrence increases prior to age 1, whereas kwashiorkor occurrence increases after 18 months. It can be distinguished from kwashiorkor in that kwashiorkor is protein wasting with the presence of edema. The prognosis is better than it is for kwashiorkor.
Q.99. A 6-month old boy presented with fever. Antipyretics should be given in this boy to prevent which of the following complication?
Correct Answer : A
Q.100. A 8 months old boy presented with fever, Shortness of breath, poor feeding and sleepy. On examination, he is lethargic and ESR is high. What is the next best step in diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.101. What is the most common cause of URTI?
Correct Answer : A
Viruses cause most URIs, with rhinovirus, parainfluenza virus, coronavirus, adenovirus, respiratory syncytial virus.
Q.102. What is the association of Kawasaki disease?
Correct Answer : D
Kawasaki disease: Multisystem acute Vasculitis that primarily affected young children. Fever plus four or more of the following criteria for diagnosis:
1) fever > 40 C for at least five days
2) Bilateral, non-exudative, painless conjunctivitis
3) Polymorphous rash (primarily truncal)
4) Cervical lymphadenopathy (often painful and unilateral)
5) Diffuse mucous membrane erythema ( strawberry tongue ), dry red
6) Erythema of palm and sole
7) Other manifestations: gallbladder hydrops, hepatitis, arthritis
Untreated Kawasaki disease can lead to coronary aneurysms and even MI.
Treatment:
1) High dose ASA ( for fever and inflammation) & IVIG ( to prevent aneurysm )
2) Referral to pediatric cardiologist.
Q.103. A 7-year-old child presents with a skin rash, pericarditis, and arthritis. The child has a history of a recent sore throat. On examination, the child has a joint swelling, and the skin rash is described as pink macules on the trunk and limbs. The child is also experiencing chest pain and has a friction rub on auscultation. What is the most likely diagnosis for this child?
Correct Answer : B
Q.104. A child presented with low grade fever, erythematous pharynx, with enlarged cervical lymph nodes. Rapid streptolysin test is negative while positive EBV PCR. What would be the next step?
Correct Answer : B
Q.105. A 2-month-old infant presents with spitting up of milk after feeds. On abdominal examination, the abdomen is soft and lax, and there is no occult blood in the stool. The infant is feeding well and has no other significant symptoms. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
Correct Answer : A
Q.106. A baby with streptococcal pharyngitis was started on treatment, he is improved now after two days of treatment. How many days of antibiotic course is needed for streptococcus pharyngitis?
Correct Answer : A
If group A streptococcus is suspected, begin empiric antibiotic therapy with penicillin × 10 days. Cephalosporin, amoxicillin, and azithromycin are alternative options. Symptom relief can be attained with fluids, rest, antipyretics, and salt-water gargles.
Q.107. A newborn presents with a heart rate of 300 bpm and a narrow QRS complex on an ECG. The infant has normal blood pressure and normal respiratory rate. There are no signs of respiratory distress or other abnormalities. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
Correct Answer : C
Treatment of supraventricular tachycardia in asymptomatic patients. Ice to face and vagal maneuvers, Adenosine,Propranolol,Digoxin,Procainamide.
Q.108. A 5-year-old child presents with fever, which lasts for 2 days. After this, the child develops a sore throat and lesions on an erythematous base inside the mouth, along with gingivitis. The child also has signs of irritability and general malaise. What is the most likely cause of these symptoms?
Correct Answer : A
This child’s presentation of fever, sore throat, mouth lesions, and gingivitis is most consistent with Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD), which is commonly caused by Coxsackievirus A16 or other enteroviruses.
Q.109. Child presented to ER with fever, dyspnea, and difficulty in breathing. On investigations, sub epiglottic narrowing on x-ray. What is the probable diagnosis?
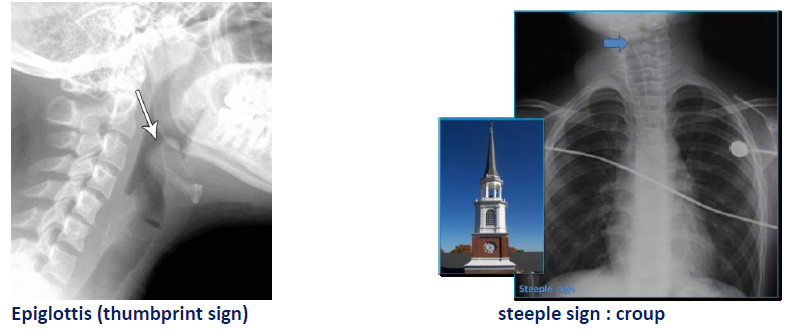
Correct Answer : A
If thumbprint sign: Epiglotittis
If steeple sign: croup
Q.110. A Child is on chemotherapy and has developed septicemia after IV cannula insertion. What is the most likely causative organism?
Correct Answer : B
Q.111. Baby was born & got discharged with his mother. 2 weeks later he developed difficulty in breathing & became cyanotic. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.112. What is the management for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children?
Correct Answer : B
A combination of medications and behavioral therapy is far superior to just medication treatment. A class of drugs called psychostimulants is a highly effective treatment for childhood ADHD. Another treatment is non-stimulant medication. These medications include Intuniv, Kapvay , and Strattera “atomoxetine”.
Q.113. Child with moderate persistent Bronchial asthma is on bronchodilator inhaler and now presented with acute exacerbation. What will you add in maintenance treatment?
Correct Answer : A
Q.114. What is the best source of iron for a 3 month old infant?
Correct Answer : A
Infants absorb 100% of the iron in breast milk (less than 1 mg/L
Q.115. A 9 month old infant developed anemia. He was started cow's milk since 2 months of age. What will you suggest?
Correct Answer : A
Q.116. A child can walk without support at what age?
Correct Answer : C
12 months walk with one hand held, 15 months independently, and takes a step up at 18 months.
Q.117. A child recognizes 4 colors, 5 words, hops on one foot. These developmental milestones are consistent with which age?
Correct Answer : C
Q.118. You received a call from a father who has a son diagnosed recently with DM-I for six months. He said that he found his son lying unconscious in his bedroom. What will you advice him?
Correct Answer : D
Q.119. All are true about congenital heart disease in children EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
The true incidence of CHD is 4-5 per 1,000 live births. Figures as high as 8-10% are inaccurate.
Q.120. A 4 year old was brought by his parents with weight > 95th percentile, height < 5th percentile & bowing of both legs. What is the appropriate management?
Correct Answer : A
Q.121. Which of the following is the appropriate milestone of a 4 year child?
Correct Answer : A
Q.122. What condition is an absolute contraindication for lactation?
Correct Answer : C
Q.123. A child is about to receive a Flu vaccine. Which allergy should be excluded before giving the vaccine?
Correct Answer : B
Q.124. A newborn is delivered via normal vaginal delivery. On postnatal examination, a mid-clavicular fracture is identified. The infant is otherwise active, feeding well, and has normal vitals. There is no significant distress noted. Which of the following statements about clavicle fractures in newborns is true?
Correct Answer : C
Most clavicles fracture in newborns with no need for treatment apart from careful handling.
If the fracture is displaced and the baby in pain, the simple sling is required
Q.125. A 5-days old baby vomits dark red blood twice over the past 4 hours. He is active and feeding well by breast. What's the most likely cause?
Correct Answer : D
Q.126. A 8-year old girl presented with fever, numerous bruises over the entire body and pain in both legs. Physical examination reveals pallor and ecchymosis and petechiae on the face, trunk and extremities. Findings on complete blood count includes a hemoglobin of 6.3 g/dl, white cell count of 2800/mm3 and platelet count of 29,000/mm3. Which of the following would be the MOST appropriate diagnostic test?
Correct Answer : B
Q.127. A 12-months old baby can do all of the following EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : C
Q.128. A 5-month old baby presented in an ER with sudden abdominal pain, vomiting & excessive crying. The pain lasts for 2-3 minutes with an interval of 10-15 minutes in between. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.129. 3 year old boy on routine examination for a surgical procedure discovered to have low pitch murmur in the right 2nd intercostal space radiating to the right sternal border; increases on sitting & decreases on lying down. How will you manage?
Correct Answer : B
Innocent Murmur Heart murmurs that occur in the absence of anatomical or physiological abnormalities of the heart and therefore have no clinical significance.
Q.130. 1 year old baby presented in your clinic with acute hepatosplenomegaly, bluish skin nodules and lateral neck mass. What is the best investigation?
Correct Answer : B
Q.131. A 6 year old girl presented with a low grade fever and arthralgia for 5 days. She had difficulty in swallowing associated with fever 3 weeks prior to presentation. Physical examination revealed a heart rate of 150/min and pansystolic murmur at the apex. There was no gallop and liver was 1 cm below costal margin. What is the MOST likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.132. A 6 days old neonate was brought in your clinic due to not feeding well, lethargic, and her mother complaints that his urine smells like burned sugar. What is the most probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.133. A 3 year old child woke up during sleep with acute bouts of cough, the differential diagnosis should include all EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : A
Q.134. A 5-year-old child is brought for routine follow-up. He had a negative tuberculin skin test (TST) 6 months ago but now has a positive TST without any symptoms of active tuberculosis. The child has received all routine vaccinations, including BCG, and has no significant past medical history. A chest X-ray is normal, and there are no systemic signs such as fever, weight loss, or night sweats. What is the most appropriate treatment for this child?
Correct Answer : A
Start a 6-month course of isoniazid (INH) for latent TB infection (LTBI).
