
Hello,
Dr. Batman
Hello Doctor, Welcome!
Profile

Name: Batman
Email: batman@gotham.com
PULMONOLOGY REVIEW
(Total Questions - 138)Q.1. A young patient presents with history of cough, chest pain, fever. CXR showed right lower lobe infiltrate, what is the treatment?
Correct Answer : A
Lobar pneumonia is often due to Streptococcus. pneumoniae. Amoxicillin is the drug of choice for treating pneumonia.
Q.2. Best thing to reduce mortality rate in COPD is?
Correct Answer : C
Cigarette smoking is the most important risk factor for COPD, and smoking cessation is, in most cases, the most effective way of preventing the onset and progression of COPD.
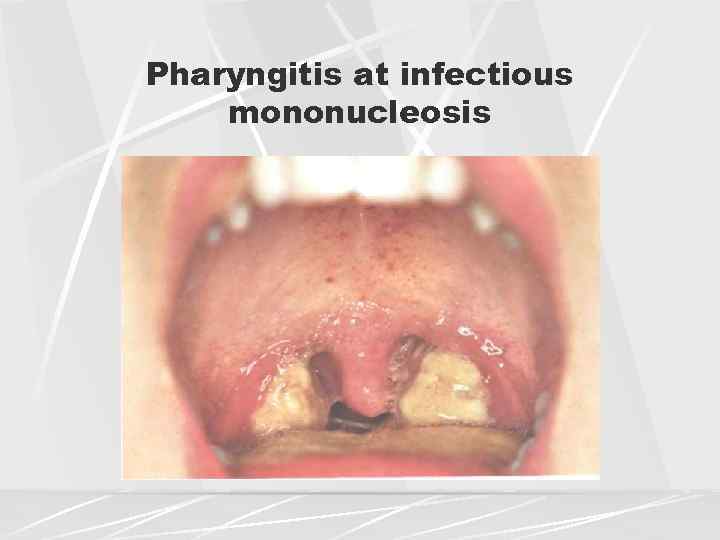
Q.3. A patient with TB, had ocular toxicity symptoms & color blindness, the drug responsible is?
Correct Answer : B
Side effects of anti tubercular drugs-
- INH: peripheral neuritis and hepatitis. [Add ( B6 pyridoxine ) for peripheral neuritis].
- Ethambutol: optic neuritis
- Rifampicin: orange discoloration of urine & tears
- Streptomycin: causes ototoxicity & nephrotoxicity.
Q.4. A patient treated for TB started to develop numbness, what's the deficiency?
Correct Answer : C
INH: peripheral neuritis and hepatitis. [Add B6 pyridoxine for peripheral neuritis].
Isoniazid [INH], a common TB medication can interfere with vitamin B6 metabolism, leading to a deficiency. Vitamin B6 is crucial for nerve function, so without enough, nerve damage can occur, causing symptoms like numbness or tingling.
Q.5. A 17-year-old patient with dyspnea; PO2 , PCO2 , X-ray are normal, pH is increased. What's the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
During an asthma attack, the airway becomes narrow, making breathing difficult and causing SOB. Even if X-rays and blood tests look normal, asthama can still cause this. Hyperventilation can lead to an increased pH.
Q.6. The most common cause of community acquired pneumonia is?
Correct Answer : B
Streptococcus pneumonia is the most common cause of community-acquired pneumonia.
Incorrect options-
- Haemophilus influenzae causes pneumonia but less often than streptococcus.
- Mycoplasma causes very mild form of pneumonia.
- Klebsiella is more common in sick and immunocompromised patients.
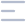
Q.7. A patient presented with sore throat, anorexia, and loss of appetite. A throat exam showed enlarged tonsils with petechiae on the palate and uvula, mild tenderness of spleen and liver, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Viral pharyngitis due to EBV presented with enlarged tonsil with exudates and petechiae on soft palate and enlargement of the uvula and sometimes present with tender splenomegaly.
Q.8. A young patient on anti TB medication presented with vertigo, which of the following drug causes this ?
Correct Answer : A
Streptomycin causes ototoxicity & nephrotoxicity.
Q.9. A known case of sickle cell disease presented with pleuritic chest pain, fever, tachypnea, and respiratory rate of 30 breaths/min, oxygen saturation is 90%. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Acute chest syndrome is the non-infectious vaso-occlusive crisis of pulmonary vasculature presented with chest pain, fever, tachypnea, and hypoxemia.
Q.10. A child with atopic dermatitis at night has stridor with barking cough on & off periodically, what's the diagnosis?
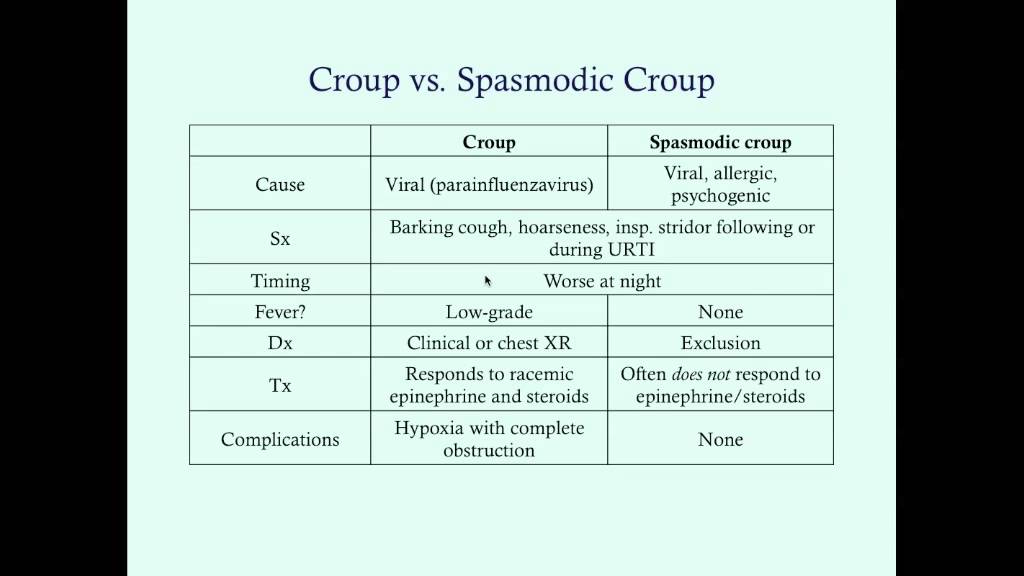
Correct Answer : C
Spasmodic croup: recurrent sudden upper airway obstruction which presents as stridor and cough. Approximately 50% of children have atopic disease.
Q.11. A patient with asthma, is well controlled by Albuterol. Now he came with a history of asthma symptoms not responding to Albuterol. What medication should be added?
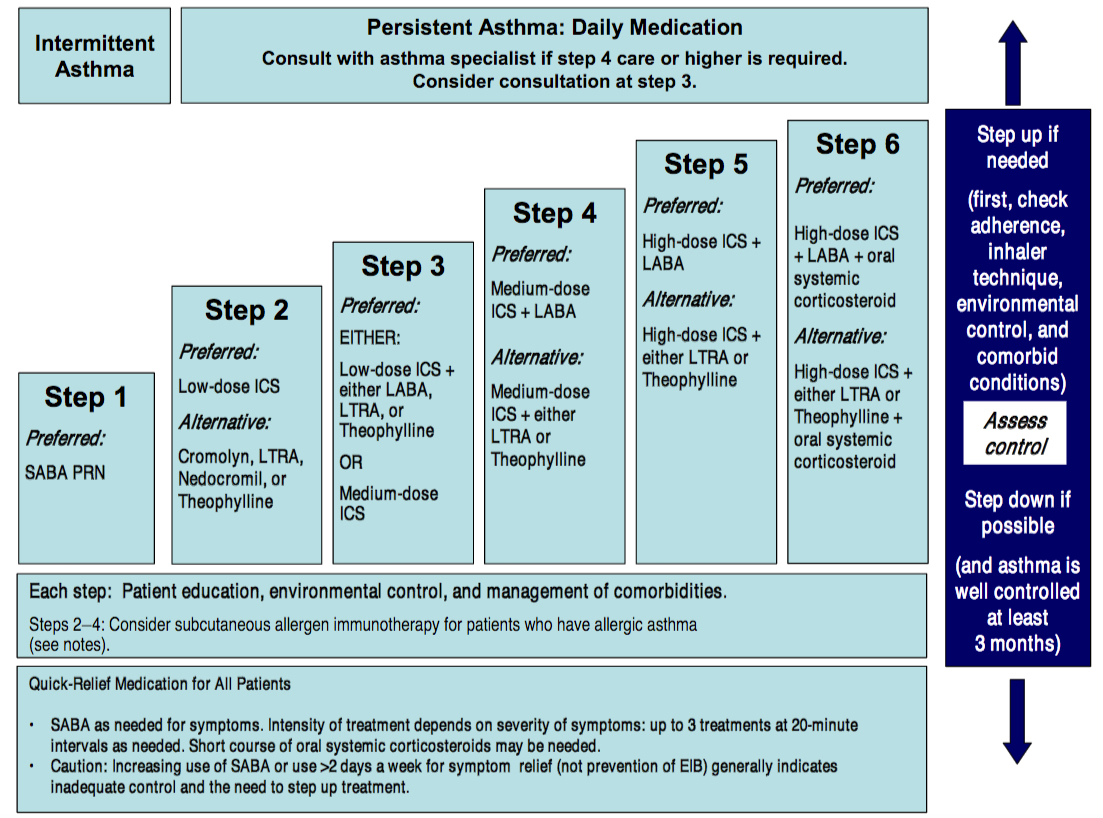
Correct Answer : A
Asthma stepwise therapy: in step 2 add ICS to control asthma.