Q.135. A 15-year-old boy presents to the clinic for a routine check-up. He is asymptomatic. Blood tests reveal the following: Hemoglobin (Hb): 11.8 g/dL, White Blood Cell Count (WBC): 6.8 x 10?/L, Red Blood Cell Count (RBC): 6.3 x 10¹²/L, Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV): 69 f, Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH): 30 Reticulocyte Count: 1.2% . What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Beta-thalassemia trait often presents as mild microcytic anemia with a disproportionately elevated RBC count relative to the degree of anemia.
Q.136. A 10-year-old boy is brought to the clinic by his parents due to concerns about his short stature compared to peers. On examination, his height is below the 3rd percentile for his age. He is otherwise healthy, with no signs of chronic illness or dysmorphic features. His growth velocity is normal for his age. A bone age assessment shows that his skeletal maturation is delayed compared to his chronological age. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.137. Mother brings her baby to you with complains of diaper rash. She has used 3 different corticosteroid drugs prescribed by different physicians, the rash is well demarcated & scaly. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.138. What is the treatment for contact dermatitis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.139. A 18 months old child was brought to you due to delayed speech. How will you assess the speech?
Correct Answer : B
Q.140. A 1 year old child presents with a history of nasal discharge and wheezing. On examination, the patient had signs of severe respiratory distress along with rales at the end inspiratory & early expiratory phase. He had prolonged expiratory phase, and was using accessory respiratory muscles. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.141. A mother has brought her 2 year old baby to you due to hematoma in his nail. How would you manage this patient?
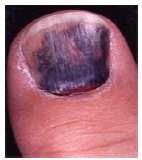
Correct Answer : B
Q.142. A 12-year-old boy presents with morbid obesity and a BMI greater than the 99th percentile for his age and gender. He has no known chronic conditions but reports fatigue and difficulty keeping up in physical activities. The family history reveals obesity in both parents. The child’s diet consists of frequent fast food and sugary beverages. Physical examination shows no signs of endocrine or genetic syndromes. What is the best initial advice for this child?
Correct Answer : A
Q.143. A child presented in an emergency room due to blood in urine since 6 hours. He also had fatigue and loss of appetite. Mother gave history of sore throat 3 weeks back. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.144. A 12-year-old girl presents with crampy abdominal pain and proximal muscle weakness. She was treated with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for a urinary tract infection (UTI) 1 week ago. On examination, there is no fever, rash, or swelling. Blood investigations reveal hypokalemia. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Q.145. A 2-year-old boy presents with a 3-day history of coryza, cough, and red eyes with watery discharge. On examination, his conjunctivae are erythematous with no purulent discharge, and he has a runny nose. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Cough, coryza, conjunctivitis (red eyes), 40 °C, Koplik's spots seen inside the mouth are pathognomonic (diagnostic) for measles.
Q.146. What are the absolute contraindications to DTP and DTaP?
Correct Answer : A
Contraindications: DTP or DTaP administration
**Absolute:
1. Severe reaction following prior DTP or DTaP
2. Immediate Anaphylaxis
3. Encephalopathy within 7 days of Vaccine
4. Relative:
5. Moderate Reaction following prior DTP or DTaP
6. Fever > 40.5 C within 48 hours of vaccine
7. Seizure within 72 hours of vaccine
8. Hypotension or Unresponsive Episode within 48 hours
9. Inconsolable Crying >3 hours within 48 hours
10. Guillain-Barre Syndrome within 6 weeks of vaccine
11. Conditions not contraindicating vaccine
12. Family History of an adverse vaccine event
13. Family History of SIDS
14. Family of Seizure disorder
15. Fever following prior vaccine <40.5 C (105 F)
16. If the Vaccine Contraindicated, then
17. Allergy Testing for anaphylactic reaction
18. Administer DT to all other groups.
Q.147. What is the initial management of a obesity child?
Correct Answer : A
Q.148. Child starts to smile at which developmental age?
Correct Answer : B
Q.149. A 2-year-old baby is brought to the clinic by parents for a routine check-up. On examination, there is a grey to green patch on the lower back. The patch is flat, non-tender, and shows no redness or increased warmth. The parents state that the mark has been present since birth and hasn’t changed in size or color. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Mongolian spot: visible in 6 months and normally disappears in 3-5 years. No need treatment
Q.150. A 6-year-old child presents for a routine examination. On auscultation, the doctor notes a mid-sternal murmur that is late systolic, with a crescendo-decrescendo pattern, a wide splitting of the second heart sound, and a click heard at the apex. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.151. A baby can sit without support, walk by holding furniture. Pincer grasp, pull to stand. What do you think, how old is he?
Correct Answer : B
Q.152. 3 days after flu symptoms, a boy has developed conjunctivitis with occipital and neck lymph nodes enlargement. Which of the following organism cause conjunctivitis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.153. What is the most common cause of failure to thrive in pediatric age group?
Correct Answer : A
Q.154. A 3-month-old baby is brought in for a routine check-up. The parents are concerned about an increase in the size of a hemangioma on the baby’s back, which has grown by about 2 cm. The hemangioma is not causing any pain, bleeding, or functional impairment but the parents are anxious about the changes. What is the most appropriate management for this baby?
Correct Answer : A
Q.155. At which age a child can copy triangle and a square?
Correct Answer : C
Q.156. A child with dental caries and a history of bottle feeding. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.157. A lactating woman presents with a rash and fever, and is diagnosed with rubella. She is breastfeeding her infant and is concerned about the safety of breastfeeding during the illness. What is the most appropriate management for this lactating woman with rubella?
Correct Answer : A
The rubella vaccine is contraindicated during pregnancy but is safe after delivery. However, breastfeeding women are not a contraindication to receiving the rubella vaccine, but it is typically given to prevent future rubella infections, not for treatment of an active infection.
Q.158. A 2-month-old infant presented with white plaques on a tongue and is greasy. Past history of chlamydia conjunctivitis after birth which was treated with clindamycin. What is the treatment for oral thrush?
Correct Answer : A
Q.159. What will you do when you see asystole rhythm on the monitor?
Correct Answer : A
Asystole is a non shockable rhythms.
Q.160. Group of diseases like cystic fibrosis, Gall stones, liver failure, bronchiectasis etc. are associated with which of the following conditions?
Correct Answer : A
α1-antitrypsin deficiency has been associated with a number of diseases:
Cirrhosis, COPD, pneumothorax, asthma, emphysema, Bronchiectasis, cystic fibrosis, Wegener's granulomatosis.
Pancreatitis, Gallstones, Primary sclerosing cholangitis & Autoimmune hepatitis, Pelvic organ prolapse, Secondary Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis, Gallbladder cancer, Hepatocellular carcinoma, bladder carcinoma, Lymphoma & Lung cancer.
Q.161. A 3-month-old infant presents to the emergency department with a fever of unknown origin. The infant appears irritable, and there is no obvious source of the fever (no rash, no respiratory distress, no signs of local infection). The child’s medical history is unremarkable, and the parents are concerned about the cause of the fever. Which of the following investigations would NOT be routinely performed during fever of unknown origin?
Correct Answer : A
Q.162. A 6-year-old child with a known history of moderate intermittent bronchial asthma is currently using inhaled salbutamol as a reliever. The child presents with worsening asthma symptoms including wheezing, shortness of breath, and coughing. The symptoms are not relieved by the usual inhaled salbutamol. What is the most appropriate management for this child with an asthma exacerbation?
Correct Answer : A
Q.163. What should we do for a child with febrile seizures?
Correct Answer : A
Q.164. A 2 month old baby is on breast feeding. The mother asks you about her baby's feeding. What would you advice?
Correct Answer : A
Q.165. A 5-year-old child falls from a bed and sustains multiple areas of erosion on the skin. The child is alert and conscious, but the injuries include abrasions on the elbows, knees, and forehead. There is no significant bleeding, and the child is not showing signs of a serious head injury. What is the most likely diagnosis for these injuries?
Correct Answer : A
Q.166. A 5-year-old child presents with symptoms of a upper respiratory tract infection (URTI), including nasal congestion, cough, and sore throat. On examination, the child also has lymphadenopathy (swollen lymph nodes) in the neck. What is the most appropriate management?
Correct Answer : B
Q.167. A boy presented to the ER complaining of sudden onset of abdominal pain & leg cramps. He had a history of vomiting 2 days ago, currently, he is dehydrated. Na = 150meq , K = 5.4meq, glucose = 23mmol, acidotic. What is the best initial investigation?
Correct Answer : C
Diagnosis - DKA.
Q.168. A 3 year old child needs oral surgery & comes to your clinic for a check-up. On examination, grade II continuous murmur in upper right sternal borders that disappears on sitting. What is the next step?
Correct Answer : B
Q.169. A 17 year old girl missed her second dose of varicella vaccine, the first one about 1 year ago. What will you do?
Correct Answer : B
Q.170. A pregnant lady came in your clinic to have an opinion about bearing a baby with polyhydramnios. What could be the cause of polyhydramnios?
Correct Answer : A
Q.171. A child with a mild trauma develops hemarthrosis at right knee, past history of similar episodes are significant. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Superficial bleeding- platelets dysfunction; Deep bleeding- clotting problems
Q.172. A 9 month old infant has newly started on cow milk. She had closed posterior fontanelle, open anterior fontanelle and presented with recurrent wheezing and cough. Sputum examination reveals hemoptysis and x-ray shows lung infiltration. What will be your action?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: infantile pulmonary hemosiderosis.
Q.173. Patient with signs and symptoms of autism came for first visit in your clinic. What would be the definitive management of autism?
Correct Answer : D
Treatment: A variety of therapies are available, including Applied behavior analysis (ABA), Occupational therapy, Physical therapy, Speech-language therapy.
Q.174. A 4-year-old child presents with bowing of the tibia (legs curved outward) and a prominent forehead. The child’s parents are concerned about the child’s growth and development. On examination, the child appears to be developing normally in other aspects but shows these distinctive skeletal changes . What is the most likely deficiency causing these symptoms?
Correct Answer : A
Diagnosis- Rickets
Q.175. A 5 year child has congested throat since 2 days. Now she has developed painless, clear, vaginal discharge. What is the probable causative organism?
Correct Answer : D
Q.176. When is the ideal time to start breast feeding after delivery?
Correct Answer : A
Q.177. A 14 year old boy with type 1 DM presented in an emergency room in the state of coma. His blood glucose level is 33 mmol/l. Na is 142 mmol/l, K is 5.5 mmol/l, bicarb is 10 mmol/l. All of the following are true EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
Hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis with a normal anion gap often persists after the resolution of ketonemia. This acidosis has no adverse clinical effects and is gradually corrected over the subsequent 24-48 hours by enhanced renal acid excretion.
Hyperchloremia can be aggravated by excessive chloride administration during the rehydration phase.
Q.178. 10 year old girl presented with 2 days history of fever and a 4 cm, warm, tender and fluctuant left anterior cervical lymph node. What is the MOST likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Q.179. A 7 month old child is brought to your office by his mother. He has an upper respiratory tract infection for the past 3 days. On examination, there is erythema of the left tympanic membrane with opacification. There are no other signs or symptoms. What is the MOST likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.180. Excessive nonbilious vomiting results in which of the following condition?
Correct Answer : A
Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia is also present.
Q.181. Which of the following medications has been shown to be safe and effective for migraine prophylaxis in children?
Correct Answer : A
Q.182. Term baby born to a mother who developed chickenpox 7 days before delivery. The baby is asymptomatic, which of the following is true?
Correct Answer : B
15% of pregnant women are susceptible to varicella (chickenpox). Usually, the fetus is not affected, but is at high risk if the mother develops chickenpox: In the 1st half of pregnancy ( < 20 weeks ), when there is a < 2 % risk of the fetus developing severe scarring of the skin & possibly ocular & neurological damage.
Within 5 days before or 2 days after delivery, when the fetus is unprotected by maternal antibodies & the viral dose is high. About 25 % develop a vesicular rash. Exposed susceptible women can be protected with varicella zoster immune globulin & treated with acyclovir. Infants born in the high-risk period should also receive zoster immune globulin & are often also given acyclovir prophylactically.
Q.183. 4 year old girl, presented in your clinic due t delayed speech. You have noticed microcephaly, and decrease social interaction. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.184. A 48-hour old newborn infant is in critical care unit with respiratory distress & Jaundice. Hb 9g/dl, retic 4%. Maternal history of previous normal term pregnancy without transfusion, Blood typing shows hetero-specificity between mother and child. Indirect Coomb’s test is positive. What is the most probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.185. A 6-year-old girl is brought to the family health center by her mother. The child today had a sudden onset of a painful sore throat, difficulty swallowing, headache, and abdominal pain. The child has had no recent cough or coryza and was exposed to someone at school that was recently diagnosed with “strep throat”. On examination, the child has a temperature of 40*C. She has tender anterior cervical nodes and exudative tonsils. The lungs, heart, and abdominal examination are normal. What treatment would you offer for this child?
Correct Answer : B
URTI has a McIsaac criterion (whether or not to start antibiotics): no cough, tender anterior cervical L.N., erythematous tonsils with exudates, fever> 38, age 3-14. if 0-1 no culture no antibiotics, 2-3 cultures if positive antibiotics, 4 start antibiotics.
Treatment is by penicillin V if allergic to erythromycin.
Q.186. Development in children, all are true EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : A
Q.187. Which one of the following component causes contact dermatitis in children?
Correct Answer : A
Primary Contact Dermatitis: is a direct response of the skin to an irritant. The most common irritants are soap, bubble bath (may cause severe vaginal prorates in prepubertal girls), saliva, urine, feces, perspiration, citrus juice, chemicals (creosote, acids) &wool.
Q.188. What can be done to prevent tetanus in neonate?
Correct Answer : C
DTP= diphtheria, tetanus & pertussis D&T are toxoids, P is inactivated bacteria Route.
Q.189. A 6 year old girl developed day-time wetting for 2 days. She is fully toilet trained. She is afebrile. What is the most appropriate diagnostic measure?
Correct Answer : C
Lab Investigations:
Urinalysis and the specific gravity of urine should be obtained after an overnight fast and evaluated to exclude polyuria secondary to diabetes as a cause of frequency and incontinence and to determine if there is normal concentrating ability.
A urine culture will determine the presence or absence of a urinary tract infection, which, when treated could improve continence.
If daytime wetting is occurring, a renal and bladder ultrasound may help rule out possible outlet obstruction.
Spine imaging or MRI may determine if there is a neurological cause.
Q.190. 7 month old boy presented with a history of interrupted feeds associated with difficulty in breathing and sweating for the last 4 months. Physical examination revealed normal peripheral pulses, hyperactive precordium, normal S1, loud S2 and Pansystolic murmur grade 3/6 with maximum intensity at the 3rd left intercostal space parasternal. What is The MOST likely diagnosis is?
Correct Answer : D
Q.191. All of the following are true about pyloric stenosis, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : C
Non bilious, forceful vomiting.
Q.192. Regarding composition of standard and reduced osmolarity ORS solutions. What is the amount of Na+ in ORS (oral rehydration solution)?
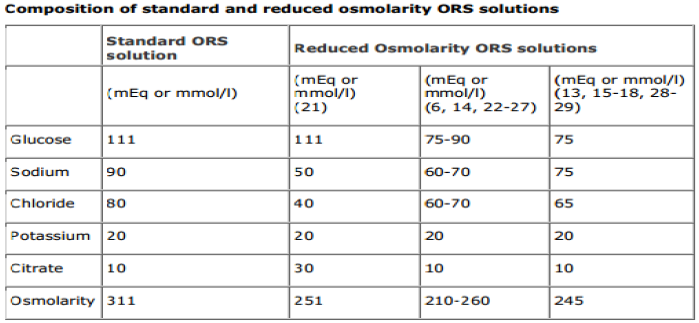
Correct Answer : C
Q.193. Risk factor of sudden death syndrome includes all of the following, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : B
Potential risk factors include
1. Smoking, drinking, or drug use during pregnancy
2. poor prenatal care
3. Prematurity or low birth weight
4. Mothers younger than 20
5. Smoke exposure following birth
6. Overheating from excessive sleepwear and bedding
7. Prone sleeping
Q.194. Which of the following is the symptom of cystic fibrosis in neonate?
Correct Answer : A
Meconium ileus is associated with CF (defect in chromosome 7, autosomal recessive).
Q.195. All of the following are true about DKA in children EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
Give fluid (volume resuscitation) is the goal. Polyuria is one of DKA symptoms, not oliguria.
Q.196. What is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in young baby?
Correct Answer : D
Missing or misplaced thyroid gland
Most babies with CH are missing their thyroid gland or have a thyroid that did not develop properly. In some cases, the thyroid gland may be smaller than usual or may not be located in the correct place.
Q.197. At what age is the MMR vaccine is to be given?
Correct Answer : C
Q.198. A 6 month old patient is admitted in intensive care unit due to sepsis. What is the most likely organism of sepsis at this age?
Correct Answer : C
Q.199. All are vaccines given to a normal children EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
Q.200. A neonate is just delivered from a term pregnancy. He has developed respiratory distress. On examination, he had decreased bilateral breath sounds & a flat abdomen. The CXR showed multicyctic lesion on the left side of the chest, mediastinum shifted to the right. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.201. A 12 year old child with BMI 24.4. How would you rate this BMI?
Correct Answer : A
Q.202. A 2 months old boy was brought in your clinic with a history of projectile vomiting. On examination, you have appreciated an olive-shaped mass in right upper quadrant of abdomen. What is the first step in investigation?
Correct Answer : D
Q.203. Signs of congestive heart failure in children are all EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
Q.204. What is the treatment of meningitis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.205. All are true about the treatment of tetralogy of fallot EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : A
Definitive management is the total correction of pulmonary stenosis and VSD this can be performed even in infancy.
Q.206. A child presented with history of restless sleep during night and daytime somnolence. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Tonsillitis and enlarged adenoids may occlude the nasopharyngeal airway, especially during sleep, this results in obstructive sleep apnea, the child will present with loud snoring punctuated by periods of silence followed by a large gasp and as a complication of interrupted sleep,child will have somnolence and sleep during the day.
Q.207. A child has attended the clinic 3 times with a history of cough for 5 days, he didn't respond to supportive treatment. Which of the following is true regarding management?
Correct Answer : B
Cough is the most common symptom of respiratory disease and indicates irritation of nerve receptors in the pharynx, larynx, trachea, or large bronchi. While recurrent cough may simply indicate that the child is having a respiratory infection, in addition to other causes that need to be considered.
Q.208. Regarding meningitis in childhood, all are true EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
May be (b)if we consider that H.influenza is becoming resistant to penicillin, but if we consider that it is an old question, then, it is true information and the answer will be (d). ? The most common pathogens in neonates are E.coli, group B streptococci, and L.monocytogenous. ? Chemoprophylaxis of contacts is not necessary to prevent the spread of pneumococcal meningitis. However, chemoprophylaxis is an important aspect of the prevention of invasive pneumococcal infections in children with functional or anatomic asplenia (e.g. SCD). Besides, the prophylaxis will be with penicillin not with rifampin.