Corticosteroids help to reduce inflammation in your airways, making it easier to breathe.
Q.12. An old patient with history of cerebrovascular disease & ischemic heart disease, presents with a pattern of breathing described as: a period of apnea followed by slow breathing which accelerates & becomes rapid with hyperpnea & tachycardia then apnea again. What is this type of breathing called?
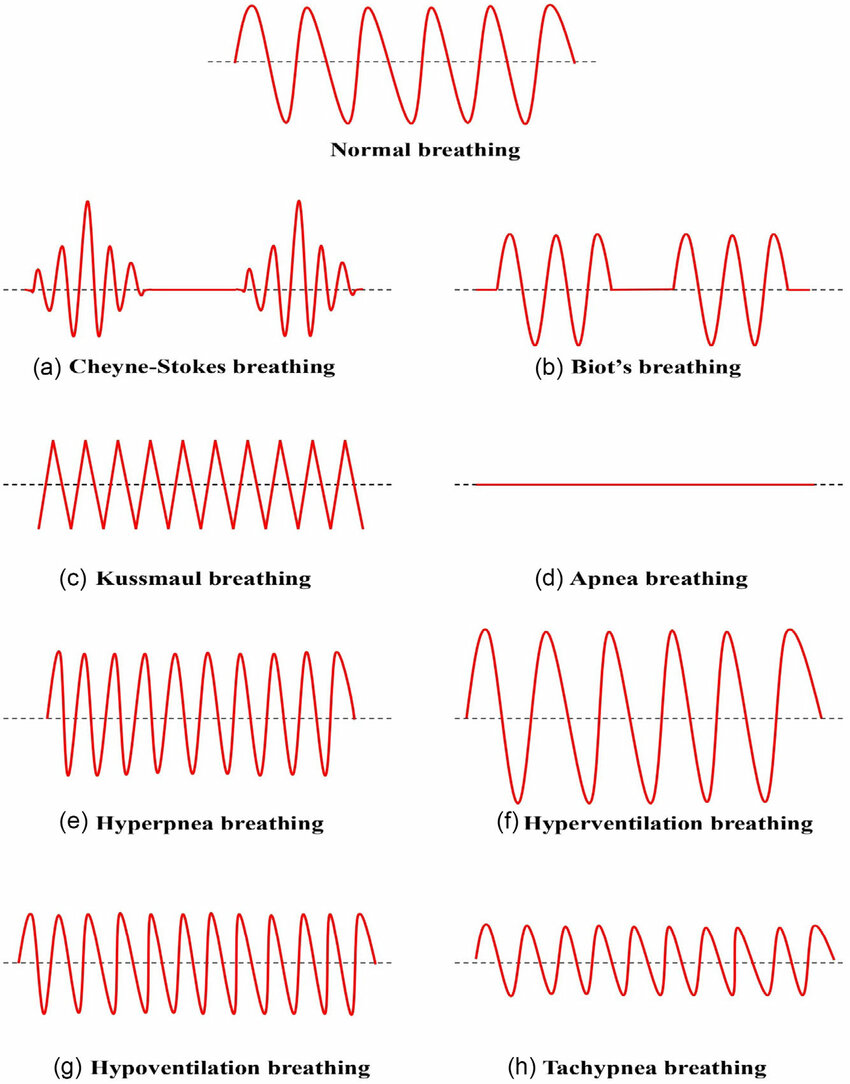
Correct Answer : B
Chyene-stokes respiration: rapid deep breathing phase followed by a period of apnea, present with heart failure, stroke, and brain trauma, also can be with sleep or high altitude.
Incorrect option-
- Abdominal breathing and normal breathing don't follow this pattern.
- Kusmmaul’s breathing is defined as rapid and deep breathing, present with metabolic acidosis particularly in diabetic ketoacidosis.
Q.13. Rheumatic fever patient has streptococcal pharyngitis , what is the percentage of risk to develop another attack is?
Correct Answer : C
If you have had RF before, there's a 50% chance of getting it again after a strep throat infection.
Q.14. The most common cause of croup is?
Correct Answer : A
Parainfluenza viruses are the main cause of croup, which leads to barking cough and noisy breathing in young children.
Q.15. A young male had pharyngitis followed by cough & fever, what is the most likely organism?
Correct Answer : B
Streptococcus pneumoniae commonly causes pneumonia. A sore throat followed by cough and fever might mean the infection has spread to the lungs.
Incorrect options-
- Staph aureus is less likely to cause pneumonia after sore throat.
- H.influenzae can cause pneumonia but less commonly than streptococcus pneumoniae
- Parainfluenza causes croup.
Q.16. A 17-year-old male with history of mild intermittent asthma attack occurs once or twice weekly in the morning and no attacks at night. What should be the initial drug to give?
Correct Answer : A
For mild intermittent asthma, a quick relief inhaler like albuterol is the go-to solution to open airways during attacks.
Q.17. Which of the following statement is true regarding bronchial carcinoma?
Correct Answer : C
Adenocarcinoma is usually located peripherally, so the upper part location is the correct option.
Other options are incorrect because-
- The most common tumor in females is breast tumors.
- Small cell carcinoma spreads faster, not squamous cell.
Q.18. A 39-year-old HIV patient with TB receives 4 drugs of treatment. What's the next step in management?
Correct Answer : D
According to various guideline committees, the standard duration of therapy for drug-susceptible TB, regardless of HIV status, should be six months;
this includes two months of isoniazid (INH), a rifamycin (eg, rifampin or rifabutin), pyrazinamide, and ethambutol followed by isoniazid and a rifamycin for four additional months.
- When to prolong therapy — The duration of TB therapy is longer in specific clinical situations, regardless of HIV status: For those patients with cavitary disease and positive sputum cultures after two months of treatment, the duration of isoniazid and rifampin treatment should be extended by three months for a total of nine months of treatment.
- For patients with bone, joint, or CNS disease, many experts recommend 9 to 12 months of therapy.
- For all other patients with extrapulmonary disease, the recommended treatment is two months of four-drug therapy followed by four months of isoniazid and rifampicin.
- The duration of therapy is also generally longer in patients with drug-resistant TB.
- HIV-infected patients with MDR TB should be treated for 24 months after the conversion of sputum culture to negative. After the cessation of therapy, patients should be examined every four months for an additional 24 months to monitor for evidence of relapse.
Q.19. Best way to secure airway in responsive multi-injured patient is ?
Correct Answer : A
A nasopharyngeal tube helps to keep the airway open in a responsive patient with multiple injuries, allowing them to breathe better.
Incorrect options-
- Oxygen supply is important for breathing but doesn't secure the airway.
- Ventilator is used in patient's who can't breathe on their own, not for responsive ones.
- Tracheostomy is a surgical procedure used for severe cases, not for responsive patients.
Q.20. A child has history of URTI for few days. He developed barky cough and SOB. What's the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Croup causes a barking cough and noisy breathing, often worse at night, and is common in children with conditions like eczema.
Q.21. In asthma case, what is the prophylactic drug?
Correct Answer : A
Beta-2 agonist relax airway muscles, making it easier to breathe, and are go-to quick-relief inhalers for asthama attack.
Q.22. A male patient working in the cotton field, presented with 3 weeks history of cough. CXR showed bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy and biopsy (by bronchoscopy) showed non-caseating granuloma. What’s your diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Non-caseating granuloma supports the diagnosis of sarcoidosis.
Incorrect options-
- Pneumoconiosis is an occupational & restrictive lung disease caused by the inhalation of dust, depending on the dust type the disease is given its name, in cotton case it is called ' Byssinosis'.Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy present in both Sarcoidosis & Pneumoconiosis.
- Berylliosis and amyloidosis don't have the following findings.