Q.209. A 2-week-old infant presents with jaundice, cirrhosis, and ascites. The infant was born at full term via spontaneous vaginal delivery, with no complications at birth. The mother denies any history of drug use or infections during pregnancy. On physical examination, the infant has visible jaundice, a distended abdomen, and signs of hepatomegaly. Blood work reveals elevated liver enzymes, bilirubin, and a prolonged prothrombin time. What is the most likely cause of this infant’s presentation?
Correct Answer : C
Q.210. Whooping cough in children, all are true EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : C
The incubation period is typically seven to ten days in infants or young children, after which there are usually mild respiratory symptoms, mild coughing, sneezing, or runny nose. T. Pertussis is fatal in an estimated 1.6% of hospitalized infants who are under one year of age. Infants under one are also more likely to develop complications (e.g., pneumonia (20%), encephalopathy, seizures (1%), failure to thrive, and death. (0.2%). Pertussis can cause severe paroxysm-induced cerebral hypoxia and apnea. Reported fatalities from pertussis in infants have increased substantially over the past 20 years.
Q.211. A child brought by his father looks pale doesn’t like to have meat. He has developed hypochromic microcytic anemia. What is the next appropriate step in management?
Correct Answer : C
Q.212. All are true about Kernicterus, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
Kernicterus: Severe hyperbilirubinemia TSB>25-30 mg/dl (428-513 micromol/l) is associated with increased risk of Bilirubin-Induced Neurological Dysfunction ( BIND) which occurs when bilirubin crosses BBB & binds to brain tissue.
The term acute bilirubin encephalopathy (ABE) is used to describe acute manifestation of BIND, the the term '' KERNICTERUS'' is used to describe the chronic & permanent sequelae of BIND. So, choice (b) is not a rule b/c early detection can prevent permanent neurological deficit & reverse the acute (ABE) but the ''KERNICTERUS'' is a term used to describe chronic sequelae.
Q.213. An Infant was brought by the mother notices that the baby has reduced feeding, activity and is lethargic. On examination- febrile 39 C, tachycardia, Bp=75/30, with skin rash. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.214. Which developmental milestone is seen in a 4 year old child?
Correct Answer : B
Q.215. All are true regarding child with moderately severe asthma, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : A
Moderately severe asthma: The R.R. is increased. Typically, accessory muscles of respiration are used, and suprasternal retractions are present. The H.R. is 100-120 b/min. Loud expiratory wheezing can be heard. Pulsus paradoxes may be present (10-20 mm Hg). Oxyhemoglobin saturation with room air is 91-95%. 250 cases in clinical medicine:
Indicators of VERY SEVERE, LIFE-THREATENING attack (NOT moderately – severe attack):
Normal (5-6 kPa, 36-45 mmHg) or increased CO2 tension.
Severe hypoxia of LESS than 8 kPa (60 mmHg).
Low pH.
In very severe, life-threatening attack: Normal or increased PCO2 -----Low pH (resp. acidosis) --High
Bicarb, level
In moderately severe attack:
Hyperventilation low PCO2 -High pH (resp. alkalosis) --Low Bicarb. Level.
Q.216. A 4-year-old child is brought to the emergency department with a history of ingesting a caustic material about 2 hours ago. The child appears ill, is drooling excessively, and is unable to swallow. There is no history of vomiting, but the child is in visible distress. What is the immediate next step in management?
Correct Answer : D
Q.217. A 3 year old baby's parents are diagnosed with TB. As a GP you did PPD test of the child, after 72 hrs you found a 10mm induration. What does this suggest?
Correct Answer : C
Q.218. A child came to an ER due to hematuria. He had a history of sore throat few days back. What is the most appropriate next step in diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Dx - Post streptococcal GN.
Diagnosis depends on:
+ve pharyngeal or skin culture
↓complement.
Elevated BUN and creatinine values
ASO titers are frequently used to document streptococcal infection, but a more sensitive test is the streptozyme test, which tests antibodies to ASO, anti–DNAse B, AHase, and anti-NAD.
Q.219. A 5 year old boy presented with headache, vomiting, photophobia and neck stiffness. CSF analysis showed - Glucose=normal, protein= high, leukocyte count= high and mainly lymphocytes 70. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.220. Risk factor for HSV II in infants are all of the following EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : C
In neonatal herpes simplex encephalitis the predominant pathogen is HSV-2 (75% of cases), which is usually acquired by maternal shedding (frequently asymptomatic) during delivery. It is usually transmitted at the second stage of labor via direct contact. Should the mother acquire genital herpes during pregnancy, the risk increases to 40%. The absence of a maternal history of prior genital herpes does not exclude risk; in 80% of cases of neonatal HSE, no maternal history of prior HSV infection is present. Prolonged rupture of the membranes (>6 h) and intrauterine monitoring (eg, attachment of scalp electrodes) are risk factors.
In about 10% of cases, HSV (often type 1) is acquired post-partum by contact with an individual who is shedding HSV from a fever blister, finger infection, or other cutaneous lesion.
Q.221. A 5 year old child came in your office with abdominal pain, after 2 weeks of URTI. Lab investigations show Hb=8gm/dl, retics 12%, WBC=normal, peripheral blood smear shows target cells and RBC inclusions. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
This child has a vast occlusive crisis of SCA that caused by URTI, Hihg retic>> hemolytic, Target>> SCA Iinclusion>> functional asplenism ( which is occurs in SCA).
Q.222. Which of the following is the most common cause of failure to thrive?
Correct Answer : B
Q.223. A 8 month child was brough in your clinic due to coryza, fever and cough. during examination, his temperature is 38C. What would be the best initial management?
Correct Answer : A
Q.224. A 7-year-old child presents to the clinic with fever and headache, which started two days after a macular lesion on the face ruptured. The parents report that the lesion initially appeared as a red spot, became fluid-filled, and later ruptured. The surrounding skin now appears red and swollen, with some yellow crusting. What is the most likely cause of the child's condition?
Correct Answer : A
Staphylococcus aureus is the most common pathogen causing secondary bacterial infection of ruptured skin lesions. The fever, redness, and swelling (suggestive of cellulitis or abscess) fit the description better than Streptococcal impetigo.
Q.225. A 12 year old boy presented in your office with jaundice & increased indirect bilirubin report. Extensive workup for hemolytic illness is done but no hemolytic cause detected. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.226. A DPT vaccine shouldn't be given to the child in which of the following conditions?
Correct Answer : C
Q.227. Vasoconstrictive nasal drops cause which of the following side-effect?
Correct Answer : A
Q.228. Which of the following is TRUE about Epididymitis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.229. All are true about childhood asthma EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : A
Regarding A: Upper respiratory tract infection is the most common cause of asthma exacerbations!!!
B, C and D are correct
Cough (nocturnal usually) can be the only symptom but cyanosis, SOB, wheezing etc can occur
Q.230. Diarrhea can occur in all of the following, EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : A
Q.231. A 18 month old baby can typically do all of the following EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : B
Can build a tower of 2 - 3 blocks, can use a spoon & cup and can say 10 words.
Q.232. Regarding acute gait disturbance in children, all of the following are correct EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : A
Q.233. All the following can cause short stature in children EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : C
Its the opposite in Klinefelter syndrome.
Q.234. In a new born baby, which of the following condition needs immediate treatment?
Correct Answer : C
Q.235. A 6 week old infant presented with yellowish eye discharge and persistent tearing of one eye since birth, all of the following are true EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : D
Q.236. Mother came with her child and the mother had botulism in the past, what you will advise her?
Correct Answer : D
Q.237. Which of the following describes the normal developmental stage for a 7 month old child?
Correct Answer : A
Q.238. What is true about acute lymphocytic leukemia?
Correct Answer : D
The total number of white blood cells may be decreased, normal, or increased, but the number of red blood cells and platelets is almost always decreased. In addition, very immature white blood cells (blasts) are present in blood samples examined under a microscope.
A bone marrow biopsy is almost always done to confirm the diagnosis and to distinguish ALL from other types of leukemia
Q.239. A 4-year-old child fell on her elbow while playing. She developed abrasions at the site of the fall. Over the next few days, the area became tender, red, swollen, and demarcated, measuring approximately 5x4 cm. The child also developed a fever of 38.5°C. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.240. A 10 months old baby was brought to your clinic due to vesicles on the face and honey comb crusting on it. Which of the following organism is responsible for this lesion?
Correct Answer : A
Q.241. You are asked to keep a child NPO, his weight is 25 kgs. What is the fluid calculation for this child?
Correct Answer : D
Q.242. Parents brought their baby to you who is on bottle feeds. On examination, whitish lesions on either side of teeth seen with black colored lesions on maxillary incisors and second molar teeth. There is history of leaving the baby with bottle in his mouth during sleeping. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.243. What is the most common cancer in children?
Correct Answer : A
ALL: most common childhood cancer
Rhabdomyosarcoma: most common soft tissue tumor.
Wilm's tumor: most common intra-abdominal childhood tumor.
Q.244. A child with moderate asthma and he is managed on b2 agonis. What you will add to decrease the recurrence of asthma attacks?
Correct Answer : A
Q.245. A 6 year old boy has a habit of eating paper and soil. What is the best initial treatment?
Correct Answer : B
Q.246. A Neonate with mucopurulent eye discharge, lid swelling and culture positive for gram negative diplococci. What is the treatment?
Correct Answer : A
Q.247. A child came to ER with high grade fever, and stridor. The x-ray showed swollen epiglottis. He was started on oxygen. What will you do next?
Correct Answer : C
Diagnosis - Epiglottitis.
Treatment - Emergency intubation.
Q.248. A child presented in an ER with aspirin overdose. What kind of acid base balance is observed during this toxicity?
Correct Answer : C
Q.249. An 8-year-old child presents to your outpatient department (OPD). Upon examination, you appreciate a late systolic murmur that is best heard over the sternal border, with a high pitch and crescendo-decrescendo type. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.250. A child was present in you clinic due to congested throat , cough, coryza , and high grade fever. Which of the following is TRUE regarding this condition?
Correct Answer : B
Q.251. A baby with red macules & dilated capillaries on the right side of the face. What is the likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Q.252. A 3 year old presented due to the acute urinary tract infection symptoms like urgency and burning micturition. Which of the following you would like to do in this condition?
Correct Answer : A
Q.253. A child with fever, runny nose, conjunctivitis and cough. He developed maculopapular rash on 2nd day of illness that started on his face and descended down to involve the rest of the body. What is the causative organism?
Correct Answer : C
Q.254. 4 year old child, was diagnosed to have sickle-cell disease. He Had multiple admissions due to dyspnea, dactylitis, bone pain. What is the best strategy for maintaince therapy?
Correct Answer : C
Q.255. A child while playing football, the ball hit his hand on the lateral fingers, after a while the child complains of pain and swelling on those fingers and painful middle finger with hyperextension of interphalangeal joint, swelling was more in the DIP and IP joints, there was pain on his palm as well. What is the most likely cause?
Correct Answer : A
Q.256. A child transferred to another city, moved to a new school, and he loses his attention and doesn’t interact with students. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.257. A child has 39*C fever, erythematous tonsils with no exudate, slightly enlarged LN but not tender. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.258. A 8 days old neonate presented with bilious vomiting, he also didn’t pass meconium. What will be the next investigation?
Correct Answer : B
R/o Hirschrung disease
Q.259. A child was brought to a well-baby clinic. During developmental assessment, he is able to name 4 colors, say 5 words, and hop on one leg. What would be his developmental age?
Correct Answer : A
Q.260. A child was playing but unfortunately he fell down while playing with the toy. His leg got trapped and twisted and since then he is not able to walk. What would be the cause?
Correct Answer : B
Q.261. A 4-year-old child presents with a history of losing previously acquired skills, such as language or motor abilities, and has become increasingly isolated. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
The scenario described, where a child loses previously acquired skills and becomes socially withdrawn, is characteristic of Rett Syndrome, a rare neurodevelopmental disorder that primarily affects girls and usually presents between 6-18 months of age.
Q.262. Which of the following is the best measure to prevent infections in pediatric clinics?
Correct Answer : A
Q.263. Which is the most common parotid gland tumor in children?
Correct Answer : A
Mixed tumour is the most common parotid gland tumor in children.
Q.264. What is the most common malignant parotid tumor in children?
Correct Answer : A
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is the most frequent malignant tumor of the salivary glands in both children and adults.
Q.265. A 3 year old child fell from the bed & vomited twice. He has reported mild headache but no loss of consciousness. What is the next step in his management?
Correct Answer : B
Q.266. A 2 year old child with patchy hair loss especially in the temporal area and boggy swelling in the head with multiple pustules. What is the probable diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.267. A doctor is talking to his patient, and the patient looks to his right side most of the time. Upon asking, the patient replied that his mother is there but in fact no one is there. The patient's family reported that his mother died when he was a child. What is the diagnosis of his current condition?
Correct Answer : A
Q.268. A child on nutritional supplementation landed in an ER with 2 hours history of vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and vomiting. The vomitus was black in color. What is the possible cause?
Correct Answer : B
Q.269. A child, after his father's death, has started to talk to himself. He walks naked in the house and upon asking he responded that his father asked him to do that. Episodes were recurrent since 3 days. After such episodes, he remains completely normal and he does not remember. What is the possible diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Explanation: It could be transient hallucination under stress
Q.270. Child with high-grade fever for 5 days and sore throat. On examination, there was bilateral tonsillar enlargement and white patches on the gingiva. No Lymph node enlargement, ASO titer is negative. What is the most likely causative organism?
Correct Answer : A
Q.271. A 4 year old child presented with mild dehydration with gastroenteritis, how will you will manage him?
Correct Answer : B
Maintenance fluid is different and it depends on the age of the patient (500 mL/day for children
younger than 2 years, 1000 mL/day for children aged 2-10 years, and 2000 mL/day for children older
than 10 years) I think they mentioned the age of the child but I can’t recall it. Also, in the choices I'm
not sure if it says (with each bowel motion or as a maintenance).
Q.272. A child presented with diarrhea, fatigue, abdominal pain and jaundice for few days. There was a history of drinking contaminated water. What is the most likely organism?
Correct Answer : A
Q.273. A 5 weeks old infant presented with difficulty in breathing and mother reported that he occasionally turns blue. On examination, there was pansystolic murmur, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.274. A child presented with sore throat and fever. She had a history of impetigo and that was resolved completely with an appropriate course of antibiotic, ASO titer was positive. The same antibiotic was prescribed for her condition, what is the proper duration for this case?
Correct Answer : C
Q.275. A child presented in your office with flu like illness with red non-blanching papules, sore throat and enlarged cervical lymph nodes. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.276. A mother came to your clinic and she is worried about her overweight child. What is your advice for reducing child's weight?
Correct Answer : A
Q.277. A 3 month old child was brought in your OPD due to low-grade fever and wheezing. The CXR shows hyperinflation and some infiltrates. What’s the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.278. A 7-year-old child presents with a 3-day history of low-grade fever and sore throat. On examination, you notice non-tender, enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, but there is no exudate on the pharynx. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.279. A pediatric patient from a developing country presents with muscle wasting and weight loss but no edema. The child has no signs of infection or systemic disease. What is the most likely diagnosis?
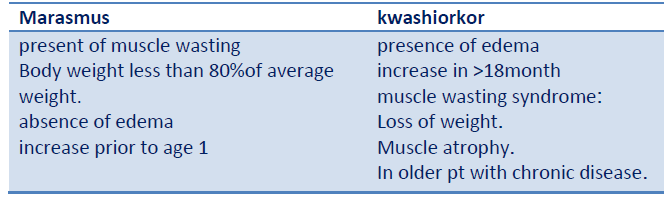
Correct Answer : A
Q.280. A 6-month-old infant is brought to the emergency department with high-grade fever, irritability, and a general appearance of being very sick. The infant has not urinated for the past 4 hours. On examination, multiple petechiae and purpura are noted on the body. The infant's heart rate 160 bpm and blood pressure 80/50 mmHg. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.281. A 5 year old baby presented with his parents in your OPD dur to pallor. His Hb= 9gm/dl, peripheral smear shows microcytic, hypochromic anemia. What you will do next?
Correct Answer : A
Q.282. A 3 month old baby was brought by his parents with history of abdominal distention, bilious vomiting, constipation. The parents informed that the constipation has been an issue since his birth. What is the single diagnostic investigation?
Correct Answer : A
Q.283. A 7-year-old child presents with sudden onset knee pain. The child has normal movement of the knee, and there is no effusion or swelling. There is no history of trauma or injury. The child denies fever or other systemic symptoms. What is the most important next step in the management of this patient?
Correct Answer : C
Q.284. All are TRUE regarding Perthes disease EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : B
Legg-Calve-Perthes disease (LCPD) is avascular necrosis of the proximal femoral head resulting from compromise of the tenuous blood supply to this area. LCPD usually occurs in children aged 4-10 years. The disease has an insidious onset and may occur after an injury to the hip. In the vast majority of instances, the disorder is unilateral. Both hips are involved in less than 10% of cases, and the joints are involved successively, not simultaneously.
Q.285. A 6-year-old child presents with complaints of fever and a sore throat. The physical examination is normal, and there are no signs of a respiratory tract infection such as swollen tonsils or exudates. What is the most appropriate treatment for this child?
Correct Answer : C
Q.286. A baby was brought in your clinic with complaint of blood in the stool and he was crying intermittently since morning. X ray abdomen shows intussusception. How will you manage?
Correct Answer : B
Q.287. What is the most common cause of epistaxis in children?
Correct Answer : B
Q.288. A newborn is delivered and has an Apgar score of 3, presenting with cyanosis, limpness, decreased breathing effort, and a heart rate less than 60 bpm. What is the most appropriate immediate action?
Correct Answer : C
Q.289. Which one of the following mimics as croup?
Correct Answer : A
Q.290. What is TRUE about Malaria in a child?
Correct Answer : D
Q.291. What is the cause of scaly purple lesions in the face of a child?
Correct Answer : B
Q.292. A 7-year-old child presents with a recent history of sore throat and fever. Several weeks later, the child develops migratory arthritis, carditis, and erythema marginatum. What is the mechanism by which a Group A Streptococcus (GAS) infection leads to rheumatic fever?
Correct Answer : B
Q.293. What is the treatment to increase fetal hemoglobin (HbF) in sickle cell disease?
Correct Answer : A
Q.294. A 5-year-old child with leukemia presents with septicemia. The infection is suspected to have originated from a central venous line (CVL) that was recently placed for chemotherapy administration. Which of the following organisms is most commonly associated with septicemia from a venous line in immunocompromised patients such as those with leukemia?
Correct Answer : B
Q.295. A 6 year old child presents with waddling gait and inability to stand or walk without support. He is irritable and had 3 vomiting since yesterday. His mother revealed that he had a history of chickenpox 3 weeks ago. O/E all are normal except nystagmus. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.296. A 10-year-old child presents with a distinct garlic-like odor coming from their body. The child is otherwise not showing any obvious signs of illness but has been having some gastrointestinal upset. What is the most likely cause of this odor?