Q.23. A patient with untreated bronchogenic carcinoma has dilated neck veins, facial flushing, hoarseness and dysphagia (SVC syndrome). CXR showed small pleural effusion. What’s your immediate action?
Correct Answer : C
Consult oncologist for radiation therapy ± chemotherapy because SVC syndrome symptoms and hoarseness suggest unrespectable lesion.
Q.24. An old patient presents to you. He is a k/c/o DM2, emphysema & community acquired pneumonia, best management will be?
Correct Answer : C
This patient is at high risk of pneumonia and flu complications. Waiting 4 weeks lets the body recover fully before getting vaccinated, which can cause mild side effects.
Q.25. Radiological feature for miliary TB is?
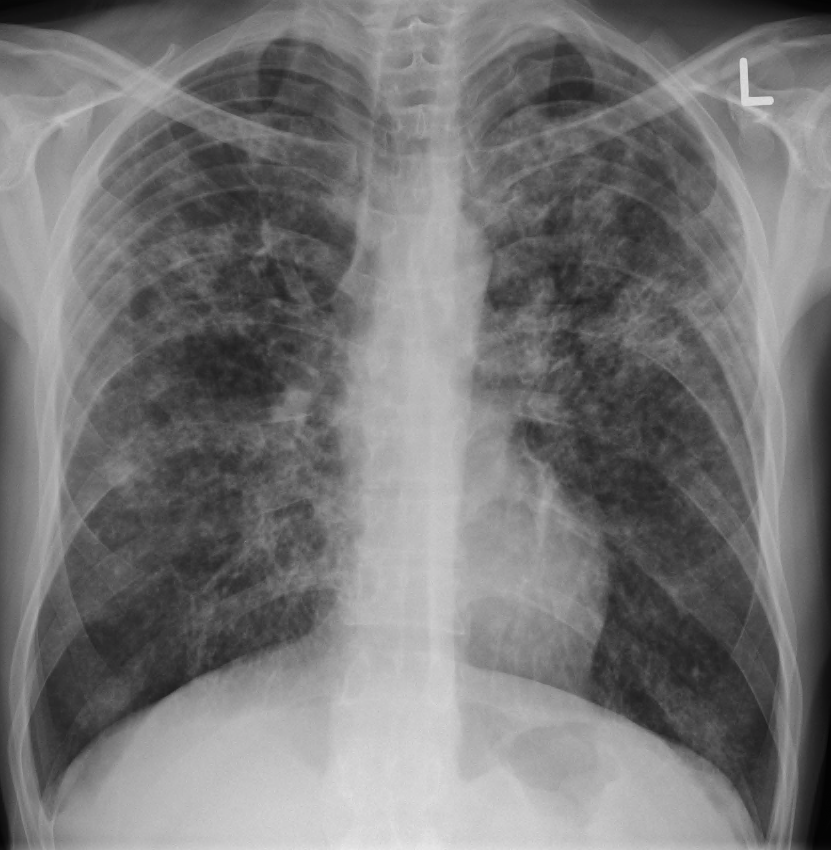
Correct Answer : B
The classic radiographic findings of evenly distributed diffuse small 2–3-mm nodules, with a slight lower lobe predominance, are seen in 85% of cases of miliary TB.
Q.26. A patient presented with sudden chest pain and dyspnea, tactile vocal fremitus and chest movement is decreased, in x-ray there is decreased pulmonary marking on left side, what is the diagnosis?
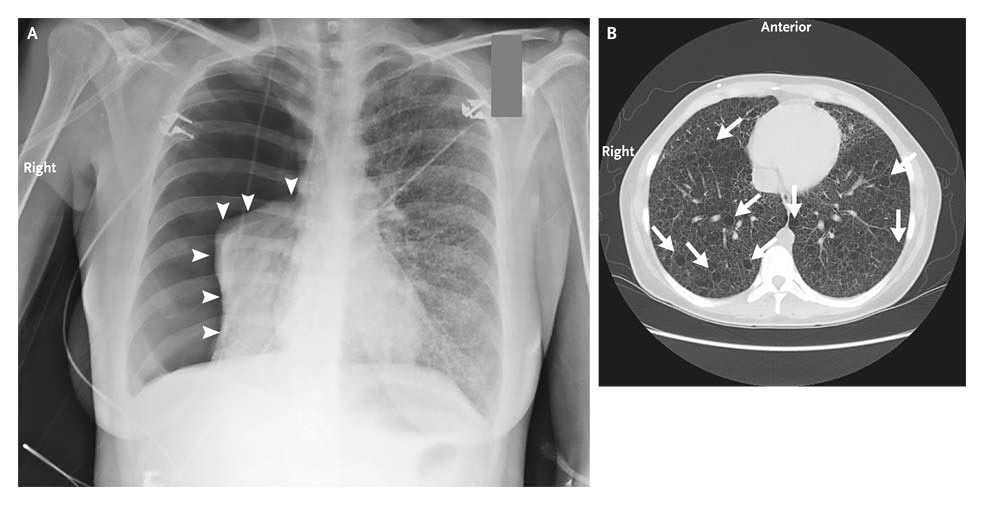
Correct Answer : B
A pneumothorax is when air leaks into the space around the lungs, causing them to collapse. This leads to sudden chest pain, difficulty breathing, and signs like decreased tactile fremitus and chest movement on one side, along with specific X-ray findings.
Q.27. A patient ingested some amount of aspirin, now she presents with nausea, vomiting & hyperventilation, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Salicylate ingestion causes metabolic acidosis (from lactate, ketones) + respiratory alkalosis due to stimulation of CNS respiratory centers.
Q.28. A 20-year-old male who is a known asthmatic presented to the ER with shortness of breath. PR 120, RR 30, PEFR 100/min. Examination revealed very quiet chest. What is the most probable management?
Correct Answer : A
Salbutamol quickly relaxes airway muscles, making it easier to breathe. Nebulized salbutamol delivers it directly to the lungs for fast relief during an asthma attack.
Incorrect options-
- IV aminophylline takes longer to act, so its not the first choice.
- Pleural aspiration is used to drain fluid around lungs not for asthma attacks.
- Heimlich maneuver is used in choking not asthma.
Q.29. A patient is a known case of moderate intermittent bronchial asthma. He is using ventoline nebulizer, oral steroids. He develops 3 attacks per week. The drug to be added will be?
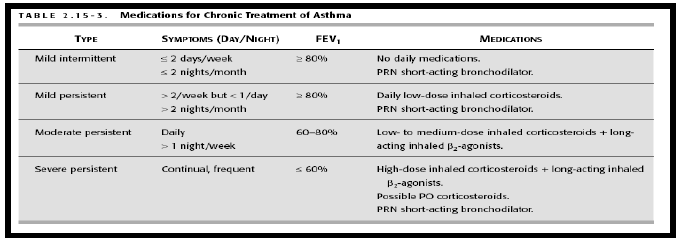
Correct Answer : B
By asthma stepwise management guidelines if the patient is on Ventolin and the asthma is still not controlled (partially controlled 3 attacks per week) then add LABA which will help in preventing attacks by keeping the airways relaxed.
Q.30. Which one of the following is true about the home treatment of COPD?
Correct Answer : A
For COPD patients, oxygen is only given when blood oxygen levels drop below 88%, as this ensures they get the support they need without overloading their system.
Q.31. A 58-year-old male patient came with history of fever, cough with purulent foul smelling sputum and CXR showed: fluid filled cavity. What is the most likely diagnosis is?
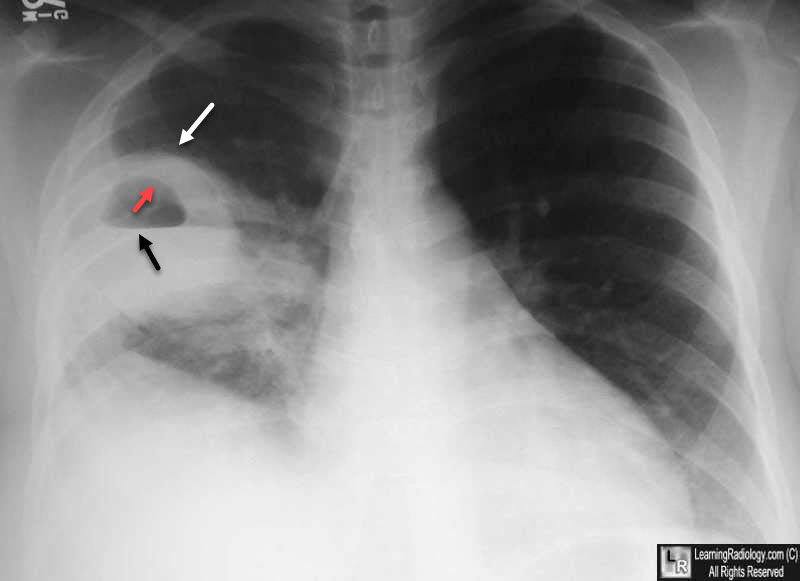
Correct Answer : A
A lung abscess is a pocket of pus caused by infection. Symptoms like fever, foul-smelling sputum, and a fluid-filled cavity on X-ray strongly suggest the diagnosis.