Correct Answer : B
The characteristic garlic-like odor coming from a child’s body is most commonly associated with organophosphate poisoning. Organophosphates are chemicals found in certain insecticides and pesticides.
Q.297. A newborn presents with conjunctivitis within the first few days of life. The baby is otherwise healthy, but the eyes appear red and there is mild discharge. What is the most appropriate treatment for this condition?
Correct Answer : B
Case of infection with chlamydia intrauterine infection.
Tx - Erythromycin or Azithromycin
Q.298. A 2-week-old newborn presents with vomiting after every meal, although the physical examination is otherwise normal. The baby is showing signs of dehydration, such as dry mouth, reduced urine output, and lethargy. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
Correct Answer : D
Q.299. A 3-month-old baby presents with a history of bronchiolitis. The baby had symptoms of respiratory distress, wheezing, and a runny nose. What is the most likely cause of this condition in a 3-month-old infant?
Correct Answer : A
Q.300. A 3-year-old child presents with shortness of breath (SOB), a runny nose, and fever (38°C). The child shows signs of respiratory distress, including tachypnea, nasal flaring, and intercostal retractions. On auscultation, there is diffuse wheezing throughout the chest with prolonged expiration and inspiratory crackles. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.301. 5 year old child had abdominal blunt trauma, and the emergency department team has confirmed the presence of internal hematoma in 1st and 2nd part of duodenum, and also he has high amylase levels. How will you manage?
Correct Answer : C
Q.302. A 5 month old baby presented to ER with sudden abdominal pain and excessive crying, since lasts 2-3 min with intervals of 10-15 mins between each attack. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.303. A 10-year-old child presents with small macules, mainly on the chest, along with knee and elbow joint pain. There is no history of trauma, and the child is otherwise well. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.304. A 6-year-old child presented in your OPD with jaundice, vomiting, and during examination, you found a hepatomegaly. Based on these symptoms, which hepatitis virus is most likely the cause of this child's condition?
Correct Answer : A
Q.305. A 3-year-old child presents after ingesting a large quantity of iron supplements. The child has abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, and lethargy. What is the most appropriate management for this child?
Correct Answer : D
Forgot the rest of choices, but there was no deferroxamine or charcoal.
Q.306. Which vitamin will you give to prevent hemorrhagic disease of newborn?
Correct Answer : A
Q.307. A 5-year-old child presents with a characteristic skin rash consisting of dew drops on rose petal-shaped lesions. The child also has mild fever and malaise. What is the most likely diagnosis??
Correct Answer : D
Q.308. A 1-month-old infant presents with vomiting, abdominal distension, and constipation since birth. There is no history of feeding intolerance, but the baby has poor weight gain. What is the next step in management?
Correct Answer : B
Q.309. A 2-month-old infant presents with non-bilious vomiting and abdominal distension. On examination, there is an olive-shaped mass palpated in the epigastric area. An X-ray shows an elongated pylorus and narrow lumen. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.310. If a child sleeps with milk bottle in his mouth, what would be the most common complication?
Correct Answer : A
Q.311. An infant is diagnosed with a clavicle fracture after a difficult vaginal delivery. The baby is crying and showing signs of pain when moving the arm, but there are no signs of neurological impairment. What is the most appropriate management for this condition?
Correct Answer : C
A clavicle fracture is one of the most common fractures in neonates, especially following difficult or shoulder dystocia deliveries. Most of these fractures occur in the middle third of the clavicle and are often non-displaced.
Q.312. A 6-year-old child presented in your clinic due to a swelling of the parotid glands, fever, and headache. What is the most common complication of mumps in this age group?
Correct Answer : C
Meningitis is a known complication of mumps, but it is less common in this age group (children under 10). It presents with symptoms like fever, irritability, and a stiff neck, but orchitis remains more common.
Q.313. A child can sit without assistant, stands holding the furniture, says “dada” and uses pincer grasp, how old is the child?
Correct Answer : C
Q.314. A 7-month-old infant presents with a low-grade fever, dry cough, wheezing, and hyperinflation on chest X-ray, along with some mild infiltration. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.315. How will you manage mild dehydration in a 10 months old child who weighs 8kgs?
Correct Answer : A
Q.316. A newborn in the NICU is found to have a heart rate of 300 beats per minute, but the blood pressure is normal. The baby appears stable without signs of shock. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
Correct Answer : D
Q.317. A newborn in the NICU presents with a heart rate of 300 bpm, normal blood pressure, and normal respiratory rate. After an ECG is performed, the diagnosis of atrial flutter is confirmed. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
Correct Answer : A
Synchronized cardioversion is indicated because atrial flutter is a reentrant tachycardia that is unlikely to respond to vagal maneuvers.
Q.318. A 7-year-old child presents with sore throat, fever, and swollen anterior cervical lymph nodes. The throat examination reveals erythema, exudates, and the rapid antigen detection test confirms streptococcal pharyngitis. Which of the following statements about streptococcal pharyngitis is TRUE?
Correct Answer : D
Q.319. A child with hyperemia, redness and bulging of tympanic membrane, he had previous history of impetigo. What will be the appropriate treatment?
Correct Answer : B
Q.320. A 6-month-old baby presents with a runny nose, low-grade fever, cough, and wheezing. The parents report that the baby has had difficulty feeding and increased work of breathing over the past 24 hours. On examination, the baby has tachypnea, intercostal retractions, and diffuse wheezing on auscultation. A chest X-ray shows hyperinflation. What is the most appropriate management for this case of bronchiolitis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.321. A child who is a known case of sickle cell anemia is present in your clinic with ultrasound abdomen report showing gallstones. How will you manage?
Correct Answer : A
Q.322. Which one of the following is the killed vaccine?
Correct Answer : A
Q.323. What is the contact prophylaxis of meningitis case?
Correct Answer : A
Q.324. Mother came with her 12 year old obese child and she is worried about the weight of the child, what will you advice?
Correct Answer : A
Q.325. What is the best management in case of child with iron overdose ingestion?
Correct Answer : A
Q.326. What is the pediatric CPR compression to ventilation ratio?
Correct Answer : A
Q.327. About varicella vaccine in adult, which of the following is TRUE?
Correct Answer : A
Q.328. A 8 months old child presented with 3 days history of fever 40C, vomiting, convulsions, poor feeding & disturbed sleep. On examination : dehydrated, depressed anterior fontanelle, red ears, no neck stiffness, his 3 year old sibling is asymptomatic. Which of the following will give the definitive diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Q.329. At what age a child starts speaking few words?
Correct Answer : A
Q.330. A 10-year-old child presents with low-grade fever, congested throat, and bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy. Blood tests reveal a negative antistreptolysin O (ASO) titer and positive Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) IgM antibodies. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: The classic criteria for laboratory confirmation of acute infectious mononucleosis include: 1) Lymphocytosis. 2) Presence of at least 10% atypical lymphocytes on peripheral smear. 3) Positive EBV.
Q.331. A 12-year-old child presents with edema of the lower limbs (LL), upper limbs (UL), and face. The child also complains of shortness of breath and has a history of sore throat 2 weeks ago. On examination, the child has periorbital edema, hypertension, and mild respiratory distress. Laboratory tests show hematuria, proteinuria, and a low C3 complement level. The antistreptolysin O (ASO) titer is elevated. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Dry beriberi = neurological symptoms. Wet beriberi = cardiac symptoms.
Q.332. Child came in ER with iron tablet ingestion, several hours ago. Lab investigations show serum iron concentration of 700 mg/dl, how do you treat?
Correct Answer : C
Explanation:
Patients with iron toxicity should be treated with IV deferoxamine in the following circumstances:
1) Severe symptoms: altered mental status, hemodynamic instability, persistent vomiting, diarrhea.
2) High anion gap metabolic acidosis.
3) Serum iron concentration > 500 mcg/dL.
4) Significant number of pills on X-ray.
Q.333. A 7-year-old child presents with fever. On examination, the child appears lethargic, BP= 60/40mm Hg and has decreased urine output over the past 12 hours. Laboratory results show elevated serum creatinine, decreased urine sodium, and positive blood cultures for Escherichia coli. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.334. A 6-year-old child is being treated with antibiotics for a bacterial infection. After a few days, the child develops white patches in the mouth and throat. The child is not complaining of pain, but the parents are concerned. What is the most likely diagnosis and the next step in management?
Correct Answer : A
The white patches on the mucosa (commonly seen on the tongue, palate, or inner cheeks) are characteristic of oral candidiasis (thrush).
Q.335. A 7-year-old child with a history of asthma presents with worsening symptoms, including wheezing and shortness of breath, triggered by seasonal allergies. What is the most appropriate approach to decrease the child’s allergic triggers?
Correct Answer : C
Q.336. A 4 years old child came to your clinic with complaints of diarrhea for 2 days and is complaining of anal rashes. What advice will you give to the mother?
Correct Answer : B
Q.337. A 6-year-old child presents with vomiting, nystagmus, and difficulty walking. The child appears to be uncoordinated and has difficulty maintaining balance. What is the most likely cause of these symptoms?
Correct Answer : A
Dry beri beri - Neurological symptoms
Q.338. Regarding infant with sickle cell anemia, what is TRUE about prophylaxis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.339. A 11-year-old patient with sickle cell disease. What is true about pneumococcal vaccine?
Correct Answer : D
All SCD patients < 5 years should receive prophylactic antibiotics (penicillin).
Regarding pneumococcal vaccine for SCD patients:
7-valent (heptavalent) “conjugate” pneumococcal vaccine < 2 years old.