Q.32. An elderly male patient who is a known case of debilitating disease presented with fever, productive cough, and sputum culture which showed growth of Gram negative organisms on a buffered charcoal yeast agar. What is the organism?
Correct Answer : D
Buffered charcoal yeast extract (BCYE) agar is a selective growth medium used to culture or grow certain bacteria, particularly the Gram-negative species Legionella pneumophila
Q.33. A 27-year-old girl came to the ER, she was breathing heavily, RR 25/min. She had numbness & tingling sensation around the mouth & tips of the fingers. What will you do?
Correct Answer : B
The patients symptoms, like numbness and tingling, could be due to an electrolyte imbalance, especially if they have had vomiting and diarrhea.
Incorrect options-
- Breathe in bag is a method used for hyperventilation.
- Giving glucose treats hypoglycemia not electrolyte imbalance
- Reassurance will not alone be sufficient.
Q.34. A patient with lung cancer shows signs of pneumonia, what is the most common organism?
Correct Answer : C
The primary respiratory infections in early phase (non-immunocompromised phase) include those caused by pathogens common to the general public. The predominant organisms are Streptococcus pneumonia, Haemophilus influenza, and community-acquired respiratory viruses.
Q.35. A patient who is 18 years old admitted for ARDS and developed hemothorax. What is the cause?
Correct Answer : C
In ARDS, high oxygen levels are sometimes used to help support breathing. However prolonged use of high levels of oxygen can cause oxygen toxicity. This damage can make blood vessels leak and may lead to hemothorax.
Q.36. A COPD patient with emphysema has low oxygen, prolonged chronic high CO2, the respiratory drive is maintained in this patient by?
Correct Answer : A
The respiratory drive is normally largely initiated by PaCO2 but in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) hypoxia can be a strong driving force and so if the hypoxia is corrected then the respiratory drive will be reduced. There will also be a loss of physiological hypoxic vasoconstriction.
Q.37. There is an outbreak of TB, as a prophylaxis what you should give?
Correct Answer : A
INH is the go to medication for preventing TB. It works by stopping the bacteria from growing and spreading.
Q.38. A patient presents with typical finding of pleural effusion, what's the management ?
Correct Answer : A
A chest tube is the best way to drain excess fluid from around the lungs, helping them expand properly again.
Q.39. The most common cause of cough in adults is ?
Correct Answer : C
The most common causes of chronic cough are-
- Postnasal drip
- Asthma
- Acid reflux from the stomach.
These three causes are responsible for up to 90 percent of all cases of chronic cough.
Q.40. A patient has fever, night sweating, bloody sputum, weight loss, PPD test was positive. X-ray shows infiltrate in apex of lung, PPD test is now reactionary ,what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
The symptoms of fever, night sweats, bloody sputum, and weight loss- along with a positive PPD test and apex lung infiltrate on X-ray, are classic signs of reactivated TB.
Incorrect options-
- Sarcoidosis may present with fever, weight loss but doesn't cause sputum and positive PPD.
- Adenocarcinoma/Lung cancer can mimic TB but doesn't have positive PPD test.
Q.41. The best early sign to detect tension pneumothorax is?
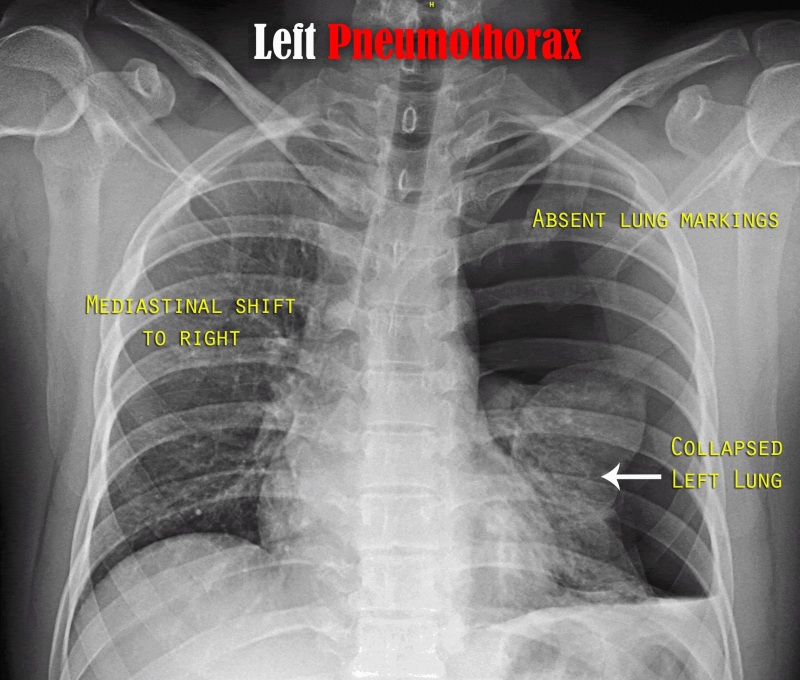
Correct Answer : A
In tension pneumothorax, trapped air in the pleural space builds pressure and pushes the mediastinum, and trachea away from the affected side.
- All other options are a late sign.
Q.42. Regarding breath holding spells, which of the following statement is true?
Correct Answer : C
Breath-holding spells are the occurrence of episodic apnea in children, possibly associated with loss of consciousness, and changes in postural tone.
Breath-holding spells occur in approximately 5% of the population with equal distribution between males and females. They are most common in children between 6 and 18 months and usually not present after 5 years of age. They are unusual before 6 months of age. A positive family history can be elicited in 25% of cases.
- They may be confused with a seizure disorder. They are sometimes observed in response to frustration during the disciplinary conflict.
Q.43. A 55-year-old male with COPD complains of fever since 1 week, productive cough, on CXR showed left upper pneumonia and culture of sputum shows positive H. influenza, what is the treatment?
Correct Answer : C
Cefuroxime is a 2nd generation cephalosporin used in respiratory infections “H. influenza and M. catarrhalis” whcih commonly causes pneumonia in COPD patients.
Q.44. An obese 60-year-old lady on 5th day post cholecystectomy presents to your clinic, she complains of SOB & decreased BP 60mmHg systolic. On examination unilateral swelling of right leg, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
After surgery, patients are at increased risk of DVT. A DVT can dislodge and travel to the lungs causing pulmonary embolism.
- Classic signs include SOB, hypotension, and unilateral leg swelling.
Incorrect options-
- Hypovolemic shock will have a history of significant blood loss.
- Septic shock would have history of fever and other signs of infection.
- MI unilateral leg swelling isn't a feature of heart attack.
Q.45. For close contact with TB patients, what do you give?
Correct Answer : D
INH is the standard preventive therapy for close contacts of active TB patients. It reduces the risk of developing active TB after exposure.
Q.46. Klebsiella causes which of the following disease?
Correct Answer : A
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a major cause of bacterial pneumonia, especially in hospitalized or immunocompromised patients. It often leads to severe symptoms like fever, cough, and difficulty breathing.
Q.47. A patient presents with h/o hemoptysis, several month back his PPD was positive, he has taken all vaccination, his X-ray showed apical filtration, his PPD test has been done again, it came negative, what's the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
The history of positive PPD test, apical infiltration, and hemoptysis are classic signs of old, inactive TB. A previously positive PPD test reflects prior TB exposure, while apical changes on X-ray support the diagnosis.
Q.48. A patient who sustained a major trauma presented to ER, the first thing to do is?
Correct Answer : B
The first priority in trauma management is ensuring a clear airway to prevent obstruction. Trauma can also cause blood, vomit, or broken teeth to block the airway, so clearing it is critical for effective breathing.
Q.49. A patient with history of shortness of breath and hemoptysis presents at your clinic, the appropriate investigation is?
Correct Answer : B
These are the basic investigations for TB patient
- CXR
- PPD
- AFB “Ziehl Neelsen stain”
.
Q.50. Treatment of community acquired pneumonia is?
Correct Answer : A
Azithromycin is the first-line treatment for CAP. It's effective against common pathogens like Streptococcus pneumoniae and Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
Incorrect options-
- Ciprofloxacin is used for specific bacteria like pesudomonas.
- Gentamycin is not used for CAP due to toxicity concerns.
- Tetracycline is rarely used in adults for CAP.
Q.51. A patient was febrile after he went through a surgery one day back. What’s your diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Atelectasis, or partial collapse of lung, is a common cause of fever shortly after surgery. Pain and shallow breathing post-surgery can lead to poor lung expansion, causing this condition.
- Postoperative atelectasis generally occurs within 48 hours.
Q.52. The best prophylaxis of DVT in the post-operative patient is?
Correct Answer : A
LMWHs, like enoxaparin, are the gold standard for DVT prevention after surgery beacause they're highly effective, safe, and easy to administer subcutaneously without frequent monitoring.
Incorrect options-
- Warfarin has delayed effect and requires regular monitoring.
- Aspirin is less effective than LMWH for post-op DVT prevention.
- Unfractioned heparin is effective but inconvenient .
Q.53. A 3-year-old presented with shortness of breath and cough at night which resolved by itself in 2 days. He has history of rash on his hands and allergic rhinitis. He most likely had?
Correct Answer : B
Nigh time cough and shortness of breath are hallmark asthma symptoms. The history of rash and allergic rhinitis indicates an atopic predisposition, commonly linked to asthma.
Q.54. A pediatric patient came to you in ER with wheezing, dyspnea, and muscle contraction, what's best to give initially?
Correct Answer : B
Albuterol, a short-acting beta-agonist, is the first-line treatment. It relaxes airway muscles quicly, relieving bronchospasm and easing breathing during an acute asthma episode.
Q.55. Prophylaxis for asthma is?
Correct Answer : B
Inhaled corticosteroids are the most effective for long-term asthma control. They reduce airway inflammation, preventing frequent and severe attacks.
Q.56. Smoking withdrawal symptoms peaks at which day?
Correct Answer : B
Symptoms of nicotine withdrawal generally start within 2 - 3 hours after the last tobacco use, and will peak about 2 - 3 days later.
Q.57. A 6 month old baby with cough and wheezy chest presented at your clinic. Which of the following is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
- Wheezing and chest complaints in babies less than 1 year old - Bronchiolitis.
More than One year old - ARDS.
Q.58. Physiological cause of hypoxemia is?
Correct Answer : C
A V/Q mismatch occurs when the balance between ventilation and perfusion is disrupted. This is a common cause of hypoxemia, seen in conditions like asthma, pulmonary embolism, or pneumonia, where certain lung areas get airflow but lack adequate blood flow or vice versa.
Incorrect options-
- Hypoventilation reduces overall oxygen intake but isn't the primary mechanism compared to V/Q.
- Improper alveolar diffusion causes hypoxemia in diseases like pulmonary fibrosis, but is less common than V/Q mismatch.
- Elevated 2,3-DPG enhances oxygen release from hemoglbin, typically improving oxygen delivery, not causing hypoxemia.
Q.59. A child with asthma uses betamethasone, most common side effect is?
Correct Answer : C
Inhaled corticosteroids like betamethasone can slightly affect growth in children by mildly supressing the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. While this effect is usually minimal and temporary, regular monitoring is recommended to ensure the child's growth stays within the normal range.
Q.60. Respiratory distress syndrome after an injury is due to which of the following?
Correct Answer : B
ARDS etiologies:
- Direct injury: pneumonia, inhalation injury, aspiration, lung contusion, and near drowning.
- Indirect injury: sepsis, pancreatitis, shock, trauma/multiple fractures, DIC, and transfusion.
Q.61. For interstitial lung disease all are true, except?
Correct Answer : C
- All patients with interstitial lung diseases develop exertional dyspnea and non-productive cough.
- The examination revealed typical coarse crackles and evidence of pulmonary hypertension.
- PFTs show evidence of restrictive pattern (decreased volumes).
Q.62. Air bronchogram is characteristic feature of which of the following?
Correct Answer : C
The most common causes of an air bronchogram are consolidations of various origins.
- Widespread air bronchograms are seen in hyaline membrane disease but its not always typical.
- Air bronchograms are also seen in atelectatic lobes on chest radiographs when the airway is patent, notably when atelectasis is caused by pleural effusion, pneumothorax, or bronchiectasis.
Q.63. A patient complains of bad breath smell with seek like structure, he has no dental caries & Iarynx is normal, what's the likely cause?
Correct Answer : A
Cryptic tonsilitis involves the formation of pockets or crypts in the tonsils that can trap food, bacteria, and debris. These trapped substances can harden into tonsililoliths, causing halitosis and the appearance of seed like structures.
Incorrect options-
- Tonsillitis may cause bad breath but it usually presents with symptoms like throat pain, fever, and red, swollen tonsils, not seed like structures.
- Croup is a viral condition with a barking cough and stridor, unrelated to tonsils or halitosis.
- Pharyngitis is the infalmmation of pharynx, often causing sore throat and redness, but not associated with tonsil stones or cryptic structures.
Q.64. Regarding moderately severe asthma, all are true except?
Correct Answer : B
A typical arterial gas during an acute uncomplicated asthma attack reveals normal PaO2, low PaCO2, and respiratory alkalosis.
- Hypoxemia in a PaO2 range of 60 to 80 mm Hg frequently is found even in moderately severe asthma. However; a PaO< 60 mm Hg may indicate severe disease.
Hypoxemia is due to ventilation-perfusion mismatching, whereas low PaCO2 is a result of hyperventilation. A progressive increase in PaCO2 is an early warning sign of severe airway obstruction in a child with respiratory muscle fatigue.
Q.65. The most specific investigation for pulmonary embolism is?
Correct Answer : D
Pulmonary angiography is the gold standard for diagnosing pulmonary embolism. It involves injecting contrast dye into the pulmonary arteries and directly visualizing blood clots. It's highly accurate but invasive, so it's typically used when other tests are inconclusive.
Q.66. A 62-year-old male known to have BA. He has a history of using bronchodilator & beclomethasone for one month, he had taken theophylline as well. Side effect of theophylline is?
Correct Answer : D
The most common side effects are-
- Cardiac arrhythmia,
- Anxiety,
- Tremors,
- Tachycardia & seizures.
[Always monitor ECG]
Q.67. A female presents with history of recurrent pneumonia, foul smelling sputum with blood and clubbing, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : A
Clinical features of Bronchiectasis are recurrent pneumonia because of the dilated bronchi so there’s a reduction in the ability the clearance secretions and pathogens from the airways. The sputum is copious, could have foul smell and the patients would have clubbing.
Incorrect options-
- A lung abscess also causes clubbing and foul-smelling sputum but its not a typical feature.
- COPD has frequent infective exacerbations but doesn’t cause clubbing.
- Pneumonia is an acute process and no clubbing occurs.
Q.68. In mycoplasma pneumonia, there will be which of the following?
Correct Answer : A
It is commonly associated with Mycoplasma pneumonia. Cold agglutinins are antibodies that cause red blood cells to clump together at low tempratures. This finding is a key diagnostic clue for mycoplasma infections.
Q.69. A 30-year-old man presents with shortness of breath after a blunt injury to his chest, his RR is 30 breaths/min. CXR showed complete collapse of the left lung with pneumothorax, mediastinum was shifted to the right. The treatment of choice is?
Correct Answer : A
A chest tube is the most appropriate treatment for pneumothorax caused by trauma. It drains air or fluid from the chest cavity, allowing the lung to re-expand. This is the standard care for significant pneumothorax.
Q.70. Regarding the right lung anatomy, which one of the following is true?
Correct Answer : B
The right lung has two pulmonary veins which carry oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the left atrium of the heart.
Q.71. A patient in in the ER has: dyspnea, right-sided chest pain, engorged neck veins, weak heart sounds, and absent air entry over right lung. Plan of treatment for this patient is?
Correct Answer : D
Symptoms and signs of tension pneumothorax may include the following:
- Chest pain
- Dyspnea
- Anxiety
- Acute epigastric pain (a rare finding)
- Fatigue Respiratory distress (considered a universal finding) or respiratory arrest
- Unilaterally decreased or absent lung sounds (a common finding; but decreased air entry may be absent even in an advanced state of the disease)
- Adventitious lung sounds (crackles, wheeze; an ipsilateral finding)
- Lung sounds transmitted from the non-affected hemithorax are minimal with auscultation at the midaxillary line
- Tachypnea
- Hyperexpansion of the chest wall Increasing resistance to providing adequate ventilation assistance.
- Tachycardia (a common finding)
- Hypotension (should be considered as an inconsistently present finding; while hypotension is typically considered a key sign of a tension pneumothorax, studies suggest that hypotension can be delayed until its appearance immediately precedes cardiovascular collapse).
- Pulsus paradoxus & Jugular venous distension
Q.72. A patient presents with severe bronchial asthma, which of the following drug is not recommended to give in the treatment plan?