23-valent “polysaccharide” pneumococcal vaccine > 2 years old.
Q.340. A child came with hypertrophic right atrium, which of the following congenital anomaly can lead to this condition?
Correct Answer : A
Q.341. A 4-year-old child with a known history of atopic dermatitis presents with stridor at night, associated with a barking cough that occurs intermittently. The child is otherwise well during the day. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.342. A child runs a long distance and develops pain in the thigh with no redness or tenderness. What is the best thing to do?
Correct Answer : A
Q.343. What is the first sign during increased intracranial pressure?
Correct Answer : A
Or altered level of consciousness
Q.344. A 6-year-old child presents with cough, runny nose, and fever. On examination, the child has tonsillitis (enlarged, red tonsils with white exudates). What is the most appropriate treatment for this child?
Correct Answer : A
Q.345. A 6-year-old boy presents with fever, stridor, and difficulty swallowing. On examination, he has epiglottitis, with a red, swollen epiglottis visible on direct laryngoscopy. What is the most likely causative organism for this condition?
Correct Answer : A
A most common cause of epiglottitis is Haemophilus influenza type b.
Q.346. A 6 months old baby came in ER with signs and symptom of severe respiratory distress. What is the appropriate management?
Correct Answer : A
Q.347. A 5-year-old child presents with a bright red ulcer near the angle of the mouth, measuring 1.5 cm in size. The ulcer is well-defined with a red border. What is the most likely diagnosis?
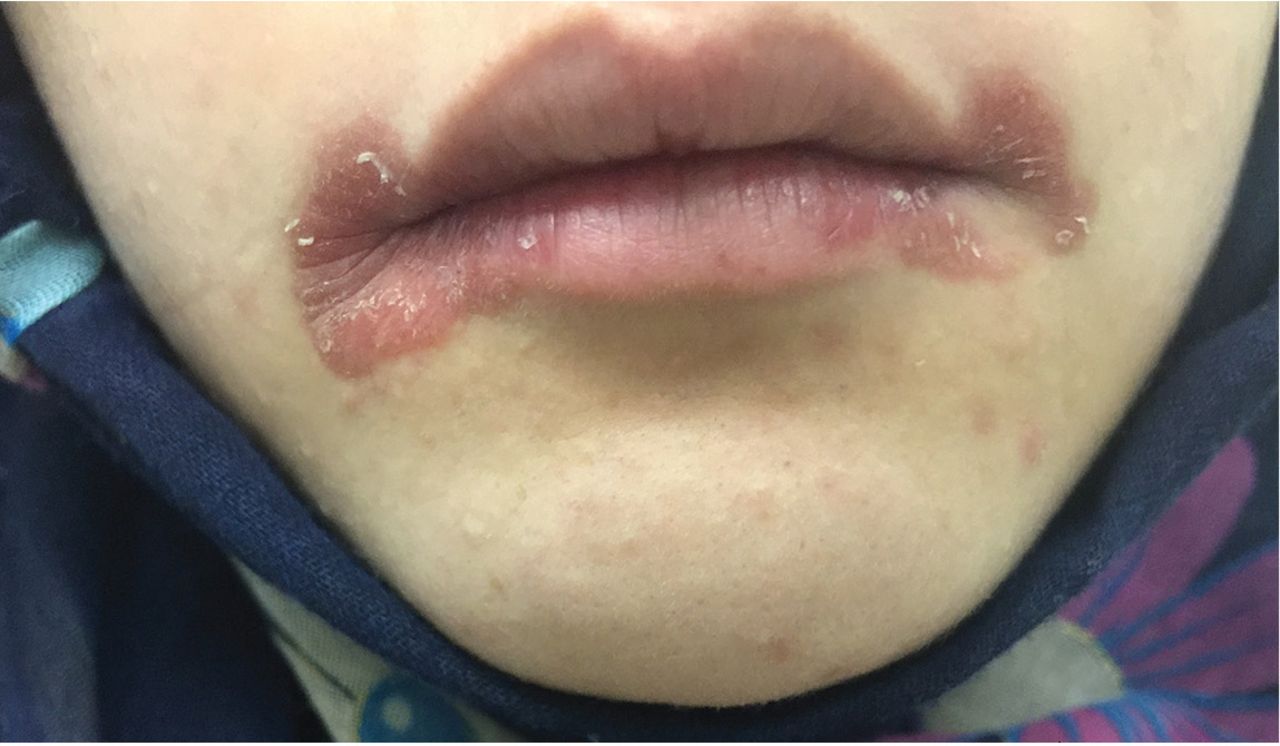
Correct Answer : D
Q.348. A 9 years old girl presented in ER after ingestion of almost 20 tablets of oral contraceptive pills and 3 tablets of another medication (name of the drug is unknown). She is clinically stable and there was no signs and symptoms. What will you do?
Correct Answer : D
In OCP overdose there is no need for intervention if the patient is clinically stable.
Q.349. A 32-week-old newborn presents with cyanosis, grunting, and flaring of nostrils. An X-ray shows diffuse air bronchograms. The mother has a history of diabetes. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Respiratory Distress Syndrome (lack of surfactant).
Hint - Diabetic mother.
Q.350. A child presents with skin lesions on the elbow. A Wood's lamp test is performed and shows fluorescence. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.351. Child came in your clinic after trauma in the play ground. The X-ray shows spiral fracture of arm. What is the appropriate management?
Correct Answer : A
Spiral fractures in children raise the suspicion of abuse. They are difficult to cast and may require surgery.
Q.352. What is the antidote of paracetamol toxicity?
Correct Answer : B
Q.353. A 18-months old child brought to you for delayed speech. What will you test first?
Correct Answer : D
Q.354. A 2-month-old infant presents with severe gastroenteritis, vomiting, and diarrhea. On examination, the infant has increased skin turgor, a depressed anterior fontanel, pale, dry mucous membranes, and is crying but has no tears. What is the most appropriate initial management?
Correct Answer : D
Severe dehydration.
Q.355. A 2 year old child starts with waddling gait, what is the appropriate investigation?
Correct Answer : D
Waddling gait at start is normal up to approximately 3 years.
Q.356. A Boy was brought to your clinic with multiple attacks of febrile convulsions. Which of the following medications would you suggest for seizures at home?
Correct Answer : A
Q.357. A 3 year old boy with acute UTI, what is the first thing to do in such acute condition?
Correct Answer : D
Indication of cystourethrography
All males with recurrent UTIs (urinary tract infections) or abnormality on ultrasound if first UTI.
Females < 3 years of age with their first UTI
Females < 5 years of age with febrile UTIs
Older females with pyelonephritis or recurrent UTIs
Suspected obstruction (e.g. bilateral hydronephrosis)
Suspected bladder trauma or rupture
Stress incontinence (urine)
Q.358. A child presents with a sore throat, ear pain, fever, and the presence of a nodule on examination. What is the most likely causative organism?
Correct Answer : A
Q.359. In a 10 year old boy, at what length does the spinal cord stop?
Correct Answer : A
Q.360. A 4 year old child was brought by her parents with complains of vaginal discharge. What is the probable cause?
Correct Answer : A
Explanation: Most common cause of vaginal discharge in pediatric patients is FB.
Q.361. A child drank something poisonous and is now present in an ER due to nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, hypersalivation, and constricted pupil. What is the appropriate management?
Correct Answer : A
OP poisoning
Q.362. Which of the following is TRUE regarding German measles (Rubella)?
Correct Answer : B
The incubation period for postnatal rubella is 14 to 23 days. The characteristic signs of rubella are retro auricular, posterior cervical, and posterior occipital lymphadenopathy accompanied by an erythematous, maculopapular, discrete rash. The rash begins on the face and spreads to the body and lasts for 3 days. Rose-colored spots on the soft palate, known as Forchheimer spots, develop in 20% of patients and may appear before the rash.
Q.363. A boy who was bitten by his brother, received tetanus shot 6 months ago and had now laceration. You have cleaned his wound. What will you do next?
Correct Answer : A
Since the booster dose has been taken then it is not required to take the tetanus vaccine, however, if the vaccine hasn’t been taken or 5 years have passed since vaccination a booster dose is indicated.
Q.365. Which condition is least commonly associated with endocarditis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.366. A 10 year old child had an episode of rheumatic fever with carditis but without any residual heart defect. For how long does the patient need to take the antibiotic prophylaxis?
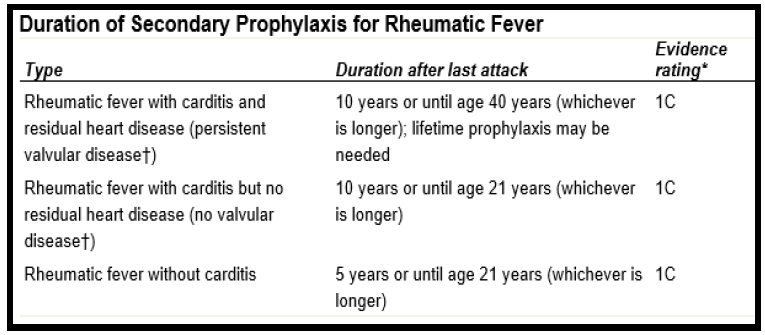
Correct Answer : C
Q.367. After doing a CPR on a child, the rhythm shows asystole. Which drug will you give?
Correct Answer : B
Q.368. A mother brings her child with a sore throat and barking-like cough. The child has a temperature of 38°C, is irritable, and shows signs of respiratory distress. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Q.369. A 3-month-old baby presents with a 2-day history of upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) and now has respiratory distress, is agitated, and lethargic. On examination, the baby has bilateral rhonchi. Investigations were done, and the baby was treated with ribavirin. What is the most likely causative organism?