Correct Answer : A
Sodium gluconate isn't a standard treatment for severe bronchial asthma. It mainly adresses calcium deficiencies and is rarely used in asthma care.
Q.73. Which of the following radiological features is a characteristic of miliary tuberculosis?
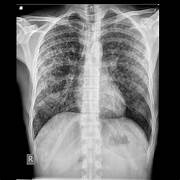
Correct Answer : D
Small cavities on chest X-ray are a hallmark of miliary TB, caused by lung damage from TB bacteria.
Q.74. A 24-year-old woman develops wheezing and shortness of breath when she is exposed to cold air or when she is exercising. These symptoms are becoming worse. Which of the following is the choice of treatment for asthma in this circumstance?
Correct Answer : A
These are the first choice for quick relief of asthma symptoms like wheezing and breathlessness. They relax airway muscles, easing breathing.
Q.75. Which one of the following regimens is the recommended initial treatment for most adults with active tuberculosis?
Correct Answer : C
This combination is the standard treatment for active TB, effectively killing bacteria and preventing drug resistance.
Q.76. A 55-year-old male presented to your office for assessment of chronic cough. He stated that he has been coughing for the last 10 years but the cough is becoming more bothersome lately. Cough is productive consisting of mucoid sputum, occasionally becomes purulent. Past history: 35 years history of smoking 2 packs per day. On examination: weight- 124 kg, wheezes while talking. Auscultation: wheezes all over the lungs. The most likely diagnosis is?
Correct Answer : D
An elderly male with a long history of heavy smoking and a change in character of cough is chronic bronchitis which is a clinical diagnosis (cough for most of the days of 3 months in at least 2 consecutive years).
Incorrect options-
- Emphysema is a pathological diagnosis (dilatation and destruction beyond the terminal bronchioles).
- Smoker's cough is not a formal diagnosis.
- Bronchiectasis presents with chronic cough and recurrent infection.
Q.77. A 25-year-old man had fixation of fractured right femur. Two days later he became dyspneic with chest pain and hemoptysis. ABG:-pH: 7.5, PO2:65,PCO2: 25, initial treatment is?
Correct Answer : D
After fracture, fixation (immobile), dyspnea means pulmonary embolism. You should start treatment with heparin for a few days then warfarin.
Q.78. All of the following are true about pulmonary embolism, except?
Correct Answer : A
In Pulmonary embolism ABG will show decreased PaO2 and PaCO2.
- ECG - S1Q3T3 with sinus tachycardia.
Q.79. In a child with TB, which of the following is true?
Correct Answer : D
Each option is a potential sign of TB in a child-
- History of exposure- Close contact with TB patient increases the risk.
- Chest X-ray findings can reveal abnormalities suggestive of TB.
- Splenomegaly and positive culture are indicative of precense of active infection.
Q.80. All of the following indicate severity of bronchial asthma ,EXCEPT?
Correct Answer : C
Severe bronchial asthma features:
- PEFR<60%
- Sa O2 <90%
- PO2<60
- PCO2 >45
- Dyspnea at rest, inspiratory & expiratory wheezes, accessory muscle use
- Pulsus paradoxus>25 mmHg
Q.81. A patient came with scenario of chest infection, first day of admission he was treated with cefotaxime. Next day, patient state became bad with decreased perfusion and x-ray showed complete right side hydrothorax, causative organism is?
Correct Answer : A
Parapneumonic effusion/empyema especially seen with S. pneumoniae
Q.82. Which of the following treatment is contraindicated in asthmatic patient?
Correct Answer : A
These block beta-2 receptors in the airways causing bronchoconstriction, which can worsen asthma symptoms or trigger severe attacks.
Q.83. Which of the following shift the O2 dissociation curve to the right?
Correct Answer : B
Low oxygen levels in tissues trigger rightward shift in oxygen-Hb dissociation curve, helping Hb release oxygen more easily.
Incorrect options-
- Respiratory alkalosis shifts the curve to the left, making oxygen harder to release.
- Hypothermia causes shift to left.
- Respiratory acidosis causes shift to the right but is not the primary driver like hypoxia.
Q.84. A 3-year-old baby's parents has TB, as a GP you did PPD test, after 72 hours you find a 10mm induration in the child. What does this suggest?
Correct Answer : C
- High risk because of contact + PPD 10mm induration
Q.85. An old patient presented with sudden onset of chest pain, cough and hemoptysis, his ECG result shows right axis deviation and right bundle branch block. What is the diagnosis?
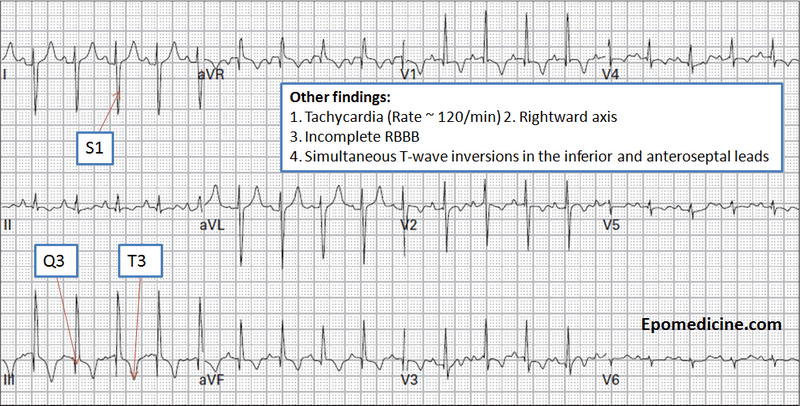
Correct Answer : B
ECG in Pulmonary embolism:
- Sinus tachycardia
- Right axis deviation, P pulmonale, RBBB, S1Q3T3, and T wave inversion V1-V4.
Q.86. PPD positive, CXR negative. What's the management?
Correct Answer : A
A PPD positive, CXR-negative case indicates latent TB infection. INH for 6 months is the standard treatment to prevent progression to active TB.
Q.87. Where is the chromosome abnormality in cystic fibrosis?
Correct Answer : B
Cystic fibosis is caused by a mutation in the CFTR gene, located on the long arm of chromosome 7.
Q.88. A lady known to have recurrent DVT came with superior vena cava thrombosis, what is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
Nephrotic syndrome causes protein loss in urine, increasing the risk of thrombosis, including recurrent DVT and SVC thrombosis.
Incorrect options-
- SLE can cause clots but is not the primary cause of recurrent DVT.
- Hemophilia B causes bleeding not thrombosis.
- Lung cancer can cause clots but is less likely to present as recurrent DVT.
Q.89. A patient who is smoking for 35 years with 2 packets daily presents to your clinic. Since 3 days he developed cough with yellow sputum, and for the past 3 hours the sputum became blood tinged, X-ray shows opacification and filtration of right hemithorax. What's the most likely diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
The patient's history of cough with yellow and blood tinged sputum- suggests a bacterial lung infection like lobar pneumonia, often caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Q.90. In a known case of asthma prevent exposure to which of the following?
Correct Answer : D
Asthma is triggered by allergens like dust mites, cat hair, and others. Avoiding these allergens is key to managing symptoms and preventing attacks.
Q.91. An 82-year-old female presented to the ER in confusion with hypotension. BP was 70/20, P=160/min, rectal T 37.7oC. The most likely of the following would suggest sepsis as a cause of hypotension?
Correct Answer : A
Special features of septic shock:
- 1) High fever
- 2) Marked vasodilatation throughout the body, especially in the infected tissues.
- 3) High cardiac output in perhaps one-half of patients caused by vasodilatation in the infected tissues & by high metabolic rate & vasodilatation elsewhere in the body, resulting from bacterial toxin stimulation of cellular metabolism & from high body temperature.
- 4) DIC
Q.92. A child with clinical picture of pneumonia was treated with cefotaxime, but he got worse with cyanosis, intercostals retraction and shifting of the trachea and hemothorax on x-ray, the causative organism is?
Correct Answer : C
Severe pneumonia with cyanosis, tracheal shift, and hemothorax suggests a toxin producing organism. Stap aureus can cause significant lung damage and complications like hemothorax.
Incorrect options-
- Pneumocystis carnii affects immunocompromised patients.
- Strep pneumoniae usually lacks severe complications like hemothorax.
- Pseudomonas is linked to hospital acquired infections or chronic lung condtions.
Q.93. What is the most effective measure to limit the complications of COPD?
Correct Answer : B
Smoking is the leading cause of COPD. Quitting reduces further lung damage, slows disease progression, and lowers complications like infections and cancer.
Q.94. Goodpasture's syndrome is associated with which of the following?
Correct Answer : C
Goodpasture syndrome is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the lungs and kidneys, causing bleeding in the lungs and kidney inflammation.