Correct Answer : A
Q.370. A 6-year-old child is diagnosed with Hepatitis A infection (Hep A+), and the mother is also Hepatitis A positive. What is the most appropriate vaccination for the child?
Correct Answer : D
Post-exposure prophylaxis should be considered in individuals who have been exposed to HAV and
have not previously received HAV vaccine. Such patients should receive a single antigen vaccine or IG
(0.02 mL/kg) as soon as possible.
Q.371. Child comes with meningococcal infection, swab was obtained, and the patient was discharged. The culture showed group A, meningitis was diagnosed. You followed up the child and found that he was asymptomatic. What is the best next step?
Correct Answer : B
Q.372. A 2 year old child developed fever for 2 days then on the 2nd day he became drowsy with vomiting and diarrhea and had appearance of petechial rashes on skin which spread rapidly all over the body. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Initial symptoms:
1) Fever
2) Nausea
3) Emesis (vomiting)
4) Lack of appetite
Late symptoms:
1) abdominal pain
2) Rash
The most characteristic feature of RMSF is a rash that develops on days 2 to 4 of illness after the onset of
fever, and it is often quite subtle. Younger patients usually develop the rash earlier than older patients.
Most often the rash begins as small, flat, pink, non-itchy spots (macules) on the wrists, forearms, and
ankles. These spots turn pale when pressure is applied and eventually become raised on the skin. The
characteristic red, spotted (PETECHIAL) rash of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever is usually not seen until
the sixth day or later after the onset of the symptom.
Q.373. A 6-year-old child presents with generalized lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly. The child also reports a sore throat and mild fever for the past few days. On examination, the child appears mildly ill but is alert. Which of the following tests would most likely confirm the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.374. Parents brought their 5 year child in your OPD with complains of limping and not walking steadily. The baby other milestone was normal according to his age. He had mild lordosis, Trendelenburg gait, Gower sign +ve. What is the best investigation to reach the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.375. A 8 year old boy's BMI was 30, weight and height above 95 percentile. What is the next step of management?
Correct Answer : B
Q.376. A child scheduled for surgery is found to have a continuous murmur on examination in the right sternal area. What is the next step in management?
Correct Answer : A
Q.377. A 5-month-old child presents with liver failure. No other systemic findings except for yellow discoloration of the skin, which has now turned greenish. What is the likely cause of this condition?
Correct Answer : A
Q.378. A 15 year old boy presented with dark colored urine, dark brown stool, positive occult test. How will you manage?
Correct Answer : A
Q.379. A 6 year old baby presented in your clinic with hematuria, all of the following investigations are needed EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : B
Cystoscopy is not generally required in children with non-glomerular hematuria. The only indication is a suspicious bladder mass revealed on ultrasonography.
Q.380. A 7-year-old child presents with a history of head trauma sustained 3 days ago. The child now complains of hemiparesis, dizziness, and loss of proprioception on the left side. There is no loss of consciousness at the time of injury, but the child is now presenting with neurological deficits. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.381. A child was brought with compliant of high grade fever. on examination, patient has meningitis symptoms but no nuchal rigidity, what is the next diagnostic investigation?
Correct Answer : A
Q.382. What is the most diagnostic test if the child has positive "Gower's sign"?
Correct Answer : A
Gowers' sign indicates weakness of the proximal muscle of the lower limb. seen in Duchenne muscular dystrophy & myotonic dystrophy “hereditary diseases”.
Q.383. A 8 years old child came to your OPD due to back pain that wakes him up from sleep. What is the likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
JRA or Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) is the most common form of persistent arthritis in children. JIA may be transient and self-limited or chronic. It differs significantly from arthritis seen in adults. The disease commonly occurs in children from the ages of 7 to 12.
Q.384. A 5-year-old child presents with a urinary tract infection (UTI). What is the best investigation to exclude potential complications of UTI, such as renal scarring or reflux nephropathy?
Correct Answer : A
Q.385. 13 year old child presented in a ER with complaint of cola colored urine, oedema & hypertension. What is the next step to diagnose?
Correct Answer : B
Case of Nephritic syndrome.
Q.386. A 12-year-old female is brought to the emergency room (ER) after ingesting an unknown number of paracetamol (acetaminophen) tablets. The child is clinically stable, but blood paracetamol levels suggest toxicity. What is the most appropriate treatment?
Correct Answer : A
IV infusion: 150mg/kg in 200ml D5% over 15mins then 50mg/kg in 500ml D5% over 4hrs then finally 200mg/kg in 1L D5% over 16 hours.
Q.387. A 5-year-old child presents with scrotal swelling but no fever. On examination, there is a blue dot on the superior posterior aspect of the scrotum. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Patients with torsion of the appendix testis and appendix epididymis present with acute scrotal pain, but there are usually no other physical symptoms, and the cremasteric reflex can still be elicited. The classic finding at physical examination is a small firm nodule that is palpable on the superior aspect of the testis and exhibits bluish discoloration through the overlying skin; this is called the “blue dot” sign. ? Approximately 91%–95% of twisted testicular appendices involve the appendix testis and occur most often in boys 7–14 years old.
Q.388. What is initial investigation in cases of painless hematuria?
Correct Answer : A
Q.389. A 2 years child has swallowed a battery and was brought to an emergency room urgently. How will you manage?
Correct Answer : D
Q.390. A newborn is diagnosed with a tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF). Which of the following interventions should not be done as part of the management?
Correct Answer : C
Q.391. A newborn is brought to the neonatal unit with a history of no anal opening. Upon examination, there is no visible anus, and the abdomen is soft, without any signs of abdominal distension. The child is otherwise stable, with normal vitals and no signs of other obvious congenital anomalies. What is the most useful diagnostic procedure to assess the extent and type of the malformation in this newborn with suspected imperforate anus?
Correct Answer : A
Q.392. A 5-year-old child was bitten by an insect and presented 18 hours later with erythema (redness) and itching around the left arm at the site of the bite. The child is otherwise stable and alert, with no signs of systemic illness like fever. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
Correct Answer : A
Q.393. A step mother gives history of a baby falling down from stairs and presented with multiple contusions injuries, some were old. X-ray showed fracture in radius. What will you do?
Correct Answer : B
Explanation: Because we are suspecting child abuse.
Common question asked in your exam.
Q.394. A 7-year-old child was bitten by an insect 14 days ago. The child now presents with lip swelling and erythema at the site of the bite. There is no fever or systemic symptoms. The reaction appears to be localized to the area of the previous insect bite. What type of hypersensitivity is most likely responsible for this reaction?
Correct Answer : D
Q.395. Which is the preventable nutritional disease in a child?
Correct Answer : B
Q.396. A 3 years old child developed macules that are progressing to vesicular lesions, since 4 days. What is the differential diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Q.397. A child was brought by the parents complaining of teeth bleeding after brushing and gingival bleed. He also had history of discrete vesicles all over the body. Which of the following is the responsible organism?
Correct Answer : C
Q.398. An asthmatic presented in your OPD and his mother complaints that whenever he is exposed to dust mites, he has an asthmatic attack. What will you advise his family regarding mites at home?
Correct Answer : B
Q.399. A 6-year-old child presents to your OPD with swelling in front of both ears along with a discharge. The child is otherwise well but reports that the swelling has been present for a few days and has been associated with pain in the region. On examination, you note that the swelling is tender, red, and there is purulent discharge from the area. What is the most likely complication of this condition?
Correct Answer : B
Q.400. 5 year old female child with history of pharyngitis for 4 days and persistent odourless vaginal discharge. What is the most likely etiology?
Correct Answer : A
Q.401. What is the class of antibody responsible for hemolytic disease of the newborn?
Correct Answer : B
Q.402. A 3-month-old child is diagnosed with a hemangioma on the eyelid. The hemangioma is causing partial occlusion of the eye, and there is concern about the development of amblyopia (lazy eye) due to visual deprivation. The parents are concerned about the child's vision and potential long-term effects on eye development. What is the most appropriate timing for surgery to prevent amblyopia in this child?
Correct Answer : C
Surgery before 4 months of age is the most appropriate approach when dealing with eyelid hemangiomas that could cause visual deprivation. The critical period for visual development is within the first year of life, particularly the first few months, and early surgical intervention can help prevent amblyopia from developing due to persistent obstruction of the visual axis. Early surgery helps to ensure that the eye has a chance to develop proper vision, especially if the hemangioma is obstructing the eye.
Q.403. A 6 years old child was brought in your OPD with complaints of polyuria, polydipsia & poor weight gain. Random blood sugar is >200 mg/dl, and fasting blood sugar >147 mg/dl. This disease is mostly associated with which of the following?
Correct Answer : A
Read 1st aid of the USMLE step 2 CK 7th edition p.114.
Q.404. A young baby was brought by his family with severe rash over his groin region, the family tried many medications such as topical steroids, benzoyl, magnesium but has no improvement. How will you manage this patient?
Correct Answer : A
See the 1st aid of the USMLE step 2 CK 7th edition p.96 (diaper rash).
Q.405. A young child complains of pain behind the left ear with tenderness, past history of AOM for which he received Abx but didn't complete the treatment. On examination: tender, redness over the mastoid, otoscope shows congested TM & loss of cone light reflex. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Q.406. A infant of 28 weeks of gestation weighing 900 g is shifted to NICU. After resuscitation the ABGs shows increase of Pa CO2 with normal PH. What will be the next step in management?
Correct Answer : B
This case is compensated res. acidosis < high pco2 with normal ph >.