Q.95. An old male, who is a heavy smoker presents to you. On his chest X-ray there is a mass, he also has hyponatremia and hyperosmolar urine, what is the cause?
Correct Answer : A
The patient's hyponatremia, hyperosmolar urine, and chest X-ray mass strongly indicates SIADH, often linked to tumors like small cell lung cancer. Excess ADH causes water retention, diluting sodium levels.
Q.96. A patient is a k/c/o of uncontrolled asthma, moderate persistent on bronchodilator. He came with exacerbation and is now ok, what you will give him to control his asthma?
Correct Answer : B
Inhaled steroids are the primary treatment for long-term asthma control. They reduce airway inflammation, improve lung function, and prevent asthma attacks with fewer side effects than oral steroids.
Q.97. A patient comes with PPD test positive for TB, before anti TB treatment, what should be done?
Correct Answer : B
The Mantoux test is used to diagnose TB infection. A positive result indicates exposure to TB, and a second test can help confirm the result before starting the treatment.
Q.98. An old patient, smoker, with COPD, is having cough and shortness of breath during day time not at night, how do you treat him?
Correct Answer : B
Ipratropium bromide is an anticholinergic bronchodilator that helps relax the airways, making it easier to breathe. It's ideal for daytime COPD symptoms and offers long-lasting relief.
Q.99. A patient with asthma uses short acting beta agonist and systemic oral corticosteroids, what is the type of asthma classification?
Correct Answer : D
The patient's use of both systemic corticosteroids and short-acting beta agonists suggests poor asthma control, indicating severe asthma. These treatments are typically for intense flare-ups or uncontrolled asthma.
Q.100. An obese patient has h/o snoring while he is sleeping and the doctor records that he has about 80 apneic episodes to the extent that PO2 reach 75%, no other symptoms are present. Examination is normal. What's you next action ?
Correct Answer : C
.The patient's severe obstructive sleep apnea [OSA] requires CPAP, the gold standard treatment. CPAP helps keep the airway open during sleep, and monitoring ensures effective use and adjustments as needed.
Q.101. A patient came with Pneumocystis carinii infection. What is your action?
Correct Answer : B
Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia is an oppurtunistic infection commonly seen in patients with weakened immune systems, particularly those with HIV. Early HIV diagnosis is essential for appropriate treatment including antiretroviral therapy.
Q.102. A patient woke up with inability to speak, he went to a doctor. He still couldn't speak but he can cough when he is asked to. His larynx looks grossly looks normal on laryngoscope. What is your diagnosis?
Correct Answer : C
Functionl aphonia is when a person suddenly loses their voice despite having no physical issues with their vocal cords. The patient can still cough, which shows the vocal cords are functioning but not being used for speech.
Q.103. A young patient with mild intermittent asthma presents to your clinic, he has attack once or twice a week, what's best for him as prophylaxis?
Correct Answer : A
Inhaled SABAs are the preferred treatment for mild intermittent asthma, where symptoms are infrequent. They help prevent asthma attacks by relaxing the airways.
Q.104. A patient with COPD is coughing greenish sputum, what's the organism?
Correct Answer : D
Haemophilus influenzae is a common cause of pneumonia in patients with COPD, who are prone to infections due to chronic lung inflammation and weakened immune response. Also presence of greenish sputum is typical of bacterial pneumonia often caused by Haemophilus influenzae in COPD patients.
Q.105. An old patient was coughing, then he suddenly developed pneumothorax, which of the following is the next best management?
Correct Answer : C
Tube thoracostomy is the standard treatment for pneumothorax, where air collects in the pleural space, compressing the lung.
Q.106. A patient presents with bilateral infiltration in lower lobes (pneumonia). Which organism is suspected?
Correct Answer : A
Legionella causes Legionnaires disease which is a severe form of pneumonia with characterstic bilatral lower lobe infiltrates on chest X-ray. It often presents with high fever, chills, cough, and shortness of breath.
Q.107. A patient with adult respiratory distress syndrome, is now suspected of tension pneumothorax, what is the probable cause?
Correct Answer : A
Tension pneumothorax can result from air entering the pleural space and becoming trapped, which increases pressure in the chest. Severe lung injury, like ARDS, can cause tear in lung tissue, allowing air leak into the pleural space, leading to tension pneumothorax.
Q.108. A patient has pharyngitis, later he developed high grade fever, then cough, then bilateral pulmonary infiltration on CXR, WBC was normal and no shift to left. What is the organism?
Correct Answer : B
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a common cause of commuity acquired pneumonia and typically presents with symptoms like pharygitis, high fever, productive cough, and bilateral pulmonary infiltrates on chest X-ray.
Q.109. A patient is suffering from wheezing and cough after exercise, he is not on any medications. What’s the prophylactic medication?
Correct Answer : A
Inhaled beta-2 agonist is the treatment of choice.
Q.110. An old patient stopped smoking 10 years ago, h/o from shortness of breath after exercise but no cough and following report - FEV1=71% FVC=61% FEV1/FVC=95% TLC=58%. What's the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : D
The patient's history and pulmonary function tests suggest both obstructive and restrictive component.
- Obstructive component- The history of smoking and reduced FEV1/FVC ratio [95%] point to airflow obstruction, typical of COPD.
- Restrictive component- The reduced FVC and TLC indicate limited lung expansion, a hallmark of restrictive lung disease.
Q.111. A patient with asthma is on daily steroid inhalers and short acting B2 agonist. These drugs belong to what category?
Correct Answer : C
- Daily steroid inhalers are used for persistent asthma often in moderate to severe cases.
- Short-acting beta-agonists- Regular use of these indicate ppor asthma control supporting a moderate classification.
Q.112. A patient who is a k/c/o asthma, lives near industrial area. He came with complaint of SOB, he is not on any medications. What will you start?
Correct Answer : A
Beta-2 agonists are the go to treatment for acute astma excerbations, providing rapid relief from symptoms like SOB.
Q.113. A young patient with unremarkable medical history presented with SOB, wheeze, and long expiratory phase. Initial management is?
Correct Answer : A
They are the go to treatment for acute asthma excerbations. They work quickly to relax the muscles in the airways, easing breathing during an attack.
Q.114. If there is relation between anatomy and disease, pneumonia will occur in which anatomical location of the lung?
Correct Answer : C
Generally the right lower lung lobe is the most common site of infiltrate formation due to the larger caliber and more vertical orientation of the right mainstem bronchus.
Q.115. A COPD patient, with chronic CO2 retention, presented to ER with shortness of breath and was given 100% O2 and his condition worsened. What's the possible explanation?
Correct Answer : A
In patients with chronic CO2 retention, their body relies more on CO2 levels than oxygen levels to regulate breathing.
- Giving 100% oxygen can trick the body into thinking that the oxygen levels are sufficient, reducing the drive to breathe, which leads to worsening hypoxemia.
Q.116. A 19-year-old girl with URTI, lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly, the most likely diagnosis is?
Correct Answer : A
Infectious mononucleosis caused by the EBV, is common in young adults and presents with fever, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes.
- Other symptoms include fatigue, muscle aches, and splenomegaly, all of which are seen in this patient.
Q.117. The Screening Questionnaire to recognize primary snoring from OSAS is ?
Correct Answer : B
The Horchover questionnaire is designed to differentiate between primary snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. It assesses symptoms and risk factors associated with OSA, such as age, weight, and neck circumference.
Q.118. A patient presents with symptoms of mild intermittent asthma progressed to mild persistent asthma and the patient is on albuterol. What will you add?
Correct Answer : B
They help in inflammation control and are the first-line treatment for long-term control in this stage of asthma
Q.119. A patient has asbestosis, what you will see on his chest X-ray?
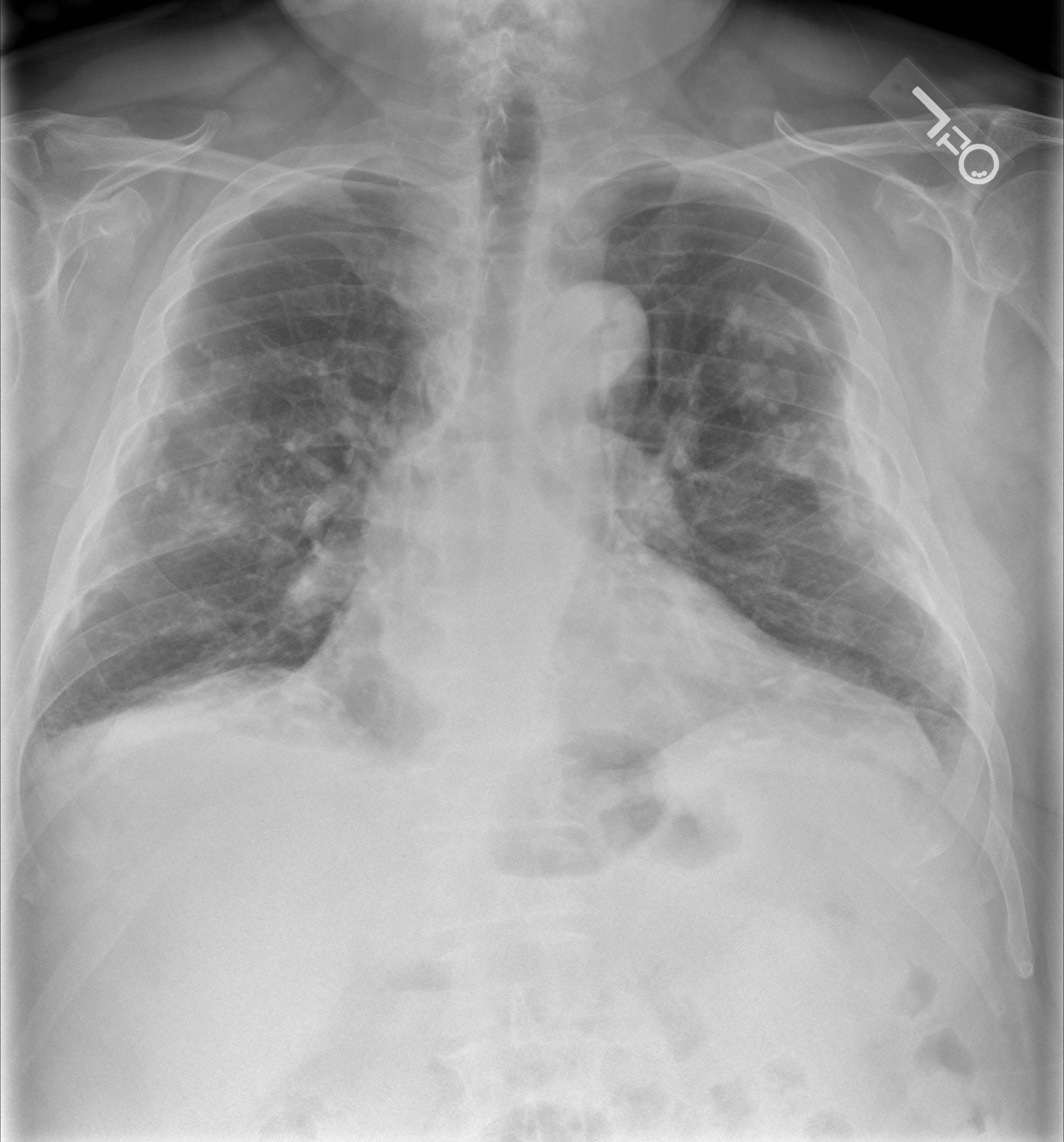
Correct Answer : C
Asbestosis is a chronic lung disease caused by asbestos exposure, leading to inflammation and scarring of the lungs. On a chest X-ray, it typically shows diffuse interstitial infiltrates, which are abnormal shadows throughout the lung, indicating widespread scarring.
Q.120. Which one of these patients with pneumonia will you treat as an outdoor patient?
Correct Answer : C
According to the pneumonia severity index calculator (class IV and V need hospitalization class III depend on clinical judgment) high blood pressure is not involved in the calculation.
Q.121. A patient presents with severe asthma, tight chest, tachypnoea and CO2 = 50. He is drowsy. What is the next step in management?
Correct Answer : B
The patient shows signs of severe asthma with tachypnea and dangerously high CO2 levels, which suggests respiratory faliure. Intubation is needed to secure the airway and provide proper ventilation in this critical condition.
Q.122. A young lady was diagnosed with emphysema. What is the possible deficiency?
Correct Answer : A
Alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency is a genetic condition leads to low levels of a protein that protects the lungs. It makes the lungs more vulnerable to damage, which can cause emphysema, even in non smokers.
Q.123. A 35-year-old male patient complains of allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma which is poorly controlled presented with history of skin rash ,diffuse severe abdominal pain and hand joints pain for 2 days , on examination there are diffuse purpuric skin rash and small joint tenderness with mild effusion , the most likely diagnosis is?
Correct Answer : A
It is a rare condition characterized by inflammation of blood vessels and a triad of symptoms - Asthma, eosinophilia and vasculitis.
Q.124. A 34-year-old female presented with cough and dyspnea for months, her examination showed cervical lymphadenopathy , she also has hepatomegaly. What's the investigation done to confirm diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
Sarcoidosis is a chronic inflammatory disease often affecting the lungs, and symptoms like cough, dyspnea, and systemic involvement suggest the diagnosis. Bronchoscopic lung biopsy is the best way to confirm the diagnosis by obtaining lung tissue. This allows for the detection of non-caseating granulomas, which are characterstic for sarcoidosis.
Q.125. A patient who is a k/c/o asthma, has no symptoms at night, she is using herbal for 2 months with no improvement. What is the next step in management?
Correct Answer : A
First step - Inhaled B2 agonist
Q.126. A patient with recent history of URTI, develops severe conjunctivitis with redness, tearing, and photophobia. What is the treatment?
Correct Answer : D
Photophobia is caused by adenovirus is treated by topical steroid.
Q.127. In moderate to severe asthmatic patient you will find all the following, EXCEPT ?
Correct Answer : C
In severe asthma attack, there is usually respiratory acidosis due to CO2 retention. The kidneys try to compensate by reabsorbing bicarbonate, which would lead to elevated bicarbonate,levels not low levels.
Q.128. A patient with moderate persistent BA, is on short acting beta-2 agonist and low dose steroid inhaler. What will be the next step of management?
Correct Answer : A
For moderate persistent asthma, the standard treatment involves adding LABA to the existing inhaled corticosteroid. This combination improves control by reducing inflammation and providing long lasting bronchodilation.
Q.129. Which of the following is clinical feature of asbestosis?
Correct Answer : C
Clubbing is when the tips of fingers or toes become rounded and bulbous. It often indicates long-term lung diseases, including asbestosis, due to chronic inflammation and scarring in the lungs.
Q.130. Regarding lung cancer what is the most accurate answer given below?
Correct Answer : B
Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of lung cancer, especially in non-smokers. However, it typically arises in the peripheral parts of lungs.
Q.131. How do you confirm the diagnosis of asthma patient by using spirometry after giving beta agonist?
Correct Answer : B
In asthma, the airways are typically obstructed, and beta-agonists help open them up, improving airflow increasing FEV1. If FEV1 shows no change after using beta-agonist, it suggests obstruction is not reversible whcih is a characteristics of conditions like COPD, not asthma.
Q.132. A young male patient presented to you with history of falling down from a ladder. The physical exam was going with pneumothorax. Next step of management is?
Correct Answer : D
Pneumothorax occurs when air leaks into the pleural space, causing the lung to collapse. A chest tube is the most effective treatment to remove excess air and allow the lung to re-expand.
Q.133. A COPD patient presented with acute symptoms not responding to bronchodilators , what is the next step of management?
Correct Answer : B
For COPD patients severe excerbations that don't respond to bronchodilators, IV steroids are the next step. they help reduce inflammation and imptove breathing by lowering airway resistance.
Q.134. A young adult in an endemic area, presents with crepitation bilaterally with monophasic sound on auscultation. What vaccination should be given?
Correct Answer : A
Haemophlius influenzae type b is a common cause of pneumonia, especially in endemic areas, and is often associated with crepitations and a monophasic sound on examination.
Q.135. A patient presents with chest pain, his x-ray revealed pleural effusion, high protein & high HDL. What is the diagnosis?
Correct Answer : B
CHF leads to fluid buildup in lungs, causing pleural effusion. The pleural fluid in CHF often has a high protein content. Elevated HDL is also seen sometimes in heart faliure patients.
Q.136. A young patient presented with pleuritic chest pain, decreased breath sounds and chest movements on the right side. No history of trauma, X-ray was given. What is the next appropriate step?
Correct Answer : C
The patient presents with pleuritic chest pain, decreased breath sounds, and reduced chest movements, raising concern for a lung collapse or mass. A CT scan provides detailed images to identify issues like pneumothorax, pleural effusuion, lung mass. It also helps in determining the severity of the issue and guides treatment.
Q.137. A patient with ARDS in hospital develops tension pneumothorax. What is the cause?
Correct Answer : A
Both negative & positive can cause pneumothorax. [If any one of them is there in the option choose it, if both are present choose positive because it is more likely].
Q.138. An asthma patient is complaining of attacks before exercise and exposure to cold, what you will give him as prophylaxis?
Correct Answer : B
First-line drug of choice in such scenarios is always inhaled beta-2 agonist